
In this tutorial, I'm going to explain how to test the ignition system of the 1993-1998 3.0L Nissan Quest (Mercury Villager).
You'll be able to find out if any of the following ignition system components are bad or not: ignition coil, power transistor, spark plug wires, and distributor cap.
Contents of this tutorial at a glance:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Power Transistor Or Ignition Coil.
- Symptoms Of A Bad Distributor Cap And Spark Plug Wires.
- Basic Nissan Ignition System Theory.
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition System?
- Power Transistor Circuits.
- Ignition Coil Circuits.
- TEST 1: Testing For Spark At The Spark Plug Wires.
- TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Distributor Cap.
- TEST 3: Testing The Ignition Coil's High Tension Wire For Spark.
- TEST 4: Testing The Ignition Coil For Spark.
- TEST 5: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting 12 Volts.
- TEST 6: Testing The Ignition Coil's Activation Signal.
- TEST 7: Making Sure The Power Transistor Is Getting Ground.
- TEST 8: Testing The Power Transistor's Activation Signal.
- Other Causes Of A Misfire.
APPLIE TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.0L V6 Nissan Quest: 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998.
- 3.0L V6 Mercury Villager: 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998.
CMP SENSOR DIAGNOSTICS: You can find the camshaft position sensor test here:
IGNITION SYSTEM WIRING DIAGRAM:
CYLINDER MISFIRE DIAGNOSTICS:
Symptoms Of A Bad Power Transistor Or Ignition Coil
The power transistor's job is to activate the ignition coil.
When the power transistor fails, the ignition coil is not going to spark. If the ignition coil doesn't spark then your Nissan Quest (Mercury Villager) will not start due to a lack of spark.
The ignition coil's job is to provide spark to the distributor. When the ignition coil fails the distributor is not going to distribute any spark to the cylinders. The end result is an engine that won't start due to lack of spark.
Symptoms Of A Bad Distributor Cap And Spark Plug Wires
The job of the distributor cap and the spark plug wires is to distribute and deliver the spark that the ignition coil creates to the engine cylinders.
The distributor cap and spark plug wires are not going to last forever. When a distributor cap fails you'll usually see one or two towers that cannot transmit spark to their spark plug wires.
The end result of this particular type of problem is an engine cylinder misfire that will light up the check engine light with misfire trouble codes.
A bad distributor cap can also cause the engine to not start due to lack of spark.
When spark plug wires fail, you'll usually see one or two that can no longer deliver spark from the distributor cap to the spark plug.
In these cases you'll notice that the engine suffers from a cylinder misfire. This cylinder misfire will light up the check engine light with a misfire trouble code.
You'll also see one or more of the following symptoms:
- Engine misfires.
- No power when accelerating the vehicle down the road.
- Idles rough.
- Bad gas mileage.
- Black smoke coming out of the tail-pipe.
- Rotten egg smell coming out of the tail-pipe.
- Smell of unburned gasoline coming out of the tail-pipe.
- Won't pass the state emissions test.
Basic Nissan Ignition System Theory
In a nutshell this is how the ignition system works:
- The camshaft position sensor starts to generate and feed two position signals to your Nissan's PCM (Powertrain Control Module=Fuel Injection Computer).
- Once the fuel injection computer receives the camshaft position sensor signals, it sends the power transistor an activation signal.
- Once the power transistor receives its activation signal, it activates the ignition coil by interrupting the ignition coil's primary current circuit.
- Once the ignition coil is activated by the power transistor, it starts to spark.
- The ignition coil's spark is transmitted to the center of the distributor's cap by a high tension wire.
- The distributor rotor then distributes the spark to the distributor cap towers.
- From the distributor cap towers the spark is transmitted to the spark plugs via high tension wires.
With the help of this tutorial you'll be able to check the ignition coil's high tension wire, the spark plug wires, the distributor cap, the ignition coil, the power transistor.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition System?
Although the tests in this article are easy and simple, you do need some specific tools to perform them with. Here's the list:
- An HEI spark tester
- You can see an example of this tool here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester.
- An LED light.
- You can see an example of this LED light here: The LED Light Test Tool And How To Make One (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- Battery jump start cables.
- A multimeter.
- If you don't have a multimeter or would like to upgrade yours, see my recommendations here: Buying A Digital Multimeter For Automotive Diagnostic Testing (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- A helper.
An ignition system wiring diagram always comes in handy and you can find one here: Ignition System Wiring Diagram (1993-1998 3.0L Nissan Quest).
Power Transistor Circuits
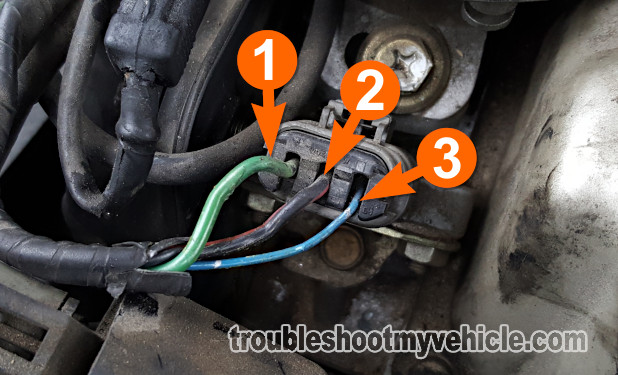
| 1993-1995 3.0L Nissan Quest (Mercury Villager) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Green (GRN) | Ignition Control Signal |
| 2 | Black (BLK) | Chassis Ground |
| 3 | Blue (BLU) | Power Transistor Control Signal |
| 1996-1998 3.0L Nissan Quest (Mercury Villager) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Green (GRN) | Ignition Control Signal |
| 2 | Black With Red Stripe (BLK/RED) | Chassis Ground |
| 3 | Blue (BLU) | Power Transistor Control Signal |
Ignition Coil Circuits
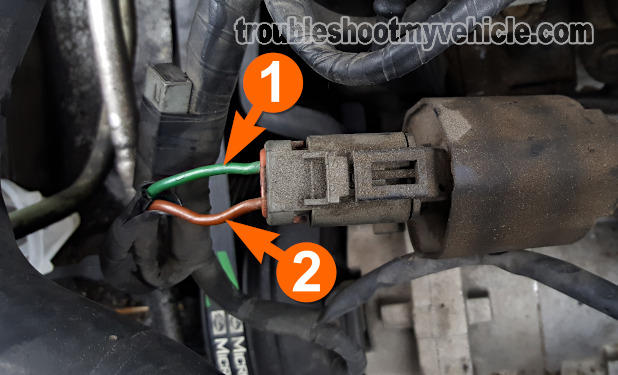
| 1993-1995 3.0L Nissan Quest (Mercury Villager) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Green (GRN) | Ignition Control Signal |
| 2 | White With Red Stripe (WHT/RED) | 12 Volts |
| 1996-1998 3.0L Nissan Quest (Mercury Villager) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Green (GRN) | Ignition Control Signal |
| 2 | Brown (BRN) | 12 Volts |

