
The single wire oxygen sensor, on the 1991-1994 1.5L Honda Civics, can easily be tested using only a multimeter. This multimeter test can tell you if it has failed or not and all without having to remove it from its place on the exhaust manifold.
In this tutorial, I'll show you how in a step-by-step way.
NOTE: This tutorial applies to the single wire oxygen sensor equipped 1.5L Honda Civic. If your Honda Civic has a 4-wire oxygen sensor, then the testing procedures in this tutorial do not apply to it. See the box titled Applies To: On the right column for 1.5L Honda Civic application specifics.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Oxygen Sensor.
- Oxygen Sensor Basics.
- Where To Buy The O2 Sensor And Save.
- TEST 1: Checking The O2 Signal With A Multimeter.
- TEST 2: Manually Creating A Rich Condition To Test The O2 Sensor.
- TEST 3: Manually Creating A Lean Condition To Test The O2 Sensor.
- Oxygen Sensor Codes Keep Coming Back.
- More 1.5L Honda Civic Diagnostic Test Tutorials.
ES ![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor de Oxígeno (1.5L Honda Civic) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor de Oxígeno (1.5L Honda Civic) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 1.5L Honda Civic: 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995.
- 1.5L Honda Civic Del Sol: 1993, 1994, 1995.
Symptoms Of A Bad Oxygen Sensor
The fuel injection computer in your Honda needs to know if it's injecting too much or not enough gasoline into the engine. Why? So that it can adjust the air/fuel mixture that the engine needs to burn to create power, get good fuel economy, and pollute less.
The main component it uses to control (fine-tune) the air fuel mixture is the single wire oxygen sensor that's located before the catalytic converter (your Civic only uses one oxygen sensor). Since the feedback information that the O2 sensor provides is so important, your Honda is going to perform poorly when it fails.
The effects of a bad oxygen sensor can be very subtle since they usually do not cause serious drive-ability problems. Here are the most common symptoms:
- O2 sensor will stay stuck reporting a false rich air/fuel mixture.
- O2 sensor will stay stuck reporting a false lean air/fuel mixture.
- O2 sensor will respond to slowly to changes in the air/fuel mixture being burned in the engine.
- The check engine light (CEL) will be shining nice and bright to let you know there's a problem.
- One of the following diagnostic trouble codes registered in the computer's memory:
- Code 1 Oxygen Sensor Circuit.
- Really bad gas mileage.
- Won't pass state mandated emission testing.
Oxygen Sensor Basics
As mentioned before, your 1.5L Honda Civic's fuel injection computer uses the oxygen sensor as a feedback sensor to find out whether it's injecting to much fuel or not enough.
You and I can find out if the oxygen sensor is doing its job by tapping into its signal wire with a multimeter. But to really understand how the O2 sensor reports a rich or a lean condition we need to know how it works.
Here are some more specifics:
-
As the engine runs, the computer (PCM) is constantly injecting fuel into the cylinders. When it injects too much, the oxygen sensor reacts by sending back a voltage above 0.500 Volts (this can climb as high as 0.900 to 1.0 Volt).
The PCM interprets any voltage above 0.500 Volts as a Rich condition. To correct it, the PCM responds by reducing the amount of fuel it injects.
-
As the PCM reduces fuel, it may overshoot and not inject enough. When the mixture goes lean, the O2 sensor reacts by dropping its signal below 0.500 Volts. In a very lean condition, the sensor's voltage can fall as low as 0.050 to 0.100 Volts.
The PCM interprets these lower voltage numbers as a Lean condition and compensates by increasing fuel injection again.
-
This back-and-forth correction cycle—rich, then lean, then back again—continues the entire time the engine is running, as long as the O2 sensor is working correctly. This cycle is what keeps the air/fuel mixture balanced at or near the ideal ratio.
-
You can observe these voltage swings directly with a multimeter set to Volts DC. In fact, this is the basis for the O2 sensor test I'm going to show you.
-
A properly working O2 sensor will continuously switch its output voltage between rich and lean several times every few seconds. If, during testing, the voltage stays fixed and doesn't switch, it's a clear sign the O2 sensor has failed.
Where To Buy The O2 Sensor And Save
You can buy the single-wire oxygen sensor for your 1.5L Honda Civic using the following links:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
Not sure if the above oxygen sensor fits your particular 1.5L Honda Civic? Don't worry. Once you get to the site, they'll make sure it does. If it doesn't, they'll find the one that does by asking you the specifics of your Civic.
TEST 1: Checking The O2 Signal With A Multimeter
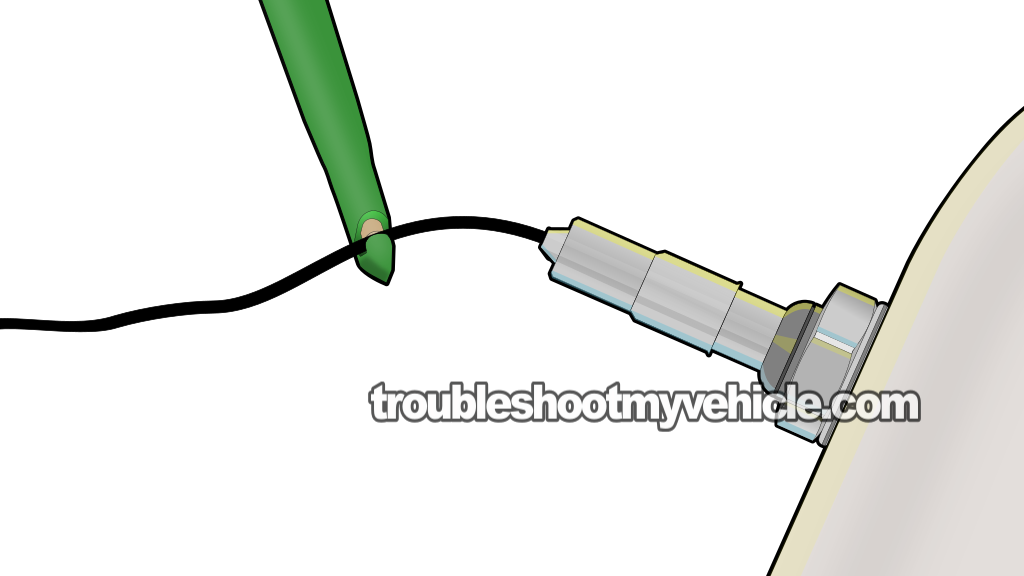
As mentioned in the previous section, the single wire O2 sensor will fail in one of 3 ways. It'll stay stuck reporting a rich condition, or stay stuck reporting a lean condition, or respond too slowly to changes in the air/fuel mixture. If the terms 'rich' and 'lean' aren't familiar to you, take a look at the section Oxygen Sensor Basics for more info.
You and I can see what the oxygen sensor is reporting by tapping into its signal wire with a multimeter. So, for our first test, we're gonna' see what the O2 sensor is reporting and determine if there's a problem or not.
IMPORTANT: Use a 10 megohm impedance digital multimeter to test the O2 sensor. If you don't own one, this is the one I use and recommend: Tekpower TP8268 AC/DC Auto/Manual Range Digital Multimeter (Amazon affiliate link).
These are the test steps:
- 1
Set your multimeter to Volts DC mode. Remember, your multimeter must be a 10 megohm impedance type.
- 2
Connect your multimeter to oxygen sensor wire. You'll need to use a wire piercing probe to accomplish this.
To see what a wire piercing probe looks like and where to buy it, look here: Goupchn 4mm Banana to Banana Plug Test Leads Kit (Amazon affiliate link). - 3
Start the engine and let it warm up till it reaches normal operating temperature.
If the engine is completely cold, accelerate it to about 2,000 RPMs for about 5 minutes till the upper radiator hose starts to get warm to the touch. - 4
Observe the multimeter voltage changes once the engine has reached normal operating temperature and you have let it return to its normal idle RPM.
If the O2 sensor is OK, then it will produce a constantly changing voltage between 0.4 to 1 Volt DC the entire time the engine is running.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The O2 sensor signal voltage moved up and down the as the engine idled. This is the correct test result since it shows the oxygen sensor reacting and reporting the lean and rich conditions the fuel injection computer is creating and compensating.
There's a good chance that even tho' the voltage is moving up and down (as it should), the O2 sensor is reacting too slowly. So, my suggestion is to see how fast it responds to a rich air/fuel mixture. If it responds too slowly, the sensor needs to be replaced. For this test go to: TEST 2: Manually Creating A Rich Condition To Test The O2 Sensor.
CASE 2: The O2 sensor voltage was stuck above 0.5 Volts as the engine idled. This test result tells you that the O2 sensor is seeing a constant rich air/fuel mixture. This could be a result of an engine performance issue or the O2 sensor could be bad.
To find out, the next step is to create a lean air/fuel mixture to see if the O2 sensor reacts to it. For this test go to: TEST 3: Manually Creating A Lean Condition To Test The O2 Sensor.
CASE 3: The O2 sensor voltage was stuck below 0.5 Volts as the engine idled. This test result tells you that the O2 sensor is seeing a constant lean air/fuel mixture. This could be a result of an engine performance issue or the O2 sensor could be bad.
To find out, the next step is to create a rich air/fuel mixture to see if the O2 sensor reacts to it. For this test go to: TEST 2: Manually Creating A Rich Condition To Test The O2 Sensor.
TEST 2: Manually Creating A Rich Condition To Test The O2 Sensor

In this test section, we're going to force a rich air/fuel mixture and see if the O2 sensor reacts to it (or not). And if it does react to this rich condition, we need to see how fast it does.
The fastest and easiest way to induce a rich air/fuel mixture is by spraying a little starting fluid into the engine while it's running. My preferred method is to spray starting fluid into a vacuum hose.
Once the starting fluid hits the engine cylinders, you'll get an instant rich air/fuel mixture. The oxygen sensor should react by immediately producing its maximum voltage (0.900 Volts +).
Alright, these are the test steps:
- 1
Start your Honda and let it idle for about 15 minutes, since you need a warmed up engine to get the O2 sensor to activate.
The multimeter should still be tapped into the signal wire from TEST 1. - 2
The voltage numbers of the O2 sensor should moving between 0.100 and 0.900 Volts constantly on your multimeter's display after the engine has been running for 15 minutes.
If the voltage value stays fixed, don't worry about this yet, continue to the next step. - 3
With the engine running, spray a little starting fluid into a vacuum hose (that has engine vacuum) while you observe your multimeter's display screen.
If you spray too much, there's a good chance that the engine will stall. If it happens, just restart the engine and repeat the step and spray less starting fluid. - 4
The oxygen sensor should immediately report 0.800 to 0.900 Volts, as you spray the short bursts of carb cleaner into the vacuum hose. And as long as you're spraying (without the engine stalling), the voltage should stay there.
- 5
When you stop spraying, the O2 sensor values should come down and within a few seconds, they should start oscillating between 0.100 Volts to 0.900 Volts.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The oxygen sensor voltage numbers immediately spiked to 0.900 Volts when you sprayed carb spray into the vacuum hose. This tells you that the oxygen sensor is OK at this point in time. It does not need to be replaced, since whatever's causing the computer to think it's fried is something else.
For more info on this, go to the section: Oxygen Sensor Codes Keep Coming Back.
CASE 2: The oxygen sensor voltage DID NOT react when you sprayed carb spray into the vacuum hose. This confirms that oxygen sensor is no longer working. You can replace the oxygen sensor.
CASE 3: The oxygen sensor voltage numbers SLOWLY spiked to 0.800 Volts after you sprayed carb spray into the vacuum hose. This confirms that oxygen sensor is too old and too slow. You should replace the oxygen sensor.
TEST 3: Manually Creating A Lean Condition To Test The O2 Sensor
Since you've verified that the oxygen sensor can react to a rich air/fuel mixture and report it, in this section we'll induce a lean air/fuel mixture. We can do this easily by:
- Disconnecting a large vacuum hose.
- The vacuum hose we're gonna' disconnect is the one that connect to the brake booster.
Once this large vacuum hose is disconnected (with the engine running), the air/fuel mixture will instantly become lean. This will cause the oxygen sensor to produce its minimum voltage (between 0.100 to 0.200 Volts). We'll be able to see this low voltage reading on your multimeter's display.
As mentioned above, the hose that we'll disconnect is the one that connects the intake manifold to the vacuum brake booster. You don't have to remove it completely, just crack it open enough to get a good vacuum leak.
Alright, here are the test steps:
- 1
Crank and start your Honda Civic's engine. Let the engine run for about 15 minutes.
Your multimeter should still be tapped into the oxygen sensor's signal wire from TEST 1. - 2
Disconnect vacuum hose with the engine running as you watch the reading of the O2 sensor's voltage reading on your multimeter's display.
If the engine is stalls, simply restart it and start from step 1 again (and disconnect the hose just a little this time). - 3
As you're letting air enter the brake booster's vacuum hose, the voltage reading of the O2 sensor should decrease to about 0.100 to 0.200 Volts. And while the vacuum hose is letting ambient air into the intake manifold, the voltage should remain at about 0.100 to 0.200 Volts.
- 4
Reconnect the brake booster's hose and stop the vacuum leak. The voltage reading should now start to move up and down between 0.100 to 0.900 Volts.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The voltage immediately dropped to 0.100 Volt as you opened the brake booster's vacuum hose. This tells you that the oxygen sensor is working well since it can react to a lean air/fuel mixture and report it.
Now, if the oxygen sensor passed the test in TEST 1 and passed this test (TEST 2), then you can conclude with certainty that the oxygen sensor is working properly and it doesn't need to be replaced. If the computer is still accusing it of being defective, take a look at this section: Oxygen Sensor Codes Keep Coming Back.
CASE 2: The voltage DID NOT drop to 0.100 Volt as you opened the brake booster's vacuum hose. This test result tells you that the oxygen sensor is defective since it can not react to a lean air/fuel mixture. Replacing the O2 sensor will solve the issue.
Oxygen Sensor Codes Keep Coming Back
There's a good chance that you have tested the O2 sensor on your Honda and it tested good or you replaced it, but it didn't solve the problem.
When this happens, it usually means that the problem (that's made us think the O2 sensor was bad) is being caused by something else. That something else is causing a Rich or a Lean condition that is causing the O2 sensor code.
Some of the things that can cause a Rich condition are:
- A cylinder misfire caused by:
- Bad spark plugs.
- Bad spark plug wires.
- Bad distributor cap.
- Clogged or leaking fuel injectors that are not atomizing the fuel correctly.
- Bad fuel pressure regulator for leaking fuel into each vacuum hose.
Some of the things that can cause a Lean condition are:
- Vacuum leaks caused by:
- Bad intake manifold gaskets.
- Leaking or broken vacuum hoses.
- Extremely clogged fuel filter.
- Bad fuel pump that is not producing enough pressure or volume.
My suggestion to you is to take a good look at some of the above components and see what condition they're in or if they need to be tested before replacing any of them.
More 1.5L Honda Civic Diagnostic Test Tutorials
I've written quite a few 1.5L Honda Civic tutorials that may help you troubleshoot the issues on your Honda Civic. You can find the complete list in this index:
Here's a sample of the 1.5L Honda Civic tutorials you'll find:
- How To Test The MAP Sensor (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
- How To Test The Throttle Position Sensor (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
- How To Test Engine Compression (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
- How To Test The Fuel Pump (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
- How To Test The Igniter, Ignition Coil Accord, Civic, CRV, and Odyssey (at easyautodiagnostics.com).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!





