TEST 1: Checking The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Signal
The very first TPS test that we are going to do is to test its ability to produce a throttle angle position signal.
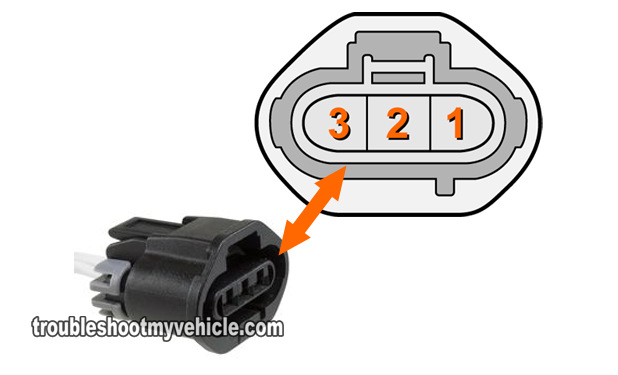
This involves connecting your multimeter (which will be set to Volts DC mode) to the wire labeled with the number 2.
And then manually opening the throttle plate to see if the sensor produces an increasing voltage as you open the plate and a decreasing voltage as you close the throttle plate back to its normally closed position.
If the signal doesn't move (increase or decrease) or the voltage signal shows gaps, then the TP sensor is bad and needs to be replaced.
If you don't have a multimeter or need to upgrade yours? Check out my recommendation: Buying A Digital Multimeter For Automotive Diagnostic Testing (found at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
IMPORTANT: Remember this is an on car test of the sensor, even though the images of the TPS show it off of the engine. The images show the TPS off of the engine just to make it easier to explain the multimeter connection you need to make.
Here are the test steps:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode and connect the red test lead to the wire that connects to circuit #2 of the TPS connector..
NOTE: The TP sensor connector needs to be connected to the TPS, so you'll need to either back-probe the connector or use a wire piercing probe to get to the signal inside the wire (to see what a wire piercing probe looks like: Wire Piercing Probe Tool). - 2
Ground the black multimeter test lead directly on the battery negative (-) post.
- 3
Manually rotate the throttle.
You'll get the best results by opening and closing the throttle directly on the throttle body instead of stepping on the accelerator pedal. - 4
The multimeter should show an increasing voltage as you (or your helper) open up the throttle.
You'll get the best results by opening and closing the throttle directly on the throttle body instead of stepping on the accelerator pedal. - 5
The multimeter should show a decreasing voltage as you begin to close the throttle.
- 6
Using a screwdriver's handle, gently tap the TP sensor as you open and close the throttle and observer the multimeter.
The purpose (of tapping the TP sensor with the screwdriver's handle) is to see if the TP sensor shows gap's in the voltage signal. Why? Because a good TP sensor will show a continuous increasing or decreasing voltage signal even while getting tapped by the screw-driver's handle.
CASE 1: The TP sensor signal's voltage increased and decreased smoothly and without gaps. This is the correct and expected TPS test result. This result tells you that the TPS is working correctly.
This test result also tells you that:
- Circuit #1 is providing Ground.
- Circuit #3 is providing power (5 Volts).
CASE 2: The TP sensor signal's voltage did not increase or decrease. In the majority of the cases this TPS result tells you that the sensor is bad. But not always.
To be sure that the TPS is truly fried, we need to do 2 more tests. These tests involve checking that the sensor is getting both power and Ground. For these tests, go to: Checking Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Power And Ground.
CASE 3: The TP sensor signal's voltage showed gaps in its voltage output as you tapped the sensor with the screwdriver. If the gaps in the multimeter's voltage readings only showed up when you were tapping on the TPS (with the screwdriver's handle) then this test result tells you that the TPS is bad and needs to be replaced.
TEST 2: Checking Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Power And Ground

Just like any other electrical device on your Ford vehicle, if the TPS doesn't get power or Ground it's not going to function.
So in this test section we're going to check to see if the TPS is getting power and Ground using a multimeter.
If the results of this test confirm that the TPS is getting both power and Ground, then we can conclude that the TPS is bad and needs to be replaced (since you have already confirmed in TEST 1 that the sensor is not producing a throttle angle signal).
With the multimeter if Volts DC mode, this is what you need to do:
- 1
Check circuit #1 for Ground with the Key On Engine Off (KOEO).
Connect your multimeter's black test lead to circuit #1 and the red lead to the battery positive (+) post.
The multimeter should register battery voltage (12+ Volts). - 2
Check circuit #3 for power with the Key On Engine Off (KOEO).
Connect your multimeter's red test lead to circuit #3 and the black lead to the battery negative (-) post.
The multimeter should register 4.5 to 5 Volts DC.
Let's take a look at your test results:
CASE 1: Both Ground and power (5 Volts) are present. This is the correct and expected test result.
Since you have now confirmed (in TEST 1) that the TP sensor is not producing a signal and in this test you've confirmed that the sensor is getting both power and Ground, you can conclude the TP sensor is bad and needs to be replaced.
CASE 2: Either Ground or power ARE NOT present. This test result exonerates the TP sensor as being bad and tells you that the reason the TP sensor is not producing an increasing/decreasing voltage signal in TEST 1 is because it's missing power or Ground.
Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial, you'll need to find out why this signal is missing to get the TP sensor back on the job.
