
In this tutorial, I'll help you diagnose a bad COP ignition coil on your Dodge 4.7L SUV or Pickup.
In case you've been wondering what the acronym COP stands for: Coil On Plug, and refers to the fact that there's an ignition coil sitting on top of each spark plug.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of A Bad COP Ignition Coil.
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The COP Coils.
- What Does The COP Coil Do/Work?
- How To Identify The Misfire Code Engine Cylinder
- Common Causes Of A Misfire Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).
- TEST 1: Checking For Misfire Codes.
- TEST 2: Check The Ignition Coil For Spark.
- TEST 3: Swap The ‘No Spark’ COP Coil.
- TEST 4: Cylinder Balance Test.
- TEST 5: Common Causes Of A P0300.
- Where To Buy The COP Ignition Coil And Save.
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Las Bobinas De Encendido (4.7L Dodge) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Las Bobinas De Encendido (4.7L Dodge) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
NOTE: The following tutorial may come in handy: How To Diagnose A Misfire (2000-2003 4.7L Dodge Dakota) (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
Symptoms Of A Bad COP Ignition Coil
The most obvious symptom, you'll see when a COP ignition coil goes bad, is the check engine light shining nice and bright to let you know that there is a problem. You'll see one or several of the following trouble codes:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes:
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder #1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder #2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder #3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder #4 Misfire.
- P0305: Cylinder #5 Misfire.
- P0306: Cylinder #6 Misfire.
- P0307: Cylinder #5 Misfire.
- P0308: Cylinder #6 Misfire.
Besides the check engine light being on, you'll also see one (or several) of the following symptoms of a bad COP ignition coil:
- Rough idle.
- Engine miss (misfire) when you accelerate the vehicle.
- Smell of raw gasoline coming out of the tailpipe.
- Bad gas mileage.
- Won't pass you state's mandated annual emissions test.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The COP Coils
The most important tool that you're gonna' need is a spark tester. I'm gonna' recommend one that is the most effective (and the most inexpensive) out there: the HEI spark tester.
From personal experience (I work full-time as an automotive tech) I can tell you that the HEI spark tester is a must-have tool. You don't need to interpret the color of the spark or the weakness of it. With the HEI spark tester, if it sparks then the ignition coil is good.
- An HEI spark tester.
- To find out more about this inexpensive yet accurate spark tester, go here: The HEI Spark Tester (The Best Spark Tester On The Market) (this article at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- If you need to buy one, you can buy it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester
- Scan tool.
- A scan tool is not needed to check the COP coils with the info I'm presenting in this tutorial but it does come in handy to retrieve the misfire DTC (diagnostic trouble code).
- Don't have one? -Check out my recommendation: Abe's Scan Tool Recommendation.
What Does The COP Coil Do/Work?
In a nutshell, the COP ignition coil's job is to create and deliver spark to the spark plug at the precise moment in the engine's combustion cycle.
This is all accomplished without all of the moving parts required of a conventional (and outdated) distributor type ignition system. Here's a basic list of things that a COP coil ignition system replaces:
- A mechanical distributor assembly.
- Distributor cap.
- Distributor rotor.
- Spark plug wires.
Now, in case you're really curious about how it works, below is a very brief description of how it works:
- Each COP ignition coil has 2 wires in their connector.
- When you turn the key and crank the engine:
- One of the two wires (in the COP coil's connector) supplies battery power (usually 10 to 12 Volts DC).
- As the engine cranks, the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor starts to generate its crank signal.
- The PCM (Powertrain Control Module = Fuel Injection Computer) gets the crankshaft position signal from the crank sensor.
- The PCM now activates each COP ignition coil.
- This activation (of the COP coil) is done by simply switching the ignition coil's primary current (the fancy name for the 12 Volts that the COP coil is fed) On and Off.
- To be a bit more specific: This ON/OFF action happens on the ignition coil's ground wire.
Now, although the COP coil ignition system on your Dodge 4.7L equipped pickup or SUV is a major step forward over a distributor based ignition system, you still have things go wrong. The most common of failures is a COP ignition coil going bad and causing a misfire (which in turn causes the check engine light (CEL) to illuminate).
How To Identify The Misfire Code Engine Cylinder
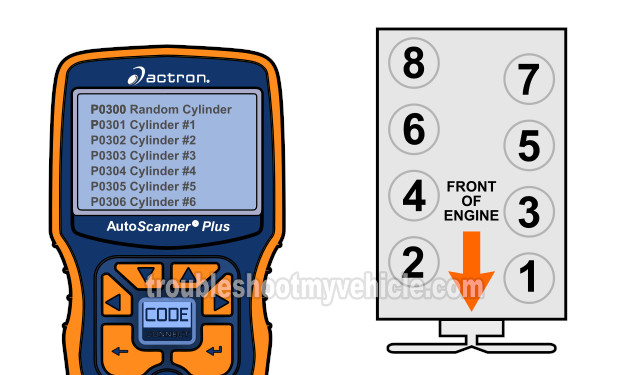
Each engine cylinder (and thus COP coil) is assigned a specific number.
This number is used to identify the ignition system firing order. Now, our concern is not the ignition system firing order. What we want is just to identify the COP coil the misfire code is accusing of Misfiring.
Using the illustration in the image viewer, you can find out which engine cylinder is the one that's misfiring.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes:
- P0301: This identifies Cylinder #1 as Misfiring.
- P0302: This identifies Cylinder #2 as Misfiring.
- P0303: This identifies Cylinder #3 as Misfiring.
- P0304: This identifies Cylinder #4 as Misfiring.
- P0305: This identifies Cylinder #5 as Misfiring.
- P0306: This identifies Cylinder #6 as Misfiring.
- P0307: This identifies Cylinder #7 as Misfiring.
- P0308: This identifies Cylinder #8 as Misfiring.
The one thing to keep in mind, is that the misfire trouble code is only a guide. It doesn't tell you that a specific part/component is bad and needs to be replaced.
This is where this tutorial comes in handy since I'll show you how to test the COP coils and see if one of them is bad and thus the cause of the misfire code and misfire condition.

