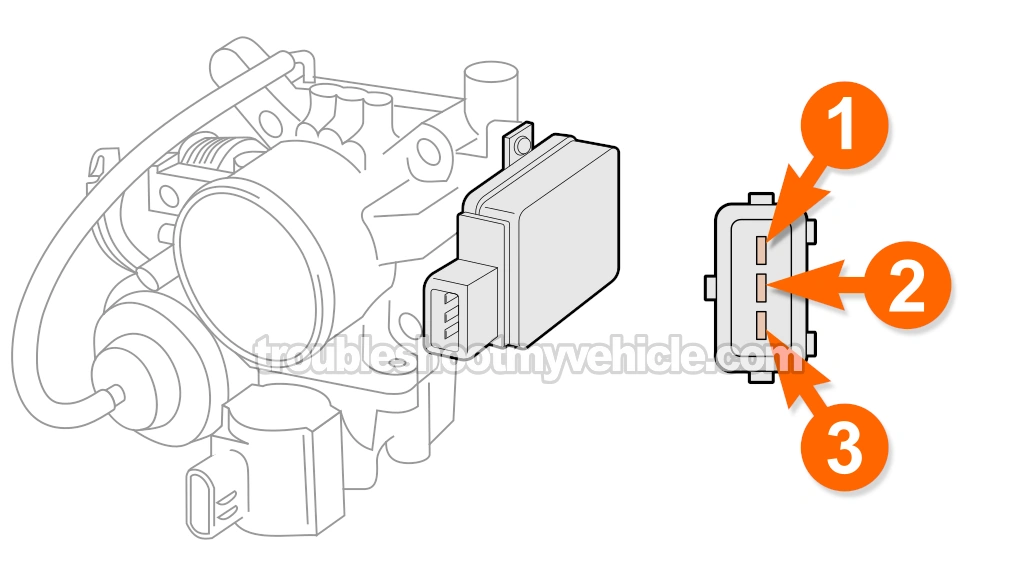
TEST 2: Making Sure The TPS Is Getting Ground
So far, your tests have confirmed:
- The BLU wire is delivering 10 to 12 Volts DC (TEST 1).
- The BLK/RED wire is delivering 4.5 to 5 Volts DC (TEST 1).
In this test section, we're going to make sure that the sensor is getting Ground. This Ground is a chassis Ground and is available at all times (this only applies to the manual transaxle equipped 2.0L Camry).
The wire that delivers this chassis Ground to the sensor is the brown (BRN) wire of the TPS 3-wire connector.
The check for the presence of Ground in the BRN, we'll do a simple multimeter voltage test on the female terminal that connects to the BRN wire.
- 1
Disconnect the TP sensor from its 3-wire connector.
- 2
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 3
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the battery positive (+) terminal.
- 4
With the black multimeter test lead, probe the female terminal of the connector that connects to the BRN wire.
- 5
Your multimeter should read 10 to 12 Volts DC.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts. This is the correct and expected test result.
Your next step is to go to: TEST 3: TPS Continuity Tests - Part 1.
CASE 2: The multimeter register DID NOT 10 to 12 Volts. Double check your connections and make sure that you're testing the correct wires.
If your multimeter still does not show Ground, you can conclude that there's an open-circuit problem in the wiring between the TP sensor harness connector and the vehicle's chassis.
TEST 3: TPS Continuity Tests - Part 1

Now that you've checked the basics in the previous two tests, in this section we'll check that the TPS is signaling that the throttle plate is closed.
This is a very simple test that involves checking the continuity of TPS terminals 1 and 2 with the throttle plate closed.
NOTE: This test is done on the male spade terminals of the throttle position sensor itself.
Here are the steps:
- 1
Disconnect the TPS from its 3-wire connector.
- 2
Place your multimeter in Ohms mode.
- 3
Insert a 0.020 inch (0.50 mm) feeler gauge between the throttle lever and the idle stop stop.
- 4
Measure the resistance between male spade terminals 2 and 3.
Terminals 2 and 3 are the Idle Switch (IDL) circuit of the TP sensor.
Terminal 2 should correspond to the BRN wire of the 3-wire connector.
Terminal 3 should correspond to the BLU wire of the 3-wire connector. - 5
Continuity should exist between terminals 2 and 3.
- 6
Measure the resistance between male spade terminals 1 and 2.
Terminals 1 and 2 are the Power Switch (PSW) circuit of the TP sensor.
Terminal 1 should correspond to the BLK/RED wire of the 3-wire connector.
Terminal 2 should correspond to the BRN wire of the 3-wire connector. - 7
Continuity SHOULD NOT exist between terminals 1 and 2.
Let's take a look at your test results:
CASE 1: The indicated terminals have continuity and no continuity. This is the correct and expected test result.
Your next step is to go to: TEST 4: TPS Continuity Tests - Part 2.
CASE 2: Terminals 2 and 3 have NO continuity. This usually points a misadjusted throttle position sensor.
Your next step is to adjust the TPS. The following tutorial will help you adjust the TPS:
CASE 2: Terminals 1 and 2 have continuity. This usually points a misadjusted or a bad TP sensor.
Your next step is to adjust the TPS. The following tutorial will help you adjust the TPS:
TEST 4: TPS Continuity Tests - Part 2

In this part of the continuity tests, we're gonna substitute the feeler gauge (from the previous test section) with a thicker one.
NOTE: This test is done on the male spade terminals of the throttle position sensor itself.
Here are the steps:
- 1
Disconnect the TPS from its 3-wire connector.
- 2
Place your multimeter in Ohms mode.
- 3
Insert a 0.035 inch (0.90 mm) feeler gauge between the throttle lever and the idle stop stop.
- 4
Measure the resistance between male spade terminals 2 and 3.
Terminals 2 and 3 are the Idle Switch (IDL) circuit of the TP sensor.
Terminal 2 should correspond to the BRN wire of the 3-wire connector.
Terminal 3 should correspond to the BLU wire of the 3-wire connector. - 5
Continuity SHOULD NOT exist between terminals 2 and 3.
- 6
Measure the resistance between male spade terminals 1 and 2.
Terminals 1 and 2 are the Power Switch (PSW) circuit of the TP sensor.
Terminal 1 should correspond to the BLK/RED wire of the 3-wire connector.
Terminal 2 should correspond to the BRN wire of the 3-wire connector. - 7
Continuity SHOULD NOT exist between terminals 1 and 2.
Let's take a look at your test results:
CASE 1: The indicated terminals have no continuity. This is the correct and expected test result.
Your next step is to go to: TEST 5: TPS Continuity Tests - Part 3.
CASE 2: Terminals 2 and 3 have continuity. This usually points a misadjusted throttle position sensor.
Your next step is to adjust the TPS. The following tutorial will help you adjust the TPS:
CASE 2: Terminals 1 and 2 have continuity. This usually points a misadjusted or bad throttle position sensor.
Your next step is to adjust the TPS. The following tutorial will help you adjust the TPS:

