No Start 1: Checking For Spark

The very first thing you need to do is check for spark and the presence of fuel. Both of these tests should be done simultaneously if possible. As mentioned before, usually one of them will be missing from the mix.
The idea behind checking for spark is to see if all of the 8 engine cylinders are getting spark. Here are the most common causes of a no spark result:
CASE 1: Spark was present in all of the cylinders. This result tells you one very important thing: the crankshaft (crank) sensor is functioning correctly and you don't have to spend any time testing it or any money replacing it.
Your next step is to verify fuel pressure and that the PCM is activating the fuel injectors with a Noid light. Go to: No Start 2: Checking Fuel.
CASE 2: Spark was NOT present in all of the cylinders. The next step is to make sure that you do have fuel pressure with a fuel pressure gauge just to make sure the fuel pump is not a secondary issue.
Now, with no spark in any of the engine cylinders, this what I would suggest:
- Check that power is reaching the coil packs or ignition coil-on-plug coils.
- If power is not reaching any of the coil-on-plugs or ignition coil packs, you'll get a bonafide ‘no spark no-start condition’.
- You can find the ignition coil-on-plug tests here: How To Test The Ford 4.6L, 5.4L Coil-On-Plug Ignition Coils (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- You can find the coil pack tests here: How To Test The 2 Coil Packs (Ford 4.6L, 5.4L).
- Test the crank sensor.
- When the crank sensor fails, the other symptom you'll see is that the PCM will not activate the fuel injectors (as checked with a Noid light).
- You can find the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor test here: How To Test The Crankshaft Position Sensor (Ford 4.6L, 5.4L).
No Start 2: Checking For Fuel
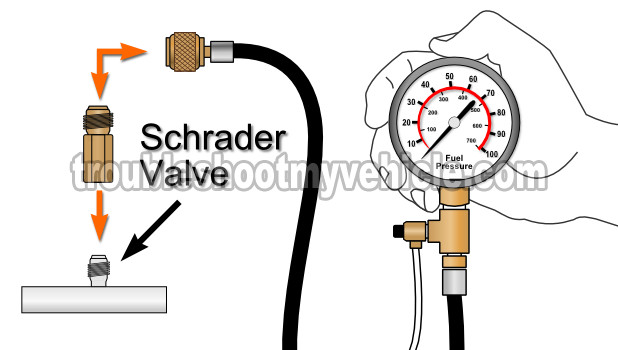
Checking for fuel involves two separate tests. One is to check that the fuel pump is functioning and supplying the correct amount of pressure.
The other test is making sure that the PCM is activating the fuel injectors. This can easily be accomplished by using a Noid light to check for these ON/OFF activation pulses the PCM sends to the injectors.
CASE 1: Fuel pressure is at specification. Not only does this result tell you that the fuel pump is OK but that the following components, that supply the fuel pump with power, are OK too:
- Fuel pump fuse.
- Fuel pump relay.
- Fuel pump inertia switch.
And so, there's no need to spend time testing them or money replacing them.
CASE 2: Fuel pressure is not present. This usually means that the pump has failed, but not always. I would recommend testing/checking the following before condemning the fuel pump:
- The fuel pump inertia switch. If the fuel pump inertia switch has activated, the fuel pump will not get power.
- If the inertia switch has been tripped, resetting it will get the fuel pump back to work and your Ford vehicle will start.
- After verifying the inertia switch's state, check that the fuel pump is getting power by tapping into the power circuit that feeds the pump with 12 Volts with a multimeter.
- Once you're tapped in, have a helper crank the engine while you observe your multimeter in Volts DC mode. If voltage is present (12 Volts), then you have confirmed that the fuel pump fuse, fuel pump relay and inertia switch are working perfectly.
- Confirming power to the fuel pump (with a multimeter) also verifies that the fuel pump has failed and needs to be replaced.
- If no voltage is present, as your helper cranks the engine, then the cause of no fuel condition is due to either a bad fuse, fuel pump relay, or inertia switch.
- The following tutorial will help you to test the fuel pump:
