Diagnosing an engine no-start condition boils down to three basic tests. In a nutshell: a spark test, a fuel-pressure test, and a compression test.
In this tutorial, I'll walk you through a diagnostic strategy that'll help you pinpoint the cause of the no-start problem on your Nissan Sentra.
Contents of this tutorial:
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 1.6L Nissan Sentra: 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999.
Difference Between A No-Start And A No-Crank Condition
To help you avoid any confusion and before I jump into the specifics of troubleshooting a no-start condition, let me tell you that a no-crank and a no-start condition are not the same thing. Here's a brief description that'll help you make sense of this tutorial:
Cranks but does not start condition: Means that your Nissan's starter motor is cranking the engine but the engine is not starting. This is usually due to a fault in the ignition system, or in the fuel system, or there's an engine mechanical problem (like a blown head gasket, etc.).
Does not crank condition: Means that the engine is not cranking when you turn the key to crank the engine. In other words, the engine doesn't turn over at all. This is usually due to a bad battery, bad starter motor, bad ignition switch, bad neutral safety switch, or the engine is locked up.
If your Nissan doesn't crank, you need to check the battery, possibly the alternator (if you find the battery is discharged), and the starter motor. The following tutorial will help you test the starter:
No Start Condition Basics
The most basic and the most important thing you need to know, to begin troubleshooting the no-start condition, is that your Nissan Sentra's engine needs three things to start and run. These are:
- Air.
- Fuel.
- Spark.
When your Nissan Sentra cranks but does not start, it's because one of these 3 things is missing from the mix.
So, troubleshooting the problem requires that you and I check for spark (with a spark tester), check fuel pressure, and if necessary, check the engine's health with a compression test.
Checking For Spark

The ignition system is usually the culprit behind most 'no-start' conditions. The basic core components of the ignition system that fail and cause a no-start are:
- The ignition control module (ICM) -called the igniter.
- The ignition coil.
- The distributor cap.
- The distributor rotor.
Checking a no-start condition should start with a spark test. Making sure that all 4 cylinders are getting spark. This involves attaching a spark tester to a spark plug wire and having a helper crank the engine. If the spark plug wire sparks, then the test is repeated on the next 3 spark plug wires.
The purpose of this spark check is to make sure that all 4 spark plug wires are feeding spark to their respective cylinder. If spark is present at all 4 spark plug cables, then you can eliminate the ignition system as the culprit behind the no-start condition on your 1.6L Nissan Sentra. Your next diagnostic test step is to make sure that the fuel pump is OK (see next heading)
If you get a no spark test result on all 4 spark plug cables, then further testing is needed to find out the exact component that's causing the no spark issue. A no spark problem is usually caused by:
- Bad distributor cap.
- Bad ignition coil.
- Bad igniter.
Checking For A Lack Of Fuel
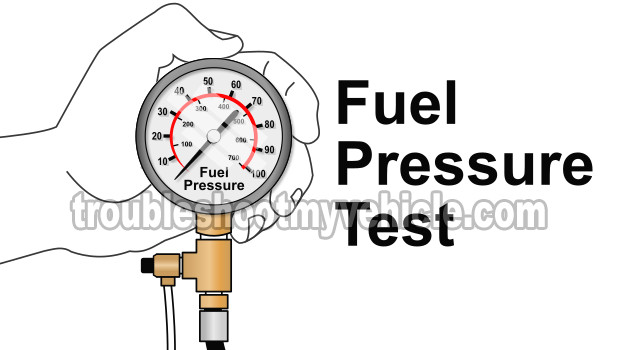
If the ignition system is not behind the no-start condition on your 1.6L Nissan Sentra, then there's a good chance that it might be due to a lack of fuel. Checking for a 'lack of fuel' condition involves checking the fuel pump's pressure with a fuel pressure gauge.
The cool thing is that if you don't have a fuel pressure tester, you can borrow it from your local auto parts store (AutoZone, O'Reilly Auto Parts, etc).
The fuel pressure gauge is placed between the rubber fuel pressure hose and the fuel injector rail with a special T adapter. Once safely in place, the engine is cranked to see what the fuel pressure reading is on the gauge.
The correct fuel pressure specification is 35-43 PSI. This tells you that the fuel pump is good.
If the fuel pump has failed and not delivering fuel to the fuel injectors, the most common fuel pressure result is 0 P.S.I.
You can find the fuel pump test explained in detail here: How To Test The Fuel Pump (1995-1999 1.6L Nissan Sentra)
Checking Engine Mechanical Condition
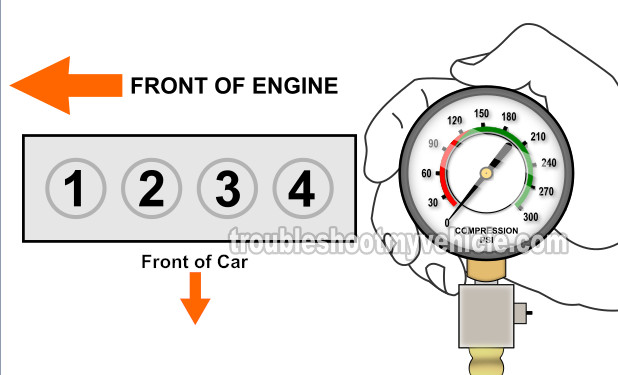
One of the most overlooked areas, when testing a hard to diagnose no-start, is the engine's compression.
If a compression problem is behind your 1.6L Nissan engine's problem, the cylinder's value will be at 0 PSI. A 0 PSI compression test result usually indicates:
- Broken timing belt.
- Blown head gasket.
- Blown engine.
A compression value of 120 + is usually considered normal for these older 1.6L Nissan engines. You can find the engine compression test explained in detail here:
The cylinder head gasket can be tested with four easy to do tests:
More 1.6L Nissan Sentra Tutorials
You can find a complete list of tutorials for the 1.6L Nissan Sentra in this index:
1.6L Nissan Sentra Index Of Articles.
Below, is a sample of articles you'll find in this index of articles:
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (1991-1999 1.6L Nissan Sentra).
- How To Test The TPS (1997-1999 1.6L Nissan Sentra).
- Front O2 Sensor Heater Test -P0135 (1995-1999 1.6 Nissan Sentra).
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Test Nissan Sentra 1.6L (1995-1999) (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- How To Test The 2000-2002 Nissan Sentra 1.8L MAF Sensor (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!


