What Tests Can I Perform To Find The Cause Of The Misfire Condition?
There is a logical starting point for troubleshooting a misfire condition and it all starts by reading the diagnostic trouble codes stored in the PCM's memory with your scan tool (Don't have a scan tool? Need a scan tool? Check out my recommendation: Actron CP9580 Scan Tool).
The misfire codes, stored in your Dodge vehicle's computer, will help you to identify which cylinder or cylinders are the ones suffering the miss (misfire).
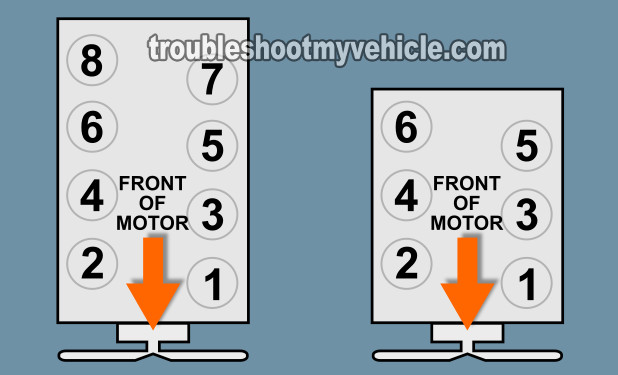
Once the misfire code or codes are retrieved, the next step is to match the misfire code to its engine cylinder using an illustration of the engine cylinders, like the one in the image viewer.
The following are my recommendations as to what to start testing first. Although you don't have to follow the list in that particular order:
STEP 1: Your starting point should always be to make sure that the misfiring cylinder is getting spark. Why? Well, because the majority of misfire are caused by a failed component in the ignition system.
The spark test is done on the spark plug wire of the misfiring cylinder and with a dedicated spark tester.
STEP 2: If you got spark from your spark tester (from the cylinder the misfire code is accusing of misfiring), the next step is to remove the spark plug or spark plugs (of the affected cylinders) and visually check them for obvious problems.
What you're looking for is cracked spark plugs (cracks on their ceramic insulator, to be more specific). Carbon tracks on the spark plugs and inside the spark plug boots. These conditions will cause the spark to bypass the spark plug and jump to Ground on the engine (instead of the sparking inside the cylinder to ignite the fuel)
STEP 3: If the ignition system components check out OK, the next step is to check the fuel injectors.
The following tutorial will help you test the fuel injectors:
STEP 4: If the fuel injectors are OK, the next step would be to test the compression of the misfiring cylinders and compare their compression readings to at least two other non-misfiring cylinders to see if the cause of the misfire is low compression.
The following tutorial explains how to do and interpret a compression test:
The above list of steps may seem/sound like troubleshooting a misfire is a complicated thing but it really isn't. Depending on your level of ‘wrenching’ experience, this is something that you can accomplish without taking it to the shop.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Misfire Code(s)?
To find out what is causing your Dodge pick up (van or SUV) to misfire, you'll need some tools. Without the proper tools, you'll end up wasting time and money.
Depending on what the root cause of the misfire is, you may need several tools. Most of these you can buy online, none of these will break the bank and I'll make some recommendations on them. Here's a guide to some of the basic tools that can be and are used:
- Ignition System Tests:
- Spark tester.
- Multimeter.
- Test light.
- Fuel System Tests:
- Noid light.
- Fuel pressure gauge.
- Multimeter.
- Engine Mechanical Tests:
- Compression tester.
Now of course, you'll also need basic hand tools like: screw-drivers, ratchet wrenches, sockets, etc. You'll also need a generic scan tool to retrieve the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the computer's memory (Don't have a scan tool? Need a scan tool? Check out my recommendation: Actron CP9580 Scan Tool).
Keep in mind that using the right tool for the job will save you time, frustration, and /or keep you from damaging the component that you're testing.

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!

