Testing the fuel pump on your 2008-2013 V8 equipped Chevrolet Express (GMC Savana) van can easily and accurately be done with a fuel pressure test gauge.
In this tutorial, I'll explain how it's done so that you can find out if the fuel pump is good or bad. I'm also gonna explain how to use starting fluid to see if the engine is not starting due to a lack of fuel.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Common Symptoms Of A Bad Fuel Pump.
- Where To Buy A Fuel Pressure Test Gauge.
- Safety Precautions To Take When Testing The Fuel Pump Pressure.
- TEST 1: Testing The Fuel Pressure With A Fuel Pressure Test Gauge.
- TEST 2: Using Starting Fluid To Diagnose A No-Start Condition.
- More Chevy Express/GMC Savana Articles And Tutorials.
ES ![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar La Bomba De Combustible (2008-2013 V8 Chevy Express, GMC Savana) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar La Bomba De Combustible (2008-2013 V8 Chevy Express, GMC Savana) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the gasoline powered 4.8L, 5.3L, and 6.0L V8 engines only:
- Chevrolet Express 1500, 2500, 3500: 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013.
- GMC Savana 1500, 2500, 3500: 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013.
2003-2007 FUEL PUMP PRESSURE TEST: You can find the fuel pump test procedure for the 2003-2007 V8 Chevy Express And GMC Savana here:
ENGINE NO-START DIAGNOSTICS: Engine doesn't start? The following guide is a good troubleshooting resource:
- How To Diagnose An Engine Cranks But Does Not Start Problem (2003-2013 V8 Chevy Express, GMC Savana).
Common Symptoms Of A Bad Fuel Pump
A fuel pump failure will generally cause one of two issues:
- Engine No-Start: The fuel pump stops working completely (producing no fuel pressure) and causes an engine no-start problem.
- Engine Starts But Run Bad: The fuel pump is failing but still produces enough fuel pressure to start the engine. Unfortunately, it's not enough fuel pressure to pump the volume of fuel the engine needs to run under load (like driving).
These are the symptoms that you'll see when the fuel pump has failed or is starting to fail:
- Engine No Start: The engine cranks but does not start.
- Stalling After Start: The engine starts but stalls after a few seconds.
- Stalling On Acceleration: The engine starts but as soon as you step on the accelerator pedal, the engine stalls.
- No Power Under Load: Lack of power while driving the vehicle.
- Backfiring: Explosions (loud popping sounds) can be heard coming from the intake manifold when you step on the accelerator while the engine is under load.
- Check Engine Light Illuminated: The check engine light is on, and lean air-fuel mixture trouble codes are stored in the fuel injection computer's memory.
I want to point out before moving on the next heading, that other components (when they fail) can also cause similar problems/symptoms and mimic a failing fuel pump. That's why it's essential to check the fuel pump's pressure output with a fuel pressure gauge before deciding to replace it. This is what this tutorial will help you do.
Where To Buy A Fuel Pressure Test Gauge
You can buy a fuel pressure test gauge just about anywhere and is one of the most important tools any serious DIY'er should have in his/her tool box.
The fuel pressure test gauge kit that'll connect to your Chevy or GMC pickup's Schrader valve and that I recommend for its low price and durability is the: BETOOLL 0-140 PSI Fuel Pressure Tester (Amazon affiliate link).
All of the following fuel pressure test gauge kits will help test your Chevrolet Express or GMC Savana's fuel pump:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
Safety Precautions To Take When Testing The Fuel Pump Pressure
Before you begin, remember to play it safe to avoid any accidents or surprises. Here are a couple of important precautions to take:
- Work with a Cold Engine: Work with a cold engine when testing the fuel pump's fuel pressure or using starting fluid to reduce the risk of burns and injuries. Additionally, working with a cold engine reduces the risk of accidental ignition of fuel vapors.
- Avoid Flames and Sparks: When working with fuel-related components, it's crucial to avoid any open flames, sparks, or sources of ignition. This includes smoking, using electrical equipment that could produce sparks, or working near any other potential ignition sources. Gasoline and starting fluid vapors are highly flammable and can ignite easily, leading to fires or explosions.
- Wear Protective Gear: Wear appropriate protective gear to protect yourself from potential fuel spills or accidents. This may include safety glasses to protect your eyes from fuel splashes, gloves to prevent skin contact with fuel or chemicals, and appropriate clothing to minimize exposure to fuel vapors.
- Have a Fire Extinguisher Nearby: Have a fire extinguisher nearby in case of an emergency. Make sure the fire extinguisher is rated for use with flammable liquids and that you know how to use it effectively.
- Follow Fuel Pressure Gauge Manufacturer Instructions: When using a fuel pressure gauge to test the fuel pump's fuel pressure, it's important to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. This ensures that the gauge is connected properly and that the testing procedure is conducted safely. Incorrect use of a fuel pressure gauge can lead to inaccurate readings.
By following these safety measures, you can minimize the risk of accidents and perform the pressure check effectively and safely.
TEST 1: Testing The Fuel Pressure With A Fuel Pressure Test Gauge
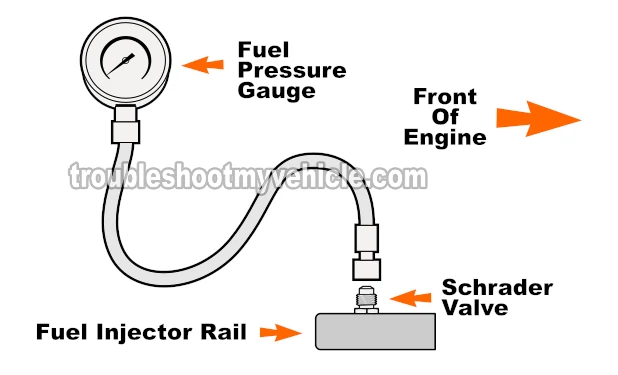
On the Chevrolet Express and GMC Savana vans, the fuel injector rail on the passenger side typically comes equipped with a fuel pressure test port, often referred to as a Schrader valve (see illustration and photo above).
This valve serves as a convenient access point for connecting a fuel pressure test gauge and simplifies the fuel pump testing process.
The other benefit of using a fuel pressure test gauge is you can accurately measure the fuel pressure in the fuel system, making it easier to diagnose a bad fuel pump than with any other method.
NOTE: You'll need a fuel pressure tester that can connect to the Schrader valve. If you don't have one, take a loot at my recommendations here: Where To Buy A Fuel Pressure Test Gauge.
FUEL PRESSURE SPECIFICATION: The fuel pressure specification for the 2008-2013 4.8L, 5.3L, 6.0L Chevrolet Express (GMC Savana) is 50 to 60 PSI.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Locate the Schrader valve on the fuel injector rail crossover line (see photos above).
- 2
Remove the dust cap from the Schrader valve and place a shop towel under the general area of the Schrader valve.
NOTE: The shop towel's job is to absorb and fuel that may leak when performing step 3. - 3
Connect your fuel pressure tester to the Schrader valve.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine while you observe the needle on the fuel pressure tester gauge.
- 5
The fuel pressure tester should give you a reading between 50 to 60 PSI.
Let's examine your test results:
CASE 1: The fuel pressure is within the indicated specification. This is the correct test result.
This test result confirms that the fuel pump in your Express (Savana) van is OK (functioning correctly).
CASE 2: You got 0 psi fuel pressure. This test result lets you know that the fuel pump is defective and is causing the engine to not start.
Before you replace a fuel pump make sure that the fuel pump relay and fuel pump fuse are supplying power to the fuel pump when the engine is being cranked.
If battery power is available to the fuel pump, when cranking the engine, then you can confidently conclude that the fuel pump is defective and that it needs to be replaced.
CASE 3: The fuel pressure was below the indicated fuel pressure specification. This test result lets you know that even though the fuel pump is supplying some fuel it's not supplying enough to have the engine run optimally.
This is an indication that the fuel pump is failing and needs to be replaced.
TEST 2: Using Starting Fluid To Diagnose A No-Start Condition

The starting fluid test is a quick and relatively simple diagnostic method that can help you identify if the engine no-start issue is fuel-related. It involves spraying starting fluid into the throttle body and then having a helper crank the engine.
If the engine starts and then dies (after spraying starting fluid into the throttle body), you can conclude the engine isn't getting fuel to start. This usually indicates a potential fuel pump problem.
If the engine does not start at all even after spraying starting fluid, the issue is not due to a lack of fuel. This helps narrow down the possible causes of the no-start problem.
While the starting fluid test can provide valuable information about the cause of the engine's no-start issue, I need to emphasize that it's not as accurate as a fuel pump pressure test for diagnosing a faulty fuel pump. However, it can still be helpful in identifying whether a lack of fuel is the root cause of the problem.
IMPORTANT: To get the most accurate test result from your starting fluid test, it's important that you first check that all 8 cylinders are getting spark. So if you haven't already checked for spark yet, you should do so before doing the starting fluid test.
CAUTION: As a safety precaution, you should never spray starting fluid into the throttle body while the engine is cranking. Instead, you should first spray starting fluid into the throttle body and then crank the engine.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Remove the intake air duct from the throttle body. You don't have to completely remove it, since you'll have to reconnect it in step 2.
- 2
Spray starting fluid down the bore of the throttle body.
After spraying a good squirt of starting fluid, quickly reconnect the air duct to the throttle body (you don't have to tighten the hose clamp). - 3
Have your helper crank the engine once the intake air duct is back on the throttle body.
- 4
You'll get one of two results with this test:
1.) The engine will start momentarily and after a few seconds will die.
2.) The engine will only crank but not start at all.
OK, let's find out what your results mean:
CASE 1: The engine did not start, not even a few seconds. This test result tells you that a lack of fuel from the fuel pump IS NOT causing the engine's no-start problem.
I want to point out that this conclusion is true only if all spark plug wires are sparking.
CASE 2: The engine started but died after a few seconds. This test result tells you that the engine's no-start problem is caused by a lack of fuel.
More Chevy Express/GMC Savana Articles And Tutorials
You can find a complete list of articles and diagnostic tutorials for the V8 Chevy Express and GMC Savana here:
Here's a sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Test The CKP Sensor (2008-2013 Chevrolet Express, GMC Savana).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (2003-2013 V8 Chevy Express, GMC Savana).
- How To Diagnose An Engine Cranks But Does Not Start Problem (2003-2007 V8 Chevy Express, GMC Savana).
- How Can I Tell If The Automatic Transmission Is Bad? (2003-2013 Chevrolet Express, GMC Savana).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!