Oxygen Sensor Basics
One of the things that's gonna' help you, to successfully diagnose a bad O2 sensor, is knowing how they work. Although, you can skip this section and jump to the test right away, I suggest you read this section first.
The ‘working theory’ of the O2 sensor I'm presenting here is nothing too deep, nothing too technical, just the info you'll need to make 'head and tails' of the tests in this article.
OK, in a nutshell, the job of the pre catalytic converter oxygen sensors is to help the PCM fine tune the fuel injection by helping it decide to either inject more or less fuel.
Now, to be a little more specific:
- 1
The 02 sensor produces a minimum of 0.100 Volt to a maximum of 1 Volt (DC) that is sent directly to the PCM. It's with these voltages that the PCM calculates if it's injecting too much fuel or not enough.
- 2
For example, an excess of fuel causes the O2 sensor to produce voltage values above 0.500 Volts. This voltage tops out at 1 Volt. Therefore, any value between 0.500 Volts and 1 Volt, is considered as the air/fuel mixture being Rich.
When the PCM sees the O2 sensor values over 0.500 Volts, it knows it has injected too much fuel and immediately starts to inject less. - 3
If it goes to far and now doesn't inject enough fuel, the O2 sensor will produce voltage values below 0.500 millivolts (between 0.100 and 0.500 Volts). When this happens, the air/fuel mixture is considered Lean.
When the PCM sees this low voltage it knows it has taken too much fuel and now needs to add more. - 4
The process of the fuel being adjusted by adding more or injecting less, according to the O2 sensor's feedback, goes on for the whole time you Ford vehicle is in operation.
If the pre-Cat O2 sensors are bad, they will not be able to sense how Rich or Lean the exhaust gas is and consequently the PCM will not be able to fine tune the fuel injection to meet emission (pollution) standards. Not only that, your gas mileage will suffer.
So, keeping all of the above in mind, your scan tool (in Live Data mode) will show you these voltages jumping up and down (if the O2 sensors are OK, that is) and this how you'll find out if the O2's are bad or not on your 4.6L, 5.4L Ford vehicle.
Where Are O2S11 And O2S21 Located?
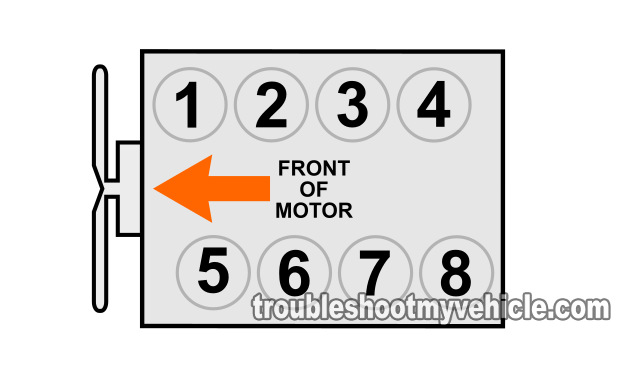
In case you've been wondering where the upstream oxygen sensors are located and/or what O2S11 and O2S21 mean, this section will clear it all up.
O2S11
- O2S11 is shorthand for Oxygen Sensor Bank 1 Sensor 1
- Bank 1 is the engine bank that houses cylinders 1, 2, 3, and 4.
- This O2 sensor is located on the exhaust pipe that connects to Bank 1' Exhaust Manifold.
- This oxygen sensor is called an upstream oxygen sensor because it's located on the exhaust pipe before the catalytic converter.
O2S21
- O2S21 is shorthand for Oxygen Sensor Bank 2 Sensor 1.
- Bank 2 is the engine bank that houses cylinders 5, 6, 7, and 8.
- This O2 sensor is located on the exhaust pipe that connects to Bank 2's Exhaust Manifold.
- This oxygen sensor is called an upstream oxygen sensor because it's located on the exhaust pipe before the catalytic converter.
In case you're wondering what the downstream oxygen sensors are called (the ones after the catalytic converter)., they are referred to as O2S12 and O2S22.
