In this tutorial I am going to show you how to test diagnostic trouble codes P0130 and P0150 on your 3.3L equipped Nissan Pathfinder.
These codes indicate a problem with the front O2 sensors which are the sensors located before the catalytic converter for Bank 1 and Bank 2.
This tutorial applies to the 1997 to 2000 3.3L V6 Nissan Pathfinder.
Contents of this tutorial:
- P0130 And P0150 Diagnostic Essentials.
- Diagnosing Trouble Codes P0130 And P0150.
- Where To Buy Your Nissan Pathfinder's O2 Sensors And Save.
- TEST 1: Checking Upstream Oxygen Sensor Performance.
- TEST 2: Manually Inducing A Rich Condition.
- TEST 3: Checking The Resistance Of The O2 Heater Element.
- TEST 4: Checking The Continuity Between The O2 Sensor And PCM.
- More Nissan Pathfinder Test Tutorials.
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Los Códigos P0130 y P0150 (1996-2000 3.3L Nissan Pathfinder) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Los Códigos P0130 y P0150 (1996-2000 3.3L Nissan Pathfinder) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
P0130 And P0150 Diagnostic Essentials
Usually what causes these two codes to pop up on your Nissan Pathfinder is a failed right (or left) upstream oxygen sensor but not always.
Thankfully, by doing some specific tests, you and I can check to see if they're bad (or not) before replacing them.
Before we jump into the tests, here's some specific information about these two codes that will help us understand exactly what they're trying to tell us:
P0130: O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 1). This trouble code lets us know that the PCM is detecting that:
- The front O2 sensor for Bank 1 is not switching between 0.2 to 0.8 Volts (as the engine is running).
- That the front O2 sensor for Bank 1 is stuck producing an output voltage of 0.2 - 0.4 Volts DC.
- That the fault could lie in the front oxygen sensor itself or in the wiring between the sensor and the fuel injection computer.
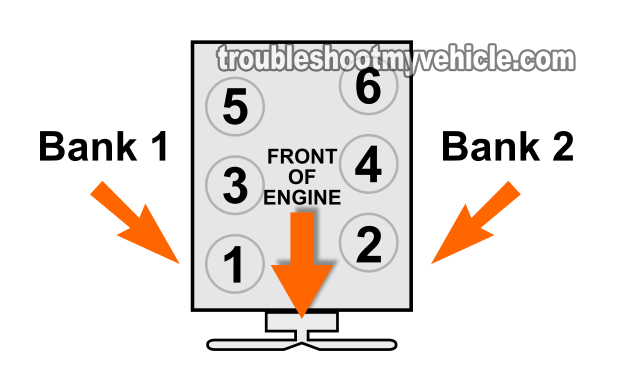
- NOTE: Bank 1 is the bank that houses cylinders 1, 3, and 5.
- Bank 1 Sensor 1 is commonly referred to as:
- Right front oxygen sensor.
- Upstream right oxygen sensor.
- Bank 1 Sensor 1.
- O2S11.
P0150: O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2 Sensor 1):
- The front O2 sensor for Bank 2 is not switching between 0.2 to 0.8 Volts (as the engine is running).
- That the front O2 sensor for bank 2 is stuck producing an output voltage of 0.2 - 0.4 Volts DC.
- That the fault could lie in the front oxygen sensor itself or in the wiring between the sensor and the fuel injection computer.
- NOTE: Bank 2 is the bank that houses cylinders 2, 4, and 6.
- Bank 2 Sensor 1 is commonly referred to as:
- Left front oxygen sensor.
- Upstream left oxygen sensor.
- Bank 2 Sensor 1.
- O2S21.
As you can see from the information above both codes (P0130 and P0150) aren't accusing either of the two upstream oxygen sensors as having failed since quite a few things can cause them to stay stuck producing a fixed voltage between 0.2 - 0.4 Volts.
Diagnosing Trouble Codes P0130 And P0150
Getting to the bottom of what's causing these 2 codes to light up the check engine light (CEL) on your Nissan Pathfinder involves 4 specific tests.
NOTE: Both the right and left upstream oxygen sensors are tested in the exact same way so all of the tests (in this tutorial) apply to them both.
- The first test is to confirm that the oxygen sensor's output isn't the right output.
- The second test involves creating a rich air fuel mixture and seeing if the right and left upstream O2 sensors react to it.
- The third test involves measuring the resistance of the internal heater of the upstream oxygen sensor.
- The last test involves testing the continuity of the oxygen sensor's wires between its harness connector and the fuel injection computer's harness connector.
Where To Buy Your Nissan Pathfinder's O2 Sensors And Save
If you walk into your local auto parts store you'll notice that the upstream O2 sensors for Bank 1 (right) and Bank 2 (left) are expensive. If you do need to buy new O2 sensors, check out the links below and save:
Right Upstream -Direct Fit:Left Upstream -Direct Fit:
TEST 1: Checking Upstream Oxygen Sensor Performance


The very first thing that we need to do is check the right (or left) O2 sensor output voltage to see if it's stuck between 0.2 to 0.4 Volts DC after the engine has started and warmed up.
This can be very easily accomplished using a scan tool with live data mode.
If you don't have a scan tool don't panic because you can use a multimeter to test for the right (or left) upstream oxygen sensor's output voltage (and I'll also include how to do it).
Is you don't have a scan tool and are thinking about buying one or need to upgrade your code reader, check out my recommendation here: Actron CP9580 Scan Tool Review.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Connect your scan tool, turn the key to the ON position, and go to its live data mode.
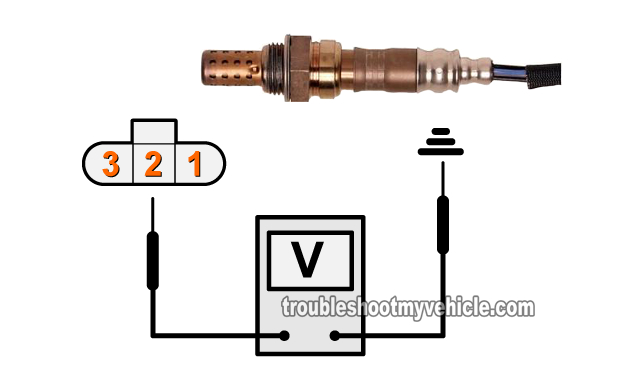
If you're using a multimeter: Place the multimeter in Volts DC mode, connect the red lead to the wire to the middle wire of the upstream oxygen sensor you're testing, and Ground the black test lead on the battery negative (-) terminal. - 2
Start your Pathfinder's engine and let it warm up.
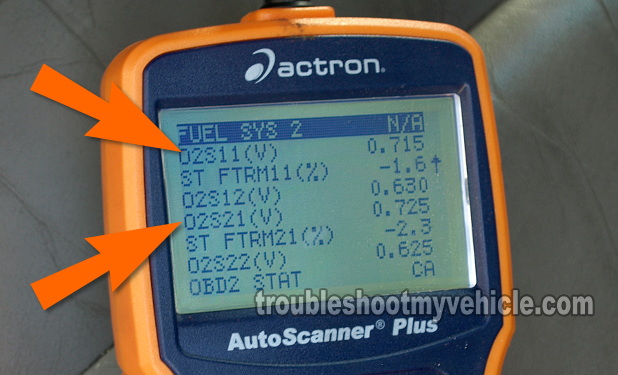
In the meantime, scroll down to the PID labeled: O2S11 and O2S21 (see the image in the image viewer).
PID O2S11 represents the output from the right upstream oxygen sensor and PID O2S21 represents the left upstream oxygen sensor. - 3
Once the engine has reached normal operating temperature, PID O2S11 and O2S21 should show a constant sweeping voltage signal of 0.2 to 0.8 Volts.
In other words: The voltage should move constantly between 0.2 Volts to 0.8 Volts the entire time the engine is running.
If you're using a multimeter: Your multimeter should register a voltage (for the upstream O2 sensor you're testing) that's constantly moving between 0.2 Volts to 0.8 Volts as the engine runs.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The upstream oxygen sensor output voltage constantly moved between 0.2 to 0.8 Volts. This test results tells you that the oxygen sensor that you're observing either on your scan tool or with your multimeter is functioning correctly at this point in time.
This test result also tells you that the problem is intermittent since it's not present at this time.
CASE 2: The upstream oxygen sensor output voltage stayed stuck between 0.2 to 0.4 Volts. This test result definitely tells you that the upstream O2 sensor you're observing on your scan tool or multimeter has a problem.
The next step is to manually induce a rich condition and see if the O2 sensor that you're observing responds to this rich condition. If it doesn't respond to it then we know that it has failed and needs to be replaced. For this test go to: TEST 2: Manually Inducing a Rich Condition.