TEST 3: Triggering Signal Test
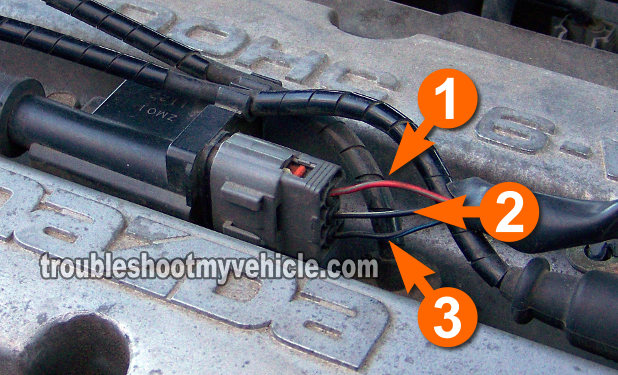
If you've reached this point, you've confirmed that the ignition coil is getting power and Ground in TEST 2. The next step is to verify that that ignition coil is receiving the triggering signal from the fuel injection computer.
We're going to test for this triggering signal with the ignition coil connected to its electrical connector. You will need to use either a back probe or a wire piercing probe to check for this signal. If you need to see what a wire piercing probe looks like, you can see it here: Wire Piercing Probe Tool Review (Power Probe PWPPPPP01).
These are the test steps:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Hertz (Hz) mode.
- 2
Probe the circuit labeled with the number 1 with the black multimeter test lead (using an appropriate tool to pierce the wire).
- 3
With the red lead of the multimeter probe the battery (+) positive terminal.
- 4
Have a helper crank the engine.
You should see fluctuating values of 2 to 20+ Hertz as the engine cranks and (possibly starts) on your multimeter.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered a fluctuating 2 to 20+ Hertz (Hz) as the engine cranked. This is the correct and expected test result and tells you that the fuel injection computer is activating the ignition call to fire spark.
You can now conclude that the ignition coil is bad needs to be replaced only if:
- You have verified that its not firing spark to its 2 cylinders (TEST 1).
- You have verified that its getting power and Ground (TEST 2).
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT register a fluctuating 2 to 20+ Hertz (Hz) as the engine cranked. This test result let you know that there is a problem in the triggering signal wire. This problem is causing the triggering signal not to reach the ignition coil. Without this signal the coil will not activate and fire spark to its two cylinders.
Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial , your next step is to see if there is an open or a short in this wire (between the fuel injection computer and the ignition coil connector).
TEST 4: Verifying The Spark Plug Wire Is Not Bad

If you've reached this point, you got a no spark test result from either #1 cylinder spark plug wire or #3 cylinder spark plug wire. This test section applies to either test result.
Alright, what we're going to do in this test section is to check for spark directly on the ignition coil tower (of the spark plug wire that did not fire off spark in TEST 1). To be a bit more specific, we're going to unplug the spark plug cable from the ignition coil tower and place the spark tester in its place.
By checking for spark directly on the ignition coil tower, we're going to find out (indirectly) if the spark plug wire is bad. Why check the spark plug wire? Because they're notorious for going bad and stopping the transmission of spark from the ignition coil tower to the spark plug.
As you can see from the photo above, this is a very simple test that we'll accomplish with the HEI spark tester. Remember, this test applies to either #1 cylinder spark plug wire or #3 cylinder spark plug wire.
OK, these are the test steps:
- 1
Remove the spark plug wire from the ignition coil. This is the spark plug wire that did not fire off spark in TEST 1.
Don't remove the ignition coil from its place on the valve cover. - 2
Place the spark tester directly in the ignition coil tower in place of the spark plug wire you just removed (see photo above).
- 3
Ground the spark tester with a battery jump start cable to a good engine Ground point or directly on the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 4
Have your assistant crank the engine. The engine may start, so be careful.
- 5
You're gonna' get one of two results: spark or no spark.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The spark tester sparked. This result lets you know that the ignition coil is good and that the spark plug wire is bad. Replace both spark plug wires.
CASE 2: Ignition coil tower for cylinder #1 spark plug wire DID NOT spark. If in TEST 1 you verified that this same ignition coil is firing off spark to cylinder #4, then you can conclude that the ignition coil is bad and needs to be replaced.
I'll explain: The ignition coil is designed to fire off spark simultaneously to both cylinders (#1 and #4). If it's only firing spark to one of the two cylinders (in this case cylinder #4), then you can conclude beyond a shadow of a doubt that the ignition coil is bad.
Replacing the ignition coil will solve the misfire condition and the misfire code lighting up the check engine light (CEL) on the instrument cluster.
CASE 3: Ignition coil tower for cylinder #3 spark plug wire DID NOT spark. If in TEST 1 you verified that this same ignition coil is firing off spark to cylinder #2, then you can conclude that the ignition coil is bad and needs to be replaced.
I'll explain: The ignition coil is designed to fire off spark simultaneously to both cylinders (#2 and #3). If it's only firing spark to one of the two cylinders (in this case cylinder #2), then you can conclude beyond a shadow of a doubt that the ignition coil is bad.
Replacing the ignition coil will solve the misfire condition and the misfire code lighting up the check engine light (CEL) on the instrument cluster.

