TEST 4: Verifying The MAF Sensor Is Getting Ground 2
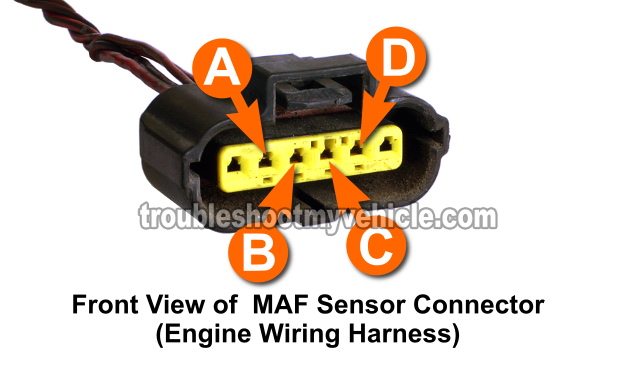
The MAF sensor on your Mazda 2.0L 626 (2.0L MX6) is fed two different Grounds. The Ground you confirmed in TEST 2 is a power Ground. This Ground connects to your Mazda's chassis and thus has a direct path to the battery negative (-) terminal/post.
The Ground we're about to verify is provided by your Mazda's fuel injection computer. This Ground is called a Signal Return and is a Ground that's part of the air flow sensing part of the sensor.
This Ground is provided to the MAF sensor by the black with blue stripe (BLK/BLU) wire of the MAF sensor electrical connector.
Testing for Ground is done with another simple multimeter voltage test.
CAUTION: Since this Ground is provided internally by your Mazda's fuel injection computer, you need to be careful you don't short this wire to 12 Volts (battery power). Shorting this wire to battery power will fry your Mazda's fuel injection computer. The multimeter voltage test described in this section is the safest way to test this circuit.
These are the steps:
- 1
Set your multimeter to Volts DC mode and turn the ignition key to its ON position (but don't crank or start the engine).
- 2
Probe the BLK/BLU wire with the black multimeter test lead.
CAUTION: Do not probe the front of the connector or you risk damaging the female metal terminal of the connector. - 3
Now connect the red multimeter test lead on the battery's positive (+) post.
- 4
If the BLK/BLU wire has Ground, then your multimeter will register 10 to 12 Volts DC.
OK, let's take a look at what your results mean:
CASE 1: The multimeter confirms that the BLK/BLU wire is feeding Ground to the MAF sensor. This is the correct test result and confirms that the MAF sensor is bad and needs to be replaced.
You can conclude that the MAF sensor is bad (and that it needs to be replaced) only if you have verified:
- That the MAF sensor is not producing the correct signal voltage values when you accelerate/decelerate the engine (TEST 1).
- That it is being fed with power on the RED/BLK wire (TEST 2).
- That the MAF sensor does have a solid path to chassis Ground on the BLK/YEL wire (TEST 3).
- That the MAF sensor does have a solid path to computer Ground on the BLK/BLU wire (TEST 4).
These test results, interpreted together, indicate that the MAF sensor is bad.
CASE 2: The multimeter confirms that the BLK/BLU wire IS NOT feeding Ground to the MAF sensor. Double check your multimeter connections and repeat the test.
If your multimeter results still do not indicate 12 Volts, then the mass air flow (MAF) sensor is not fried and not the cause of the MAF sensor diagnostic trouble code (DTC) issue.
Here's why: Without a good path to Ground, that the PCM provides internally, the MAF sensor will not work. With this test result, you have eliminated the MAF sensor as bad.
More 2.0L Mazda Tutorials
If this tutorial was helpful, check out the other Mazda 2.0L tutorials that I've written. You can find them all here: Mazda 2.0L Index Of Articles.
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (2.0L Mazda 626).
- How To Test Engine Compression (2.0L Mazda 626).
- How To Test The TPS (1994-2002 2.0L Mazda 626).
- How To Test The Fuel Pump (1994-1999 2.0L Mazda 626).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!


