The throttle position sensor (TPS for short) on your 1994-2002 Mazda 626 equipped with a 2.0L 4 cylinder can be easily tested with a multimeter. Although a scan tool is a must-have tool for any do-it-yourself'er, you don't need it to accurately test it.
In this tutorial I'll show you how in a step-by-step way and in the process, you'll find out if the TPS is good or has failed.
Contents of this tutorial:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor TPS (1994-2002 2.0L Mazda 626) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor TPS (1994-2002 2.0L Mazda 626) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
RELATED TROUBLE CODES:
- P0121 -What Does It Mean? (1996-2002 2.0L Mazda 626).
- P0122 -What Does It Mean? (1996-2002 2.0L Mazda 626).
- P0123 -What Does It Mean? (1996-2002 2.0L Mazda 626).
Symptoms Of A Bad Throttle Position Sensor
As you're probably already aware, the TPS is tasked with measuring the throttle plate's angle as you step on or off the accelerator pedal (since the accelerator pedal is connected to the throttle plate via the accelerator cable).
The throttle plate angle voltage signal, that the TPS creates, tells the fuel injection computer the exact position of the throttle plate. This information is used, among many things, to: inject more fuel, advance ignition timing, etc.
Since the TPS plays such a critical role in your 2.0L Mazda 626's engine management system, when it fails you'll see or more of the following symptoms:
- If your 2.0L Mazda 626 is OBD II equipped (1996+), you'll see one of the following trouble codes:
- P0121: Throttle Position Sensor Performance Problem.
- P0122: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit Low Voltage.
- P0123: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit High Voltage.
- P1120: Throttle Position Sensor.
- P1121: Throttle Position Sensor Out Of Range.
- P1124: Throttle Position Sensor Out Of Range.
- P1125: Throttle Position Sensor Out Of Range.
- If your 2.0L Mazda 626 is OBD I equipped, you'll see one of the following trouble codes:
- 121: TPS and MAF Do Not Agree.
- 122: TPS Voltage Too Low.
- 123: TPS Voltage Too High.
- Hesitation when accelerating the engine.
- Lack of power.
- Bad gas mileage.
Circuit Descriptions Of The TPS
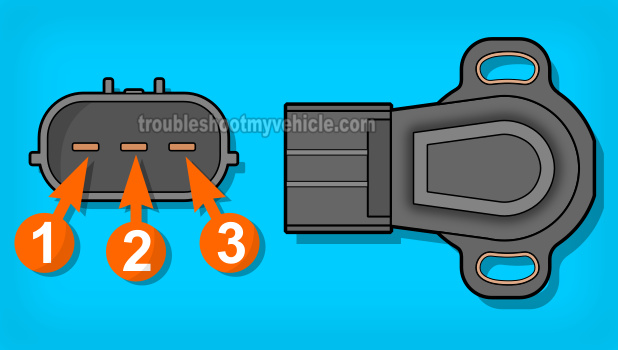
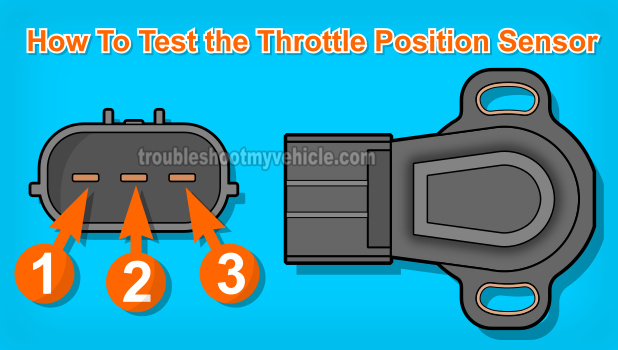
The table below has a brief description of the 3 wires that make up the TPS connector.
| Throttle Position Sensor Circuits (2.0L Mazda 626) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Terminal | Wire | Description |
| 1 | GRY/RED | Sensor Ground |
| 2 | VIO/YEL | TP Signal |
| 3 | BLK/YEL | Power (5 Volts DC) |
NOTE: The terminals on the throttle position sensor itself are male spade terminals. The terminals on the TPS engine wiring harness connector are female terminals. Also, the colors listed above apply to 1999 2.0L Mazda 2.0L 626. Your specific vehicle may have different colored wires, but the circuit descriptions will be the same.
Where To Buy The TPS And Save
The following links will help you to comparison shop for a new 2.0L Mazda 626 TPS. I think they'll save you a few bucks:
Not sure if the above TPS fits your particular 2.0L Mazda 626? Don't worry, once you get to the site they'll make sure it fits by asking you the specifics of your particular Ford vehicle. If it doesn't fit, they'll find you the right one.
TEST 1: Testing The TPS Voltage Signal

We're gonna' use a multimeter to find out if the TPS is working correctly or not. We'll do this by reading its throttle angle voltage signal. This entails tapping into the TP sensor's middle wire and reading the voltage signal as we manually open and close the throttle plate.
If your 2.0L Mazda 626's TPS is working correctly, this throttle angle voltage signal will increase as we open the throttle plate and decrease as we close it.
Now, if the throttle position sensor is bad, its throttle angle voltage signal will stay stuck in one voltage value no matter how much we open or close the throttle plate.
Alright, these are the test steps:
- 1
Turn the key to the ON position but don't start the engine, and place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 2
Probe the middle wire of the TPS engine wiring harness connector with the red multimeter test lead. This is the wire that connects to TPS male spade terminal identified with the #2 in the illustration above.
Ground the black multimeter test lead on the battery negative (-) terminal.
NOTE: The TP sensor must remain connected to its electrical connector. You'll need to use a back probe or a wiring piercing probe to tap into the signal of the middle wire. To see what a wire piercing probe looks like and where to buy one, go here: Wire Piercing Probe. - 3
Your multimeter should report a voltage between 0.2 to 0.9 Volts DC with the throttle plate closed. If your multimeter doesn't, don't worry about it just yet, continue with the other steps.
- 4
Slowly open the throttle (by hand and from the engine compartment). The voltage numbers should increase as the throttle plate opens.
This increase in voltage should be smooth and without any gaps or skips. Once the throttle is wide open, your multimeter should read somewhere between 3.5 to 4.5 Volts DC. - 5
Slowly close the throttle. As the throttle is closing, you should see the voltage decrease smoothly and without any gaps or skips, to the exact same voltage you noticed in step 3.
- 6
Lightly tap on the throttle position sensor with the handle of a screw-driver (or something similar, and I want to emphasize the words ‘lightly tap’) as you slowly open and close the throttle and observe the multimeter.
If the TPS is bad, the tapping will cause the voltage numbers to skip or go blank. If the TPS is OK, the tapping will have no effect on the voltage numbers. - 7
Repeat step 6 several times to make sure of your multimeter test results.
Let's take a look at your test results:
CASE 1: The throttle angle voltage increased and decreased as you opened and closed the throttle plate. This is the correct test result. It tells you that the TPS, on your 2.0L Mazda 626 IS NOT defective.
This test result also confirms that the TPS is getting both power and Ground from your 2.0L Mazda 626's fuel injection computer.
CASE 2: The throttle angle voltage DID NOT increase (or decrease) as you opened and closed the throttle plate. This test result usually tells you that the TPS, on your 2.0L Mazda 626, is bad.
Just to tie up any loose ends, I recommend that you make sure that it's getting both power (5 Volts) and Ground. For these tests, go to: TEST 2: Verifying Throttle Position Sensor Has 5 Volts And Ground.
CASE 3: The multimeter DID NOT register any voltage. This test result doesn't condemn the TP sensor as bad just yet.
Why? Because the TP sensor may be missing either power or Ground. So the next step is to check that the TP sensor is getting power and Ground, go to: TEST 2: Verifying Throttle Position Sensor Has 5 Volts And Ground.


