
On the 2000-2007 2.0L DOHC Ford Focus, the throttle position sensor (TPS) is one of the easiest sensors to check.
The best part: you don't need any expensive diagnostic equipment —a basic multimeter is all it takes. No scan tool required for this test.
You also don't have to remove the TPS from the throttle body. It can be tested right on the engine, in place.
In this tutorial, I'll walk you through the whole procedure step by step.
Contents of this tutorial:
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 2.0L DOHC Ford Focus: 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010.
TPS CODE DIAGNOSTICS: Click below to see what each one really means, the common causes, and what to check next:
- P0121 TPS Performance Problem Code Diagnostics (2000-2007 2.0L Ford Focus).
- P0122 TPS Circuit Low Code Diagnostics (2000-2007 2.0L Ford Focus).
- P0123 TPS Circuit High Code Diagnostics (2000-2007 2.0L Ford Focus).
Symptoms Of A Bad Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
These are the most common signs of a failing throttle position sensor (TPS) on your Ford Focus:
- Check engine light with TPS codes:
- P0121: Throttle Position (TP) Circuit Performance Problem.
- P0122: Throttle Position (TP) Circuit Low Input.
- P0123: Throttle Position (TP) Circuit High Input.
- Hesitation on acceleration: Stumbling or hesitation when you press the gas pedal.
- Loss of power: Intermittent lack of power while accelerating.
- Bad gas mileage: Noticeable drop in gas mileage.
- Hard starting: Engine takes longer than normal to crank and fire up.
- Rough/lopey idle: Idle speed surges up and down instead of staying steady.
- No-start condition: If TPS voltage is stuck high, the engine may not start at all.
The following links explain in more detail what the TPS sensor DTC lighting up the check engine light is trying to tell you:
- P0121 TPS Performance Problem Code Diagnostics (2000-2007 2.0L Ford Focus).
- P0122 TPS Circuit Low Code Diagnostics (2000-2007 2.0L Ford Focus).
- P0123 TPS Circuit High Code Diagnostics (2000-2007 2.0L Ford Focus).
Where To Buy The TPS And Save
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
TEST 1: Checking The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Signal
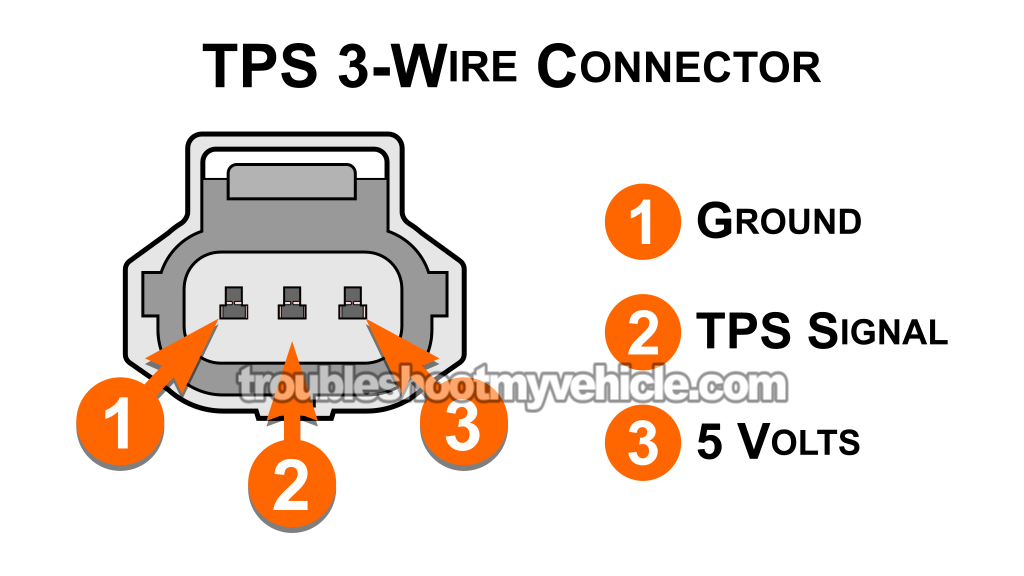
For our first test, we're going to check the output voltage signal of the throttle position sensor.
This is pretty simple to do —all we need is to tap into the middle wire of the TPS connector with a multimeter.
Once we're tapped in, we'll turn the key to the ON position (with the engine OFF) and then manually open and close the throttle plate.
You'll see one of two things:
- If everything is OK, the voltage output will rise and fall as you open and close the throttle plate.
- If the TPS sensor is bad, the voltage will stay stuck at one value.
The most important thing to remember is that the TPS must stay connected to its connector while testing. So you'll need to tap into the signal wire using either a back probe at the connector or a wire-piercing probe on the wire. If you don't have one of these tools, check out my recommendation here — it's the tool I personally use and recommend:
- Goupchn 4mm Banana to Banana Plug Test Leads Kit (Amazon affiliate link).
If you don't have a multimeter or need to upgrade yours? Check out my recommendation: Tekpower TP8268 AC/DC Auto/Manual Range Digital Multimeter (Amazon affiliate link).
Here are the test steps:
- 1
Hook up the black test lead of your multimeter to the negative (-) battery post.
- 2
Switch your multimeter to DC Volts mode.
- 3
Turn the key to the ON position (engine OFF). Do not crank or start the engine.
This step powers up the TPS. - 4
Probe the middle wire of the TPS connector with the red multimeter lead and an appropriate tool (like a back probe or a wire-piercing probe).
The middle wire of the TPS connector should be a white (WHT) wire.
NOTE: The TPS must stay connected to its 3-wire connector during this test. - 5
With the throttle plate completely closed, the voltage should read between 0.3 and 0.9 Volts DC.
This is your base reading. - 6
Open the throttle plate slowly by hand. The voltage should climb smoothly as the plate opens.
- 7
At wide open throttle (WOT), the voltage should be between 3.5 and 4.5 Volts DC.
- 8
Close the throttle plate slowly. The voltage should fall back down to the same number you recorded in step 5.
Verify that the closed-throttle reading matches your starting value. - 9
Lightly tap the TPS body with the handle of a screwdriver while opening and closing the throttle plate.
NOTE: Tapping on the sensor should not cause the readings to spike, cut out, or glitch. If it does, the TPS is faulty and must be replaced.
Here's how to interpret your results:
CASE 1: The TPS voltage signal increased and decreased smoothly with no interruptions. This is the correct and expected outcome. It confirms the TPS is working properly.
This result also confirms that the TPS is receiving both power and Ground. No further testing is needed.
CASE 2: The TPS voltage signal did not rise or fall. In most cases, this points to a bad TPS. But not always.
To confirm the sensor is truly bad, two additional checks are needed. The first is here: TEST 2: Making Sure The TPS Is Getting Power.
CASE 3: The TPS voltage signal showed spikes or drop-outs only when the sensor was tapped. If this happens, the TPS is defective and needs to be replaced.
TEST 2: Making Sure The TPS Is Getting Power

Since the TPS isn't producing a voltage signal that rises and falls as the throttle plate is opened and closed (TEST 1), the next step is to make sure it's getting power.
This power comes in the form of 5 Volts, supplied by the PCM. The wire that carries this voltage is the yellow (YEL) wire of the TPS 3-wire connector.
The YEL wire connects to the terminal I've labeled as number 3 in the TPS connector pinout illustration above.
We'll do a simple multimeter voltage test to check for the presence of 5 Volts at terminal 3.
Here's what we need to do:
- 1
Unplug the TPS from its 3-wire connector.
- 2
Switch the key to the ON position (engine off). Don't crank or start the engine —this step only powers up the TPS circuit.
- 3
Put your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 4
Attach the black multimeter lead to the battery's negative (-) post.
- 5
Probe terminal 3 of the TPS connector with the red multimeter lead.
NOTE: Terminal 3 is the 5-Volt supply and should connect to the YEL wire of the connector. - 6
The multimeter should show between 4.5 and 5.0 Volts DC.
Here's how to read your results:
CASE 1: You see 4.5 to 5 Volts on the multimeter. That's the correct and expected reading.
This confirms the TPS is receiving power. The next step is to make sure it also has Ground. For that, go to: TEST 3: Making Sure The TPS Is Getting Ground.
CASE 2: No power is present. First, make sure you're on the right terminal and repeat the check.
If the 4.5 to 5 Volts still don't show up, the TPS itself isn't the problem. Without a 5-Volt feed, the sensor can't work.
Tracking down the missing voltage is beyond this tutorial, but the next step is to find and fix the cause of these missing 5 Volts (in the circuit) to get the TPS working again.
Most of the time, the missing voltage is caused by an open-circuit problem in the 5-Volt supply wire between the TPS connector and the PCM.
TEST 3: Making Sure The TPS Is Getting Ground

Up to this point, you've confirmed that:
- The throttle position sensor isn't producing a voltage signal that rises and falls when you open and close the throttle plate (TEST 1).
- The throttle position sensor is receiving 5 Volts (TEST 2).
Now for our last test, we're going to make sure the throttle position sensor is getting Ground.
This Ground comes from the PCM. It's carried by the brown (BRN) wire of the TPS connector and goes to the female terminal labeled number 1 in the pinout illustration of the TPS 3-wire connector above.
To check for this Ground, we'll do a simple multimeter voltage test. This will tell us if the circuit has Ground or not.
IMPORTANT: Be careful when testing the Ground circuit, since it connects directly from the PCM. Do not connect this circuit straight to battery 12 Volts or you'll deep-fry the PCM. The multimeter voltage test shown below is the safe way to confirm Ground is present in the circuit.
OK, let's begin:
- 1
Unplug the TPS from its 3-wire connector.
- 2
Turn the ignition key to the ON position (engine off). Don't crank or start the engine —this step only powers up the TPS circuit.
- 3
Put your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 4
Attach the red multimeter lead to the battery positive (+) post.
- 5
Probe terminal 1 of the TPS connector with the black multimeter lead.
NOTE: Terminal 1 is the Ground circuit and should be the BRN wire in the TPS connector. - 6
Your meter should show between 10 and 12 Volts DC.
Here's how to interpret your test results:
CASE 1: Ground is present. This is the correct and expected result.
You can now confirm the TPS is bad and needs replacement if all three conditions below are true:
- The TPS did not produce a voltage signal that rose and fell as you opened and closed the throttle plate (TEST 1).
- The TPS is receiving 5 Volts (TEST 2).
- The TPS is receiving Ground (this test).
When you're ready to replace it, here's the TPS I recommend:
- SCHNECKE 5S5127-AA Throttle Position TPS Sensor (Amazon affiliate link)
CASE 2: Ground IS NOT present. Double-check that you're testing the correct terminal and repeat the test.
If you still don't see 10 to 12 DC on your multimeter, then you can conclude that the TPS itself is OK, since without Ground, it's not going to function.
Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial, your next step is to find out why the TPS isn't being supplied with Ground and restore it to the circuit (to get the TPS back on the job).
The most likely cause of this missing Ground is an open-circuit issue in the Ground supply wire between the TPS connector and the PCM.
More 2.0L Ford Focus Diagnostic Tutorials
You can find a complete list of tutorials and wiring diagrams for the 2.0L Ford Focus in this index:
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find:
- How To Test The MAF Sensor (2000-2004 2.0L Ford Focus).
- P0102 MAF Signal Low Code Diagnostics (2000-2007 2.0L Ford Focus).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (2000-2010 2.0L Ford Focus).
- How To Test Engine Compression (2000-2010 2.0L Ford Focus).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!


