TEST 1: Verifying All Cylinders Are Getting Spark

There's a good chance that the fuel injection computer, on your 1.6L Mazda Protegé, is already telling you which cylinder is misfiring via a misfire trouble code. This misfire code comes in super handy when diagnosing a bad ignition coil. But, I'm still going to recommend that you check all 4 cylinders for spark.
Why test all 4 cylinders for spark? In part because of how easy it is to test all 4 cylinders, but mainly because it will guarantee the accuracy of your troubleshooting results.
It will also give you a chance to physically and visually inspect the condition of the spark plug wire boots ignition coil boots for any obvious damage or problems.
OK, these are the test steps:
- 1
Remove the #1 cylinder spark plug wire and attach the spark tester to it. Ground the spark tester to the negative battery post using a jump start cable.
- 2
Have your helper crank the engine as you observe the spark tester. The spark tester will either spark or not spark (as your helper is cranking the engine with the starter motor).
When done, remove the spark tester from the spark plug wire. Reconnect the spark plug wire back onto cylinder #1 spark plug. - 3
Remove the ignition coil sitting on top of the #2 cylinder spark plug. Connect the HEI spark tester to the ignition coil. Ground the spark tester to the negative battery post using a jump start cable.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine as you observe the spark tester. The spark tester will either spark or not spark (as your helper is cranking the engine with the starter motor).
When done, remove the spark tester from the ignition coil. Install and bolt down the ignition coil back onto the #2 cylinder spark plug. - 5
Remove the #3 cylinder spark plug wire and attach the spark tester to it. Ground the spark tester to the negative battery post using a jump start cable.
- 6
Have your helper crank the engine as you observe the spark tester. The spark tester will either spark or not spark (as your helper is cranking the engine with the starter motor).
When done, remove the spark tester from the spark plug wire. Reconnect the spark plug wire back onto cylinder #3 spark plug. - 7
Remove the ignition coil sitting on top of the #4 cylinder spark plug. Connect the HEI spark tester to the ignition coil. Ground the spark tester to the negative battery post using a jump start cable.
- 8
Have your helper crank the engine as you observe the spark tester. The spark tester will either spark or not spark (as your helper is cranking the engine with the starter motor).
When done, remove the spark tester from the ignition coil. Install and bolt down the ignition coil back onto the #4 cylinder spark plug.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
IMPORTANT: The following test result interpretations take into account if you got no spark from testing a spark plug wire or from testing an ignition coil. Read all of the options carefully to see which fits your spark result(s):
CASE 1: You got spark from all cylinders. This indicates that the ignition coils and spark plug wires are OK. The cause of your misfire condition is not due to a bad ignition coil. Take a look at TEST 6: Misfire Due to Carbon Tracks to see further tips and suggestions.
CASE 2: If you got NO spark from the #1 cylinder spark plug wire. Your next step is to go to: TEST 4: Verifying The Spark Plug Wire Is Not Bad.
CASE 3: If you got NO spark from the ignition coil sitting on top of the #2 cylinder spark plug. Your next step is to go to: TEST 5: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil.
CASE 4: If you got NO spark from the #3 cylinder spark plug wire. Your next step is to go to: TEST 4: Verifying The Spark Plug Wire Is Not Bad.
CASE 5: If you got NO spark from the ignition coil sitting on top of the #4 cylinder spark plug. Your next step is to go to: TEST 5: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil.
CASE 6: If you got NO spark from a spark plug wire and a spark plug boot on the same ignition coil. There's a good chance that the ignition coil is bad. To make sure, you need to verify that it is getting power, ground, and its triggering signal. So, your next step is to go to: TEST 2: Verifying Power And Ground.
TEST 2: Verifying Power And Ground
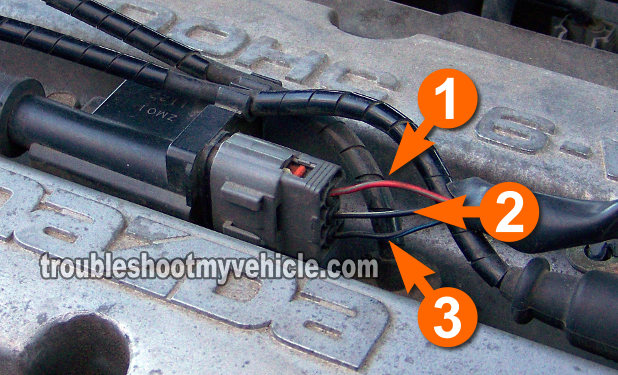
The ignition coil needs 12 Volts and Ground to be able to function. If either power or Ground is missing, the ignition coil is not going fire spark to the 2 cylinders it feeds spark to. So in this test we're going to verify that they are present.
You're going to need one of two special tools to test for power and Ground. You'll need either a back probe or a wire piercing probe. Why? Because you won't be able to test the female metal terminals of the connector with the multimeter probes. Trying to insert the multimeter probe into the female terminal of the connector, to test for power or Ground, will damage the terminal.
The method I recommend is to use a wire piercing probe on the connector's wire (to see what this tool looks like, click here: Wire Piercing Probe Tool Review (Power Probe PWPPPPP01).
These are the test steps:
- 1
Remove enough of the plastic tubing that is sheathing the ignition coil connector's three wires. The idea is to expose enough of the three wires to be able to test them.
- 2
Disconnect the ignition coil from its connector and place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 3
Verify that the wire that connects to terminal #3 of the connector has 10 to 12 Volts with the key on but engine off.
Connect the red multimeter test lead (using the appropriate tool) to the wire that connects to terminal #3. Connect the black multimeter test lead to the negative (-) battery terminal.
Your multimeter should read 10 to 12 Volts DC. - 4
Verify that the wire that connects to terminal #2 of the connector has Ground with the key on but engine off.
Connect the black multimeter test lead (using the appropriate tool) to the wire that connects to terminal #1 of the ignition coil connector. Connect the red multimeter test lead to the positive (+) battery terminal.
Your multimeter should read 10 to 12 Volts DC.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: If the multimeter registered 10-12 Volts for circuits labeled 1 and 3. This is the correct and expected test result and tells you that the ignition coil is receiving power and Ground.
Your next step is now to make sure that this ignition coil is receiving its triggering signal. For this test go to: TEST 3: Triggering Signal Test.
CASE 2: If the multimeter DID NOT register 10-12 Volts for circuit labeled 1. This test results let you know that the ignition coil is not getting power. Without power this ignition coil will not spark.
This result eliminates the ignition coil itself as bad. Repairing the cause of this missing voltage will solve the no-spark condition of this ignition coil.
CASE 3: If the multimeter DID NOT register 10-12 Volts for circuit labeled 3. This test results let you know that the ignition coil is not getting Ground. Without Ground this ignition coil will not spark.
This result eliminates the ignition coil itself as bad. Repairing the cause of this missing Ground will solve the no-spark condition of this ignition coil.

