TEST 2: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Power
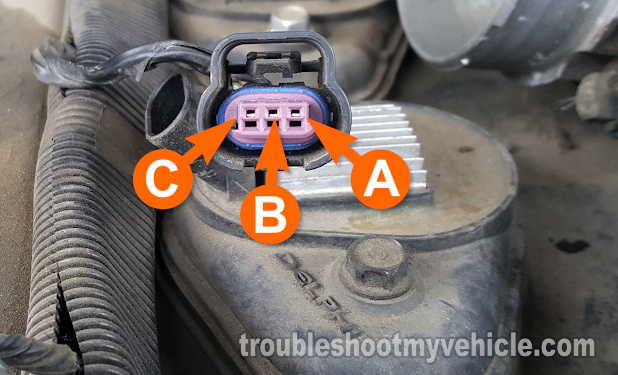
In this testing section, we're going to make sure the non-sparking ignition coil is getting 10 to 12 Volts DC.
The wire feeding these 10 to 12 Volts to the ignition coil is the pink (PNK) wire of the ignition coil's 3-wire electrical connector.
The PNK wire connects to terminal A of the connector in the photo above.
Although it's rare for power to be missing (to the ignition coil), it does happen. And the most common cause of this missing power is an open-circuit problem in the PNK wire.
If the PNK wire is feeding 10 to 12 Volts to the ignition coil, the next step is to make sure the fuel injection computer is supplying an activation signal.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil from its electrical connector.
- 2
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 3
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the PNK wire of the electrical connector.
This wire connects to terminal labeled with a letter A. - 4
Ground the black multimeter test lead directly on the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 5
Turn the key on but don't crank or start the engine.
- 6
You should see a voltage reading between 10 to 12 Volts DC on your multimeter.
Let's examine your test results:
CASE 1: 10 to 12 Volts are present. This is the correct and expected test result and lets you know the ignition coil is getting power.
The next step is to check the ignition coil is getting an activation signal. For this test go to: TEST 3: Swapping The Ignition Coils.
CASE 2: The ignition coil is not getting 10 to 12 Volts DC. Without power the ignition coil is not going to spark.
The most common cause of this missing power is an open-circuit problem in the wire feeding this voltage to the ignition coil.
Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial to diagnose this problem, you have eliminated the ignition coil itself as the source of the misfire. Once power is restored to the ignition coil, it'll spark again.
TEST 3: Swapping Ignition Coils

If you've reached this point, you have confirmed that:
- An ignition coil is not sparking (TEST 1).
- This non-sparking ignition coil is getting 10 to 12 Volts (TEST 2).
In this test section, we're going to make sure this non-sparking ignition coil is getting an activation signal from your Chevrolet TrailBlazer or GMC Envoy's fuel injection computer.
There are several ways of doing this, but the easiest and fastest way to confirm the presence of this activation signal is by swapping out the non-sparking ignition coil with a sparking ignition coil.
If the sparking ignition coil sparks while connected to the non-sparking ignition coil's electrical connector, you can conclude the fuel injection computer is supplying an activation signal (to the non-sparking ignition coil).
If the ignition coil does not spark (while connected to the non-sparking ignition coil's electrical connector), we can conclude its activation signal is missing and causing it not to spark.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Disconnect and remove the ignition coil that did not spark.
- 2
Remove one of the other ignition coil from its place. This coil should be one that sparked when tested in TEST 1.
- 3
Connect the good ignition coil to the non-sparking ignition coil's electrical connector.
Next, connect the HEI spark tester to this ignition coil.
Ground the HEI spark tester with a jump start cable directly on the battery negative (-) terminal. - 4
Place the non-sparking ignition coil in the location of the good one, connect it to the electrical connector, and bolt it down.
- 5
Have your helper crank the engine when everything is set up.
- 6
The good ignition coil should spark.
Let's examine your test results:
CASE 1: The ignition coil sparked. This is the correct and expected test result and lets you know the fuel injection computer is supplying an activation signal to the non-sparking ignition coil's electrical connector.
You can conclude the ignition coil is defective if you have confirmed that:
- The ignition coil is not sparking (TEST 1).
- The ignition coil is getting 10 to 12 Volts (TEST 2).
- The ignition coil's electrical connector is supplying an activation signal from the fuel injection computer (TEST 3).
Check out my ignition coil recommendations here: Where To Buy The Ignition Coil And Save.
CASE 2: The ignition coil did not spark. This test result lets you know the activation signal is not present in the non-sparking ignition coil's electrical connector.
Without this activation signal the ignition coil will not spark. The most common cause of this missing activation signal is an open-circuit problem in the wire between the ignition coil's connector and the fuel injection computer's connector.
Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial to troubleshoot this problem, you have eliminated the ignition coil itself as the cause of the misfire. Once the ignition coil receives its activation signal, it will function again.

