One of the things that makes testing the fuel injectors on the 2.0L DOHC Ford Focus easy is that they're super accessible. I mean, they're right there in the open.
In this tutorial, I'm going to show you how to check the resistance of each fuel injector to see if any have worn out and suffered an internal short-circuit or open-circuit problem.
I'm also going to explain a step-by-step diagnostic method that'll help you figure out the exact cause of the cylinder misfire —whether it's due to a clogged fuel injector or something else entirely.
Contents of this tutorial:
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles equipped with the double overhead cam (DOHC) engine:
- 2.0L DOHC Ford Focus: 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004.
2000-2004 SOHC FUEL INJECTOR TESTS:
Symptoms Of A Bad Fuel Injector
The fuel injectors on your Ford Focus can fail in a few different ways:
- Failure 1: The injector fails internally and just stops spraying fuel.
- Failure 2: The injector clogs with deposits that restrict its spray pattern or flow.
- Failure 3: The injector doesn't activate because it isn't getting power or the switching signal it needs.
Since the fuel each injector sprays is critical to keeping its cylinder alive and running, any clog or complete failure will lead to one or more of the following symptoms:
- Rough idle.
- Lack of power.
- Hesitation when you accelerate your 2.0L Ford Focus down the road.
- Since the 2.0L Ford Focus is OBD II equipped, you'll see a misfire diagnostic trouble code (DTC):
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder #1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder #2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder #3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder #4 Misfire.
Although in this tutorial, we're gonna focus on testing the internal resistance of the fuel injector to see if it has stopped injecting fuel altogether, I can tell you that checking for a clogged injector isn't much harder. I'll also be covering how to do that step by step in this guide.
Checking The Injector's Internal Resistance
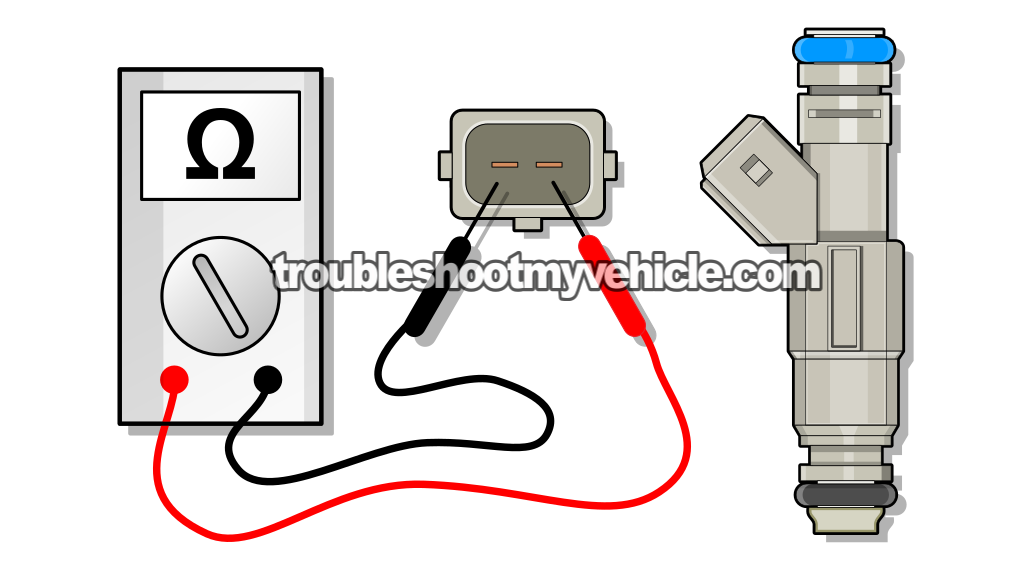
Each fuel injector has an internal coil winding, and it's this winding that opens and closes the injector's pintle so it can spray fuel.
Over time, that winding can short out, and when it does, the injector fails and stops spraying fuel.
The easiest way to find out if the coil is still good is to check its resistance with a multimeter in Ohms mode.
If the fuel injector is OK internally, we should see a resistance of 11-18 Ohms on our multimeter.
NOTE: Don't have a multimeter or need to upgrade yours? Check out my recommendation: Tekpower TP8268 AC/DC Auto/Manual Range Digital Multimeter (Amazon affiliate link).
Alright, here are the steps:
- 1
Disconnect the fuel injectors from their connectors.
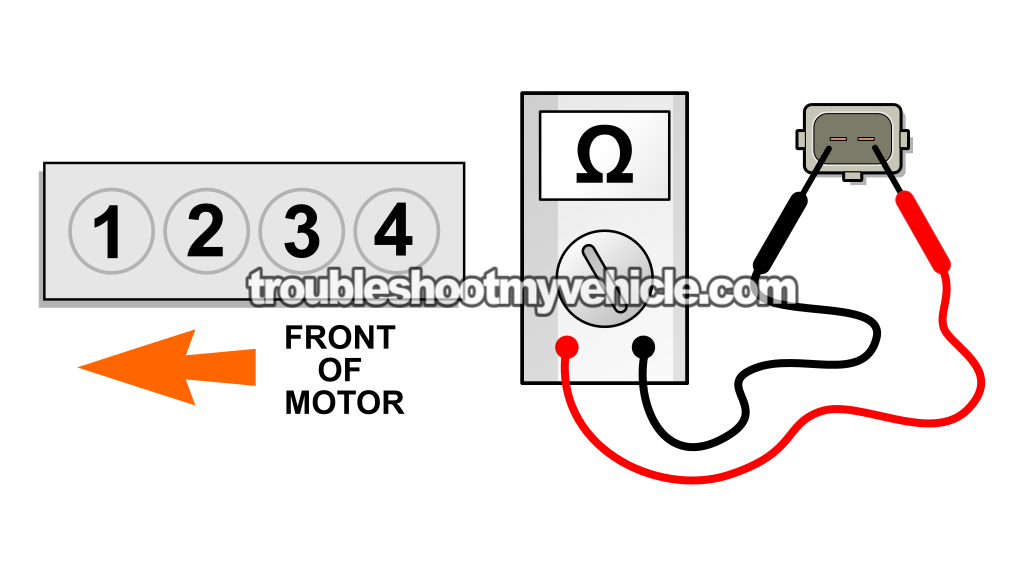
NOTE: The illustration above will help you identify the cylinder # the fuel injector belongs to. - 2
Place your multimeter in Ohms (Ω) mode.
- 3
Measure the resistance of the fuel injector across its two male spade terminals with the multimeter test leads (see the illustration above).
SPECIFICATION: The fuel injector resistance specification is: 11-18 Ohms. - 4
Write down the resistance value that your multimeter records for the specific fuel injector you're testing.
The illustration above will help you identify the cylinder # the fuel injector belongs to. - 5
Check the resistance of the remaining fuel injectors.
Let's find out what your specific multimeter test results mean:
CASE 1: The resistance of all four injectors is within specification. Great —this result tells you that none of them are shorted or open internally.
Even though the injectors don't have an internal electrical problem, you could still have a clogged one causing a rough idle or a cylinder misfire. To troubleshoot this further, go to: How To Find The Bad Or Clogged Fuel Injector.
CASE 2: You've got a fuel injector whose resistance is not within specification. This confirms that injector is toast and needs to be replaced.
How To Find The Bad Or Clogged Fuel Injector
Finding a clogged fuel injector can be a challenge, and believe it or not, there is a method to the madness for figuring out which one is causing the engine to suffer a rough idle or a cylinder misfire.
So if you've checked all four injectors and their internal resistance is within spec, the diagnostic strategy I'm outlining below will help you pinpoint whether the problem is coming from a clogged injector or something else entirely.
-
Step 1 —Identify the "dead" cylinder. This is the most important first step. All you need to do is connect a scan tool or code reader and check for specific cylinder misfire codes (P0301, P0302, P0303, or P0304).
If no misfire codes are stored, perform a cylinder balance test to pinpoint which cylinder is the "dead" one.
-
Step 2 —Confirm the "dead" cylinder is getting spark. Now that we know which cylinder is "dead", we need to make sure it's getting spark. This check is done with a spark tester.
During the spark test, we also need to:
- Inspect the spark plug boots and plugs to see if they're soaked in engine oil (a very common problem on the 2.0L DOHC engine).
- Remove the spark plugs and check for damage, like cracks or carbon tracks, that can cause misfires.
NOTE: If you find any of these problems, they need to be fixed, since they're known causes of cylinder misfires.
By confirming that the dead cylinder is getting spark, we rule out the ignition coil, spark plug boot, and the spark plug itself as possible causes. That eliminates the ignition system as the source of the misfire.
Need help testing the coil pack and spark plug wires? See this step-by-step tutorial:
The following case study is a good example of how carbon tracks —caused by oil leaking from the valve cover— can lead to a cylinder misfire:
- Carbon Tracks Are A Common Cause Of Ignition Misfires (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
-
Step 3 —Check the "dead" cylinder's compression. If a cylinder isn't producing enough compression, it's going to misfire. And in my experience, checking compression is one of the most overlooked tests when troubleshooting a misfire —especially on high-mileage engines.
I've written a step-by-step tutorial on how to do a compression test, and just as important, how to interpret the results to see if low compression is behind the misfire. You can find that tutorial here:
-
Step 4 —Perform a fuel injector Noid light test. The fuel injector needs two things to activate: power and an activation signal from the PCM. We can check for both with a Noid light test.
The Noid light is connected to the injector's connector while the engine is cranked. If power and the activation signal are present, the Noid light will flash on and off.
If you've never done a Noid light test, the following tutorial explains the procedure and shows where you can buy a Noid light kit (if you don't already have one):
- How To Use A Noid Light And Where To Buy It (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
-
Step 5 —Swap the suspect injector with its neighbor. Once everything else has been ruled out —for example, you've confirmed the dead cylinder has good compression, the injector's resistance checks out, and it's getting its activation signal with a Noid light— the next step is to swap that injector with its neighbor.
After putting everything back together, if the misfire follows the injector to its new cylinder, you now know the injector is clogged or bad and needs to be cleaned or replaced.
The diagnostic strategy I've outlined above has helped me tremendously over the years to avoid wasting time —and especially money— on parts that never would've solved the issue. It's a process of elimination: check one system, see if it's doing what it should, and then confirm or rule it out as the cause of the misfire. If it isn't, move on to the next thing.
The most important first step in this whole process is finding the dead cylinder. If you follow this strategy, you'll see that it makes nailing the exact cause of a cylinder misfire a lot easier.
More 2.0L Ford Focus Diagnostic Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 2.0L Ford Focus tutorials in this index:
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Test The Throttle Position Sensor (2000-2007 2.0L DOHC Ford Focus).
- How To Test The MAF Sensor (2000-2004 2.0L Ford Focus).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (2000-2010 2.0L Ford Focus).
- How To Test Engine Compression (2000-2010 2.0L Ford Focus).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!

