
Testing the ignition coils on your 1.6L Mazda Protegé is not that hard. It is something that you can do right at home with a few basic tools.
In this tutorial, I'm gonna' show you how in a step-by-step way. You'll be able to find out if you do or don't have a bad ignition coil on your hands.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Ignition Coil.
- What Tools Do I Need?
- Circuit Descriptions Of The Ignition Coil Connector.
- Where To Buy The Ignition Coils.
- Ignition Coil Basic Operating Theory.
- Precautions, Do's and Don'ts.
- TEST 1: Verifying All Cylinders Are Getting Spark.
- TEST 2: Verifying Power And Ground.
- TEST 3: Triggering Signal Test.
- TEST 4: Verifying The Spark Plug Wire Is Not Bad.
- TEST 5: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil.
- TEST 6: Misfire Due To Carbon Tracks.
ES ![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Las Bobinas De Encendido (1999-2001 1.6L Mazda Protegé) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Las Bobinas De Encendido (1999-2001 1.6L Mazda Protegé) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
RELATED WIRING DIAGRAM:
Symptoms Of A Bad Ignition Coil
Your 1.6L Mazda Protegé doesn't use a mechanical ignition distributor to feed spark to all 4 cylinders. Instead, it uses 2 ignition coils packs to create and feed spark to the cylinders.
Each ignition coil fires spark to 2 cylinders simultaneously. Since these ignition coils are a critical part of your Protegé's ignition system, engine performance will suffer when one fails.
Your 1.6L Mazda Protegé will display one of the following symptoms:
- The car will run and idle rough.
- No power as you accelerate the car down the road.
- Really bad gas mileage.
- The vehicle will not start.
- The car will not run on all cylinders.
- Misfire codes that are lighting up the check engine light on your instrument cluster.
- P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304
- Rotten egg smell coming out of the tail-pipe.
What Tools Do I Need?
The really cool thing about troubleshooting the ignition coils on your 1.6L Mazda Protegé, is that you don't need any expensive diagnostic equipment to do so.
You do need a few tools, but nothing that will break the bank. The most important one is a spark tester. Specifically an HEI spark Tester.
Below is the list of tools that you'll need to successfully troubleshoot the ignition coils:
- A Multimeter that can read Hz Frequency.
- An HEI Spark Tester
- This tool is a must have. To see what this tool looks like, click here: HEI Spark Tester (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- Battery Jump Start Cables.
- Someone to help you crank the car.
As you can see you don't need a whole lot of things to be able to test the ignition coils on your Mazda Protegé
Circuit Descriptions Of Ignition Coil Connector
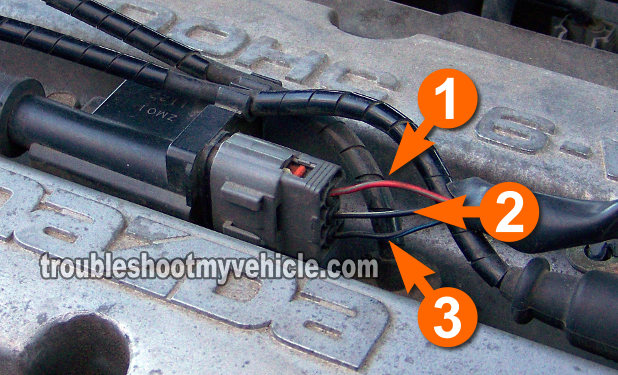
I'm pretty sure that by now you've noticed that your 1.6L Mazda Protegé has two ignition coils. One of them is sitting right on top of the #2 cylinder spark plug. The other coil is sitting right on top of the #4 cylinder spark plug.
Each ignition coil has a connector that has three wires coming out of it. I've labeled each one with the numbers 1 through 3 in the photo above. Below you'll find what each circuit does:
- Circuit labeled 1:
- Triggering Signal
- Circuit labeled 2:
- Ground (Chassis)
- Circuit labeled 3:
- Power (12 Volts).
The color of the wires is not important (to take advantage of the info in this article) as long as you're able to correctly identify the circuit by its number in the photos supplied.
NOTE: The circuit descriptions and the numbers identifying each apply to both ignition coil connectors.
Where To Buy The Ignition Coils
You can find the ignition coils for your 1.6 liter Mazda Protegé in just about any auto parts store. But if you're like me in that I love saving a few bucks on auto parts, then the following links below will help you to shop/compare and save:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
Not sure if the above ignition coils fit you particular 1.6L Mazda Protegé? Don't worry, once you get to the site, they'll make sure the parts fit and if they don't they'll ask you about your Protegé's specifics to find you the right parts.
Ignition Coil Basic Operating Theory
As you might already know, in this type of ignition system the ‘Ignition Control Module’ function is handled by a transistor inside of the ignition coil (both ignition coils have this transistor). The PCM (Powertrain Control Module=Fuel Injection Computer) is the one that controls the whole show. So, in a nutshell, here's what happens when you turn the key to crank and start the car:
- The engine starts to crank, inducing the crankshaft position sensor to start producing its crank signal.
- The crank signal, upon being received by the PCM along with other necessary sensor information, it starts to do its little song and dance and sends back a Triggering Signal to each ignition coil.
- This Triggering Signal contains the instructions for the Transistor (within each ignition coil) to start firing the ignition coil it's a part of.
- Each ignition coil then fires spark to two different cylinders at the exact same time (in what's known as the Waste Spark method).
- #1 and #4 cylinders are fed spark by the ignition coil sitting on top of the #4 spark plug.
- #2 and #3 cylinders are fed spark by the ignition coil sitting on top of the #4 spark plug.
- #1 cylinder is fed spark thru' a spark plug wire (high tension wire) and #4 cylinder gets spark directly from the ignition coil.
- #3 cylinder is fed spark thru' a spark plug wire (high tension wire) and #2 cylinder gets spark directly from the ignition coil.
The most important thing that you need to remember, when troubleshooting this type of ignition system, is that the ignition coil fires spark simultaneously to two different cylinders. The ignition coil that's sitting on top of cylinder #2 fires spark to cylinders #2 and #3. The ignition coil that's sitting on top of cylinder #4 fires spark to cylinders #1 and #4.
Precautions, Do's and Don'ts
Most of the testing that you'll be doing is with the engine cranking so take all necessary safety precautions to keep your fingers, hands and entire self safe. Here are a few other tips and suggestions:
- Do not use a regular spark plug instead of a dedicated spark tester to test for spark.
- Do not remove the spark plug wire from the spark plug or the ignition coil while the engine is cranking to test for spark.
- Start your Diagnostic from TEST 1, do not skip around from test to test unless instructed to do so by the TEST you are currently on.
- Do not use a test light where an LED light is called for.
- Once again, use the recommended/indicated tools for all of your tests.




