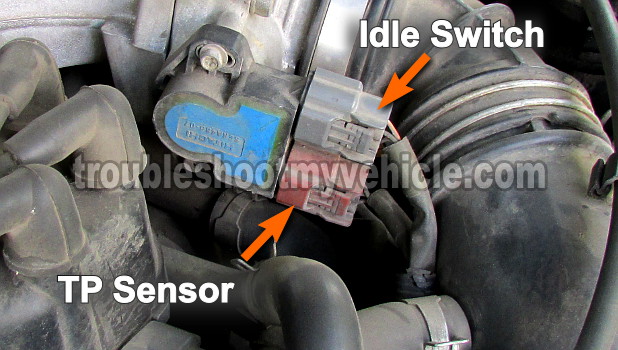
As you're probably already aware, the throttle position sensor on your Nissan is two sensors in 1. One part of the assembly is the actual TP sensor and the other part is the idle switch.
Testing the throttle position sensor (TPS) to see if it has failed and causing a TPS diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is not hard.
In this tutorial, I'm gonna' show you how to troubleshoot the throttle position sensor (TPS) on your Nissan 3.3L Pathfinder (Frontier, XTerra or QX4), with a multimeter and in a step-by-step way.
I'm also gonna' show you how to adjust it after removing and replacing it (you can find these instructions on the last page of this tutorial).
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Throttle Position Sensor (TPS).
- How The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Works.
- Circuit (Wire) Descriptions Of The TPS.
- Where To Buy Your TP Sensor And Save.
- START HERE: Troubleshooting the TP Sensor.
- TPS TEST 1: Testing The TPS Voltage Signal.
- TPS TEST 2: Verifying The TPS Has Power.
- TPS TEST 3: Verifying The TPS Has Ground.
- How To Adjust The Throttle Position Sensor Assembly.
- More Nissan 3.3L Test Tutorials.
If you need to test the idle switch part of the TP sensor assembly, the following tutorial will help: How To Test The Idle Switch (Nissan 3.3L Pathfinder, Xterra, Frontier).
ES ![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor TPS (Nissan 3.3L Pathfinder, Xterra, Frontier) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Sensor TPS (Nissan 3.3L Pathfinder, Xterra, Frontier) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
Symptoms Of A Bad Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
Since the throttle position sensor is one of several sensors that your Nissan's fuel injection computer uses to calculate how much much fuel to inject, when it fails you're going to see several symptoms.
- Check engine light (CEL) shining nice and bright.
- Diagnostic trouble codes (DTC) stored in the PCM's memory:
- P0120: TP Sensor A Circuit Malfunction.
- Your Nissan Pathfinder (Xterra, Frontier) fails the state mandated emissions test.
- Bad gas mileage.
- Hard start and/or extended cranking time (after shut off).
- Black smoke coming out of the tailpipe.
- Hesitation when accelerating your Pathfinder down the road.
How The Throttle Position Sensor Works
As you're probably already aware, the throttle position sensor (TPS) on your 3.3L equipped Nissan Pathfinder (Frontier, Xterra or QX4) is attached to the throttle body and its job is to measure throttle plate angle.
In layman's terms, this means that the TPS is tasked with the job of measuring how much you step on or step off the accelerator pedal as you're driving the down the road.
This throttle plate angle information is then sent to your Nissan's fuel injection computer as a voltage DC signal.
To give you a few more specifics:
- As you step on the accelerator pedal,
- The throttle plate opens and the TP sensor measures how much and relays this to the PCM.
- The fuel injection computer injects more fuel.
- As you let your foot off the accelerator pedal,
- The throttle plate closes and the TP sensor measures how much and relays this to the PCM.
- The fuel injection computer injects less fuel.
Circuit (Wire) Descriptions Of The TPS
The throttle position sensor (TPS) on your 3.3L equipped Nissan Pathfinder (Frontier, Xterra or QX4) is located on the side of the throttle body.
As you can see in photo 2 of 2 (in the image viewer) the TP sensor has 2 connectors for a total of 6 wires coming out of both. This is due to the fact that the throttle position sensor is two sensors in one. One part of the assembly is the idle switch and the other part is the throttle position sensor itself.
The bottom brown connector connects to the TP sensor part and supplies it with power, Ground, and relays the throttle angle voltage signal to the PCM. The gray connector connects to the idle switch part of the assembly.
To better understand how we're gonna' test the throttle position sensor (TPS), in this tutorial, I'm going to briefly describe each wire's job and how the sensor works.
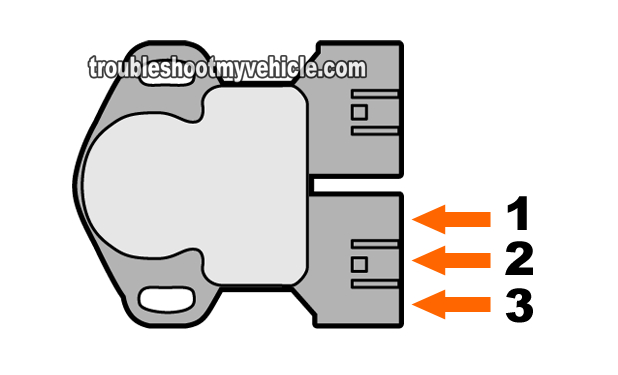
TP sensor brown connector:
- The TP sensor is a 3 wire sensor.
- wire that connects to pin labeled with the number 1.
- Feeds Ground to the TP sensor.
- Ground is provided by the PCM (internally).
- wire that connects to pin labeled with the number 2.
- Feeds the throttle angle voltage signal to the PCM.
- This voltage signal varies depending on the amount of throttle plate opening.
- wire that connects to pin labeled with the number 3.
- Feeds power to the TP sensor.
- In the form of 5 Volts DC and is supplied only with Key On Engine Off (KOEO) or Key On Engine Running (KOER).
- Power comes directly from the PCM.
- wire that connects to pin labeled with the number 1.
REMEMBER: The throttle position sensor (TPS), at closed throttle, produces a low voltage signal of around 0.5 Volts DC. As the throttle plate starts to open (as you step on the accelerator pedal and accelerate the engine), this 0.5 Volt signal starts to increase. At wide open throttle, the TP sensor will output about 4.5 Volts DC.
With this bit of information, let's move on to the next subheading,
Where To Buy Your TP Sensor And Save
Just recently one of my cousins needed to buy a TP sensor for her 1998 Nissan Pathfinder and I was shocked and how much paid for it at our local auto parts store! After all, the TP sensor she bought is a no-name brand Chinese knock-off that she paid over $100 (US) for.
I didn't have the heart to tell her that she could've bought it a whole lot cheaper online, but I will tell you and I'll show you where to buy it. You can buy it here:
Not sure the TP sensor listed fits your particular Nissan? Don't worry, they'll make sure it fits your Honda, once you get to the TP sensor site, or they'll find the right one for you.




