The camshaft position (CMP) sensor is easily tested with a multimeter. In this tutorial, I'll explain how to test the CMP sensor in a step-by-step manner.
You'll easily find out if the CMP sensor is bad with the three tests described in this tutorial.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Tools Needed To Test The CMP Sensor.
- Symptoms Of A Bad CMP Sensor.
- Where To Buy The CMP Sensor And Save.
- How Does The CMP Sensor Work?
- Circuit Descriptions Of The CMP Sensor.
- TEST 1: Testing The CMP Signal With A Multimeter.
- TEST 2: Making Sure The CMP Sensor Is Getting 12 Volts.
- TEST 3: Making Sure The CMP Sensor Is Getting Ground.
- More 3.1L V6 Buick, Oldsmobile Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.1L V6 Buick Century: 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002.
- 3.1L V6 Buick Regal: 1994, 1995, 1996.
- 3.1L V6 Oldsmobile Cutlass: 1997, 1998, 1999.
- 3.1L V6 Oldsmobile Cutlass Ciera: 1994, 1995, 1996.
- 3.1L V6 Oldsmobile Cutlass Supreme: 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997.
Symptoms Of A Bad CMP Sensor
The fuel injection computer monitors the CMP sensor's output as long as the engine is running. Therefore, when it fails, the computer will set a CMP diagnostic trouble code:
- P0341 CMP Sensor Circuit Performance.
You'll also see one or more of the following symptoms:
- Rough idle.
- Bad gas mileage.
- Your vehicle fails the state emissions test (smog check).
When the camshaft position sensor fails, it usually doesn't keep the car from starting. In other words, in the majority of the cases the car starts and runs (although it won't run like a champ).
Tools Needed To Test The CMP Sensor
You don't need any expensive tools to test the camshaft position (CMP) sensor.
The following is a list of the basic tools you'll need:
- Multimeter.
- You can use a digital multimeter or an analog multimeter although the digital one is the preferred one.
- If you don't have a multimeter or need to upgrade yours, check out my recommendation here: Buying A Digital Multimeter For Automotive Diagnostic Testing (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- Jack.
- Jack stands.
- 1/2 inch ratchet wrench.
IMPORTANT: To test the camshaft position sensor with the info in this tutorial, you'll need to lift and place your vehicle on jack stands. Think safety and use common sense. Never trust the jack alone to hold up the vehicle!
Where To Buy The CMP Sensor And Save
The important thing to remember when buying the CMP sensor is to avoid buying a knock off sensor. The following links will help you comparison shop known automotive name brand CMP sensor.
Unsure if the above camshaft position sensor fits your particular vehicle? Don't worry, once you get to the site, they'll make sure it is by asking you the specifics of your vehicle. If the above don't fit, they'll find you the right one.
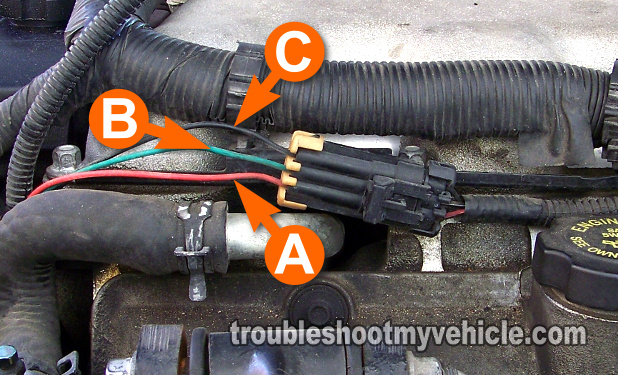
Circuit Descriptions Of The CMP Sensor

As already mentioned, three wires stick out of the CMP sensor's connector. We need to know what each one does to test the CMP sensor.
Here's a brief description of each:
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| A | 5 Volts |
| B | CMP Signal |
| C | Ground |
How Does The CMP Sensor Work?

The camshaft position sensor is a three-wire component that is easily tested with a multimeter. And the thing that will help you test the CMP sensor is knowing a little about how it works.
In a nutshell, when your turn the key and start the engine:
- The wire labeled with the letter A delivers 12 Volts to the CMP sensor.
- The wire labeled with the letter C delivers Ground to the CMP sensor.
- As the crank pulley turns, it induces the camshaft position sensor to start producing an ON/OFF voltage pulse that is sent directly to the PCM.
- The wire labeled with the letter B delivers the CMP sensor's signal to the PCM.
- The PCM (Powertrain Control Module=Fuel Injection Computer) uses the camshaft position sensor to know when the cylinder #1 is at top dead center. This information is used to start pulsing the fuel injectors sequentially (Sequential Fuel Injection mode).
The most important thing to know, is that the CMP sensor will not keep the vehicle from starting if it goes bad, although once started, it won't run right and will set a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0341.




