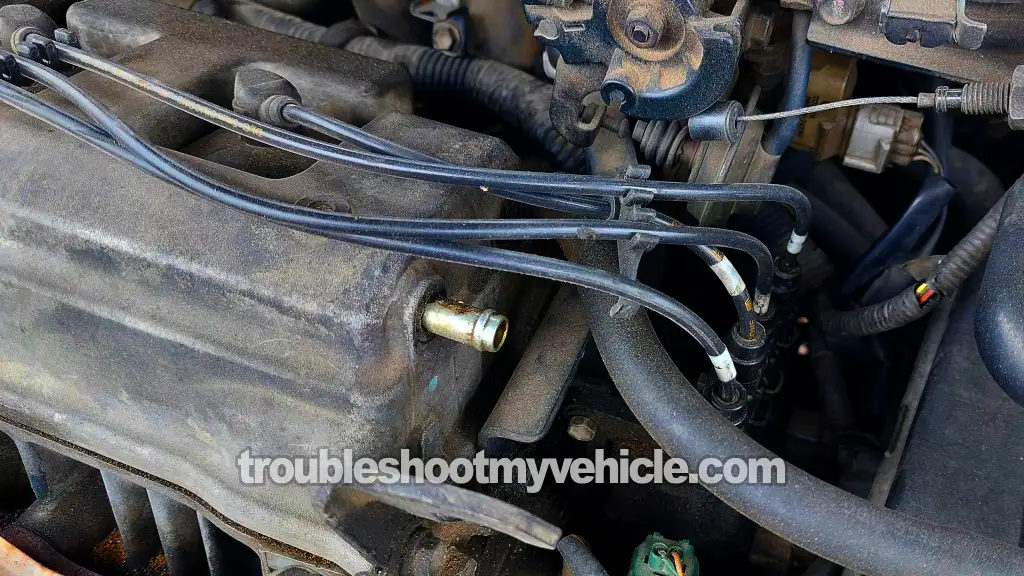

Diagnosing an ignition coil problem on the 1997-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry isn't difficult at all.
From personal experience, I can tell you that the diagnostic process is pretty straightforward. In this tutorial, I'll guide you through it step-by-step.
You'll quickly and easily troubleshoot the ignition coil problem like a pro, without wasting time or money on unnecessary parts.
All you'll need are a few simple tools: a multimeter, a spark tester, and some basic hand tools —nothing that'll break the bank.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Ignition System Basics.
- Symptoms Of A Bad Ignition Coil.
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Coils?
- Where To Buy The Ignition Coils And Save.
- TEST 1: Checking For Spark With A Spark Tester.
- TEST 2: Checking For Spark Directly On The Ignition Coil's Tower (Non-Paired Cylinders).
- TEST 3: Checking For Spark Directly On The Ignition Coil's Tower (Paired Cylinders).
- TEST 4: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Power.
- TEST 5: Checking For The Ignition Coil's Activation Signal.
- TEST 6: Checking Both Ignition Coils For Spark.
- TEST 7: Making Sure Both Ignition Coils Are Getting Power.
- TEST 8: Checking The Ignition Coils' Activation Signals.
- More 2.2L Toyota Camry Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 2.2L Toyota Camry: 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001.
Ignition System Wiring Diagrams:
- Ignition System Circuit Wiring Diagram (1997 2.2L Toyota Camry).
- Ignition System Circuit Wiring Diagram (1998-1999 2.2L Toyota Camry).
- Ignition System Circuit Wiring Diagram (2000-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry).
Ignition System Tests: The following tutorials explain how to test CKP sensor, and the CMP sensor:
- How To Test The Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor (1997-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry).
- How To Test The Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor (1997-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry).
Ignition System Basics
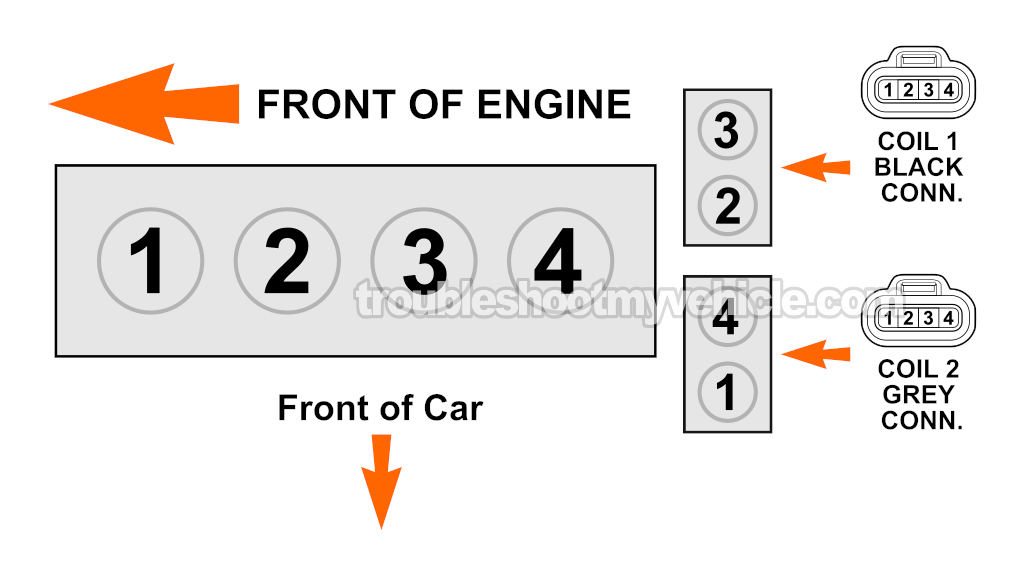
The ignition system in your Camry's 4-cylinder engine uses a waste-spark design, which means two cylinders get spark simultaneously from a single ignition coil.
Here's how it works:
- The engine is equipped with two ignition coils.
- Each coil operates on a waste-spark system, sending spark to two cylinders at the same time.
- The cylinders are paired like this:
- Cylinders 1 and 4 share an ignition coil and fire together.
- Cylinders 2 and 3 share the other ignition coil and fire together.
This design allows one cylinder to get spark on the compression stroke (where combustion happens) while the other gets spark on the exhaust stroke (wasting the spark since there's no fuel-air mixture to ignite).
When diagnosing an ignition coil problem on this type of system, it's important to remember these cylinder pairings because a failure in one ignition coil will affect both "paired" cylinders.
By keeping these "paired" cylinders in mind, you'll be able to isolate an ignition coil issue accurately, saving time and avoiding unnecessary part replacements.
| Coil 1 (Cyl 2/3) -Black Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Black with red stripe (BLK/RED) | B+ (12 Volts) |
| 2 | Yellow with red stripe (YEL/RED) | IGT Signal (ignition coil activation signal) |
| 3 | White with red stripe (WHT/RED) | IGF (Igniter Feedback signal) |
| 4 | BRN | Chassis Ground |
| Coil 2 (Cyl 1/4) -Grey Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Black with red stripe (BLK/RED) | B+ (12 Volts) |
| 2 | Black (BLK) | IGT Signal (ignition coil activation signal) |
| 3 | White with red stripe (WHT/RED) | IGF (Igniter Feedback signal) |
| 4 | BRN | Chassis Ground |
Symptoms Of A Bad Ignition Coil
An ignition coil that has failed will cause one of two problems:
- A misfire problem.
- An engine no-start problem.
If the ignition coil is causing a misfire problem, you're gonna' see one of the following engine performance issues:
- Cylinder misfire diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs):
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder #1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder #2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder #3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder #4 Misfire.
- Lack of power when accelerating the engine under load: When you step on the gas pedal to accelerate, the engine struggles to deliver power. It might feel sluggish or hesitate, failing to respond as expected.
- Bad gas mileage: A bad ignition coil will cause incomplete combustion, wasting fuel and lowering your gas mileage. This means more trips to the gas station.
- Rough idle: At a stoplight or while parked, the engine shakes or vibrates more than normal. It might sound uneven, and the RPM needle (if equipped) may fluctuate instead of holding steady.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Coils?
To test the ignition coils on your Toyota Camry, you're going to need a few basic diagnostic tools. Here's the list:
- A multimeter.
- To check the ignition coil activation (IGT) signals, you'll need a multimeter with Hertz (Hz) capability. If you don't have one and need to buy one, this is the one I use and own: Tekpower TP8268 AC/DC Auto/Manual Range Digital Multimeter with NCV Feature (at: amazon.com).
- A spark tester.
- The spark tester that I recommend (and that I use) is the HEI spark tester. This is an accurate and inexpensive spark tester and you can buy it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester (at: amazon.com).
- Basic hand tools.
- You'll need some basic hand tools to remove the bolt securing the ignition coil down to the engine.
Where To Buy The Ignition Coils And Save
The following ignition coil is a Delphi brand component (one of the most well-known automotive parts suppliers in the world -no knock-off) and will fit the 1997-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
NOTE: Not sure if the ignition coil or spark plug wires fit your particular 2.2L Toyota Camry? Don't worry. Once you get to the site, they'll ask you for the specifics of your vehicle. If they doesn't fit, they'll find you the right ones.
TEST 1: Checking For Spark With A Spark Tester
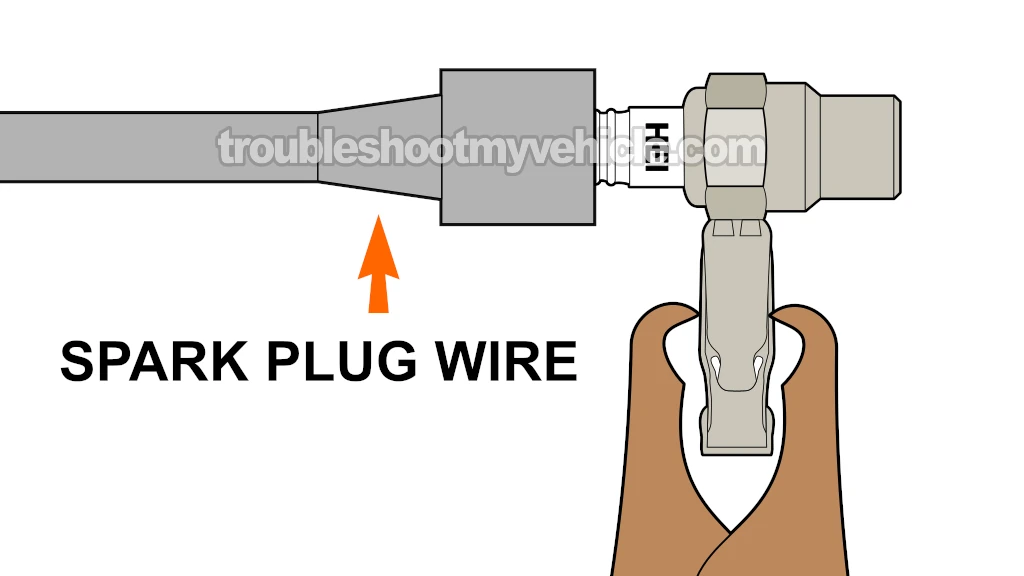
The first thing we'll do, is to test all four spark plug wires for spark with a spark tester.
It's important to remember that:
- Cylinders 1 and 4 receive spark from the same ignition coil.
- Cylinders 2 and 3 receive spark from the same ignition coil.
Once the spark test is done, we'll interpret your test results below and see what our next step is.
NOTE: To get the most accurate test result, you need to use a dedicated spark tester. If you don't have one, I recommend the HEI Spark Tester, and you buy it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester.
Let's get testing:
PART 1:
- 1
Disconnect the cylinder 1 spark plug wire and connect it to the spark tester (see photo 1 of 2 above).
NOTE: The other spark plug wires must remain connected to their respective spark plugs during this test. Only disconnect a wire when it's being tested for spark. - 2
Ground the HEI spark tester with a battery jump start cable directly on the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 3
Have a helper crank the engine while you observe the spark tester.
- 4
The spark tester should spark.
- 5
Write down your spark test result and the cylinder ID.
- 6
Remove the spark tester and reconnect the spark plug wire to its spark plug.
- 7
Repeat steps 1 thru 6 on the remaining spark plug wires.
Let's see what your test results mean:
CASE 1: All four spark plug wires sparked. This is the correct and expected test result and tells you that the ignition coils are OK.
With this test result you can also conclude that:
- The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is good.
- The camshaft position (CMP) sensor is good.
CASE 2: All fours spark plug wires DID NOT spark. This usually tells you that the the crankshaft position sensor is bad.
But before you test the CKP sensor, you need do a few more tests. Your next step is to check for spark directly on the ignition coils. Go to: TEST 6: Checking Both Ignition Coils For Spark.
CASE 3: Only one spark plug wire DID NOT spark. This test result usually means that either the spark plug wire or the ignition coil is defective.
The next step is to check for spark directly on the ignition coil's tower. Go to: TEST 2: Checking For Spark Directly On The Ignition Coil's Tower (Non-Paired Cylinders).
CASE 4: Two "paired" cylinder spark plug wires DID NOT spark. This test result usually means that either the spark plug wire or the ignition coil is defective.
The next step is to check for spark directly on the ignition coil's tower. Go to: TEST 3: Checking For Spark Directly On The Ignition Coil's Tower (Paired Cylinders).
CASE 5: Two "non-paired" cylinder spark plug wires DID NOT spark. This test result could be caused by bad spark plug wires or a bad ignition coil.
To find out, the next step is to check for spark directly on the non-sparking spark plug wire's ignition coil tower. Go to: TEST 2: Checking For Spark Directly On The Ignition Coil's Tower (Non-Paired Cylinders).



