A bad or clogged fuel injector can cause a rough idle or a misfire that will severely decrease your 1.5L Honda Civic's engine performance.
The cool thing is that testing for a bad fuel injector (or a clogged one), on your 1.5L Honda Civic DX, isn't hard. In this tutorial, I'll explain how to check for a bad fuel injector by doing a simple multimeter resistance test.
I'm also gonna' offer you a specific diagnostic guide to finding the bad (or clogged) fuel injector in case you don't know where to start your troubleshooting efforts (in page 2 of this tutorial).
Contents of this tutorial:
ES ![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Los Inyectores De Combustible (1992-1995 1.5L Civic) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Los Inyectores De Combustible (1992-1995 1.5L Civic) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 1.5L Honda Civic: 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995.
- 1.5L Honda Civic Del Sol: 1993, 1994, 1995.
WIRING DIAGRAM: The following wiring diagram may come in handy:
Symptoms Of A Bad Fuel Injector
Having worked on cars for a good part of my life, I can tell you that most fuel injector problems fall into one of two categories.
Simply put, the fuel injector stops injecting fuel completely or gets clogged and doesn't inject enough fuel.
When a fuel injector stops injecting fuel completely, it's usually due to the fact that it's internal coil winding has suffered some failure (like a short or an open). Testing this type of failure is simple and involves doing a multimeter resistance test (and this is the focus of TEST 1).
But before I get ahead of myself, let me tell you about the most common symptoms you'll see when a fuel injector fails:
- Rough idle.
- Lack of power.
- Hesitation when you accelerate your 1.5L Honda Civic down the road.
- Misfire trouble codes (OBD II equipped only):
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder #1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder #2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder #3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder #4 Misfire.
The focus of this tutorial is to see if the fuel injector's internal coil has failed (and thus causing the fuel injector to stop injecting fuel) but testing for a clogged injector isn't that much more complicated and I'll show you how in the next page.
Where To Buy The Fuel Injector And Save
Check out the following links and comparison shop the fuel injector on your 1.5L Honda Civic:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
Not sure if the above fuel injectors fit your particular 1.5L Honda Civic? Don't worry, once you click on the links and arrive on the site, they'll make sure it fits! If it doesn't, they'll find you the right one.
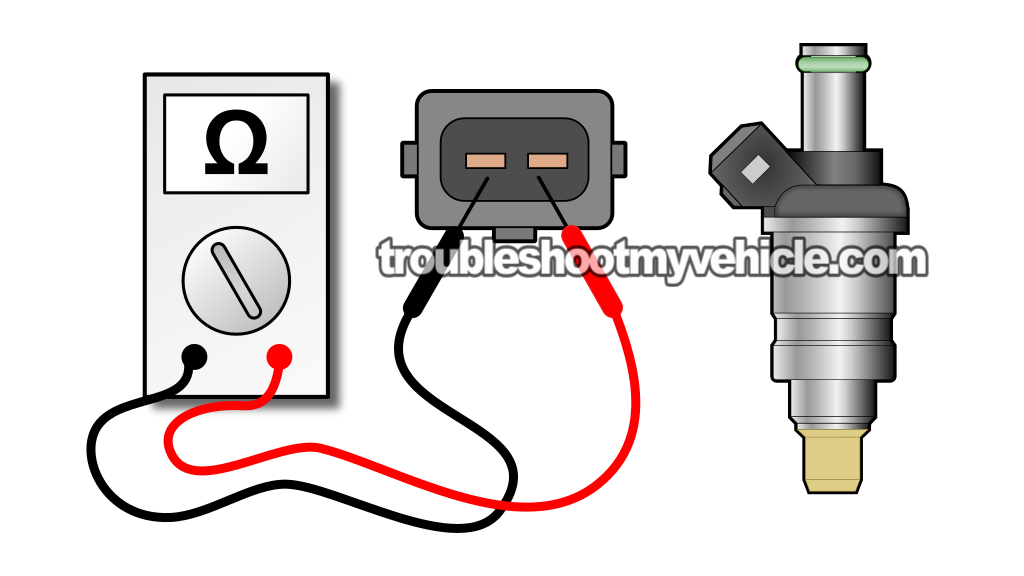
Checking The Injector's Internal Resistance
As mentioned at the beginning of this tutorial, we're gonna' test the fuel injectors' internal coil winding.
If a fuel injector's internal coil winding is fried (either because it's shorted or is open), its resistance value will not coincide with the factory resistance specification. This spec is 10 to 13 Ohms (Ω).
The test steps below assume that you're testing all four fuel injectors. Alright, let's get started:
- 1
Disconnect the fuel injectors from their harness connectors.
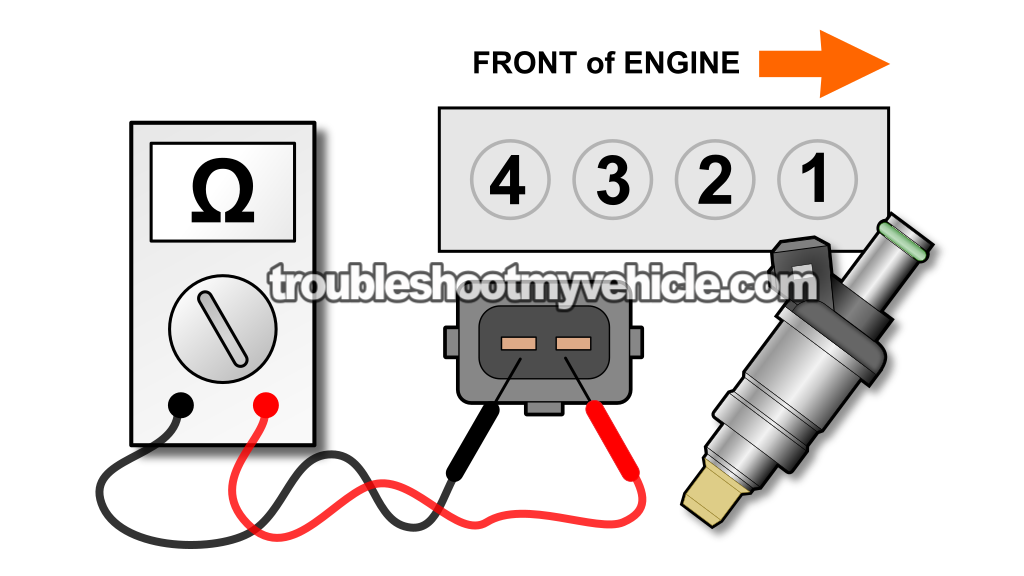
NOTE: To identify which cylinder the fuel injector belongs to, see the above illustration with the cylinder # id for the 1.5L Honda Civic. - 2
Set your multimeter to Ohms (Ω) mode.
- 3
Measure the resistance of the fuel injector across its two male spade terminals with the multimeter test leads.
NOTE: The 1.5L Honda Civic resistance specification is: 10 to 13 Ohms. - 4
Write down the resistance value that your multimeter records for the specific fuel injector you're testing.
The illustration above will help you identify the cylinder number the fuel injector belongs to. - 5
Repeat steps 3 and 4 on the remaining fuel injectors.
Let's find out what your specific multimeter test results mean:
CASE 1: The fuel injector resistance of all 4 was within specification (or similar). This confirms that the fuel injectors are OK. Specifically, that none are shorted or open internally.
Here's why: If any one of the fuel injectors were shorted or open internally, the fuel injector would have registered a radically different resistance value on your multimeter. Since the resistance values for a 4 were uniform, this test result tells you that they are not defective.
Your next step is to go to the next page and see the troubleshooting guide here: How To Find The Bad Or Clogged Fuel Injector.
CASE 2: One of the fuel injectors registered a completely different resistance value. This indicates that the fuel injector is bad. Replace the fuel injector.
How To Find The Bad Or Clogged Fuel Injector
Finding the exact cause behind your 1.5L Honda Civic's misfire (rough idle) isn't hard. But, if you're not sure if a bad or clogged fuel injector is behind the problem, the following testing suggestions will help you.
The troubleshooting strategy below, has helped to accurately diagnose a failed/clogged fuel injector about 95% of the time and this has meant saving time, frustration, and more importantly: money.
You can find even more info in the following article: How To Test A Misfire Condition (1.5L Honda Civic).
OK, below are the diagnostic steps I take when trying to diagnose a bad fuel injector:
- Find the 'dead' cylinder first.
- This is the most important first step. It involves doing a cylinder balance test first. If you've never done a cylinder balance test before, you it explained here: How To Do A Cylinder Balance Test (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
- Check that all spark plug wires are delivering spark.
- It's important to make sure that each cylinder is getting spark with a dedicated spark tester.
- You can find a step-by-step guide here: How To Test The Igniter, Ignition Coil Accord, Civic, CRV, and Odyssey (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- It's important that you check that the spark plug boot and spark plug are NOT soaked (or swimming) in engine oil.
- You should also remove the spark plugs and check them for cracks or carbon tracks (this is SO important).
- Here's a real life case study on carbon tracks and how they can cause a Misfire: Carbon Tracks Are A Common Cause Of Ignition Misfires (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- It's important to make sure that each cylinder is getting spark with a dedicated spark tester.
- Check engine compression.
- After making sure that all 4 spark plug wires are delivering spark, you need to check for low engine compression.
- This is one of the most overlooked tests when diagnosing a misfire or rough idle condition. You can find the test here:
- Noid light test.
- If every test above checks out OK, then the next step is to do a fuel injector Noid light test.
- The Noid light test will help you make sure that the fuel injector is being activated.
- The following Noid light article/tutorial may help you: How To Use A Noid Light And Where To Buy It (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- Swap the fuel injector with its neighbor on the fuel injector rail.
- If I've found out that I have a specific 'dead' cylinder and:
- The ignition system is not at fault.
- That cylinder's compression value is good (compared to the rest of the cylinders).
- The fuel injector resistance is good and...
- I think the fuel injector is clogged, I then swap out that fuel injector with its neighbor.
- If I've found out that I have a specific 'dead' cylinder and:
Finding the bad/clogged fuel injector can be a challenge on your 1.5L Honda Civic but it's doable. What will help you save a lot of time, money and frustration is to first find the 'dead' cylinder. Following the above diagnostic strategy has saved my lunch quite a few times and I think it'll help you too!
More 1.5L Honda Civic Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 1.5L Honda Civic tutorials in this index:
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Test The MAP Sensor (1.5L Honda Civic).
- How To Test The Throttle Position Sensor (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
- How To Test Engine Compression (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
- How To Test The Fuel Pump In 2 Tests (1.5L Honda Civic).
- How To Test The Igniter, Ignition Coil Accord, Civic, CRV, and Odyssey (at easyautodiagnostics.com).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!




