
Testing the fuel injectors on the 2001-2003 Ford 4.2L V6 E150 and E250 vans isn't a walk in the park. The challenge comes from their location beneath the intake manifold plenum, which needs to be removed to get to them.
To make matters worse, in most cases where a fuel injector is suspected of causing a cylinder misfire, the actual problem often lies with an ignition system component or low cylinder compression.
In this tutorial, I'm sharing my method for diagnosing these issues—a technique I've perfected over the years—that's helped me determine if a fuel injector is bad or clogged. This diagnostic approach will help you rule out a few variables before testing the fuel injectors, so you can avoid removing the upper intake manifold unnecessarily.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Fuel Injector.
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The Fuel Injectors?
- Start Here: Diagnostic Strategy.
- Where To Buy The Fuel Injector And Save.
- PART 1: Checking The Injector's Internal Resistance.
- PART 2: Checking The Fuel Injector Spray Pattern.
- Important Tips For Installing A Fuel Injector.
- Precautions To Take When Removing The Intake Manifold Plenum.
- More 4.2L Ford Diagnostic Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 4.2L V6 Ford E150: 2001, 2002, 2003.
- 4.2L V6 Ford E250: 2001, 2002, 2003.
The fuel injector tests for the 1997-2000 4.2L V6 Ford E150/E250 can be found here:
F-SERIES PICKUPS: The fuel injector troubleshooting tutorial for the 2001-2003 4.2L Ford F150/F250 pickups can be found here:
- How To Test The Fuel Injectors (2001-2003 4.2L V6 Ford F150, F250) (at: easyautodiagnostics.com)
Symptoms Of A Bad Fuel Injector
The fuel injectors on your van will typically encounter one of two main issues:
- Internal short-circuit or open-circuit: In this case, the injector's internal wiring has an electrical fault, stopping it from injecting fuel.
- Clogged fuel injector: Here, the injector can still inject fuel but fails to atomize it properly, meaning it doesn't spray the fuel in a fine mist. This lack of atomization causes the cylinder to misfire because the fuel can't combust properly.
Regardless of whether the injector has an internal electrical fault or is clogged, the end result is the same: the cylinder that it supplies with fuel will misfire.
Here are some more specific symptoms when a fuel injector fails or gets clogged:
- Rough idle.
- Lack of power.
- Hesitation when you accelerate your 4.2L Ford pickup down the road.
- Since the 4.2L Ford pickup is OBD II equipped, you'll see a misfire diagnostic trouble code (DTC):
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder #1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder #2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder #3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder #4 Misfire.
- P0305: Cylinder #5 Misfire.
- P0306: Cylinder #6 Misfire.
Whether the fuel injector is fried internally or clogged, this tutorial will offer you some specific suggestions to help you narrow down the possible solution.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Fuel Injectors?
To perform a fuel injector resistance test, you don't need a lot of stuff. Here's a basic list of tools you'll need:
- A multimeter.
- The multimeter will help you check the internal resistance (Ohms) of the fuel injector(s).
- If you need to upgrade or buy a multimeter, check out my recommendation: Buying A Digital Multimeter For Automotive Diagnostic Testing (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- Hand-held DIY fuel injector cleaning tool kit.
- This tool allows you to pulse (activate) the fuel injector while connected to a spray can of brake cleaner, making it super easy to visually check the injector's spray pattern and see if it's clogged.
- You can learn more about this tool and where to buy it in this section: PART 2: Checking The Fuel Injector Spray Pattern.
- A fuel injector pigtail connector.
- The pigtail connector comes in handy when testing the resistance of the injectors with the intake manifold plenum installed.
- OBD II scan tool or code reader.
- To actually test the fuel injectors, you don't need a scan tool (since a scan tool can't dynamically test the fuel injectors). But, having one makes the whole process easier since you're able to retrieve any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the PCM memory.
- Hand Tools.
- Since half of the fuel injectors are underneath the intake manifold plenum, you'll need hand tools like: socket wrench, extensions, sockets, etc. to remove it.
- Pen and Paper to write down your fuel injector resistance test results.
Start Here: Diagnostic Strategy
One complication when testing the fuel injectors on your Ford E150/E250 van with a 4.2L V6 engine is their location under the aluminum intake manifold plenum, which you'll need to remove to access and test them.
It's worth noting that fuel injector failures aren't very common. Other issues often cause a cylinder misfire, making it seem like the injector is at fault.
To avoid the hassle of removing the intake manifold plenum unnecessarily, I'll share the testing strategy I use to determine if a fuel injector is bad or clogged and causing a cylinder misfire:
- Identify the 'dead' cylinder first.
- This step is super important if you want to save time, money and avoid the frustration of replacing parts that won't fix the problem you're troubleshooting.
- A cylinder misfire diagnostic trouble code (DTC) will usually help you identify the 'dead' cylinder, but not always. If there's no specific DTC, you might need to do a manual cylinder balance test.
- Once you've found the 'dead' cylinder, the next step is to rule out the ignition system as the cause of the misfire.
- Test the ignition system and make sure it's delivering spark to the 'dead' cylinder.
- To check for spark, you'll need to:
- Use a spark tester on the spark plug wire.
- Inspect the spark plug wire for any damage or excessive wear and tear.
- Remove and inspect the spark plug for any signs of damage.
- The ignition system (whether it's the coil pack, spark plug wire, or the spark plug) is responsible for 90% of misfires, so it's best to eliminate it as a cause from the start.
- You can find the ignition system tests here: How To Test The Ignition Coils (1997-2000 4.2L V6 Ford E150, E250).
- If your test results confirm the 'dead' cylinder is getting spark, its spark plug wire is OK, and its spark plug is OK, your next step is to see if the cylinder has good compression. If you find that the cylinder isn't getting spark, then you've found the issue causing the cylinder misfire.
- To check for spark, you'll need to:
- Compression test the 'dead' cylinder.
- You don't have to test all 6 cylinders, but you'll need to test at least two other cylinders plus the 'dead' one (to compare your compression test results to). This will give you the necessary data to get an idea of the internal health of the 'dead' cylinder.
- You can find the test explained here: How To Test Engine Compression (1997-2004 4.2L V6 Ford E150, E250)
- If the 'dead' cylinder has good compression, the next step is to test the fuel injector's resistance. If it doesn't have compression, then you've found the cause of the cylinder misfire issue.
- Test the fuel injector.
- The first thing is to test the internal resistance of the fuel injector of the 'dead' cylinder.
- The second part of the test involves using brake cleaner spray with a special adapter tool to visually check whether the fuel injector is indeed spraying fuel.
I've used the above diagnostic strategy with a ton of success and I think it'll help you too.
Where To Buy The Fuel Injector And Save
The following links will help you comparison shop for the fuel injector on your 4.2L V6 Ford pickup:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
Not sure if the above fuel injectors fit your particular 4.2L Ford pickup? Don't worry, once you click on the links and arrive on the site, they'll make sure it fits! If it doesn't, they'll find you the right one.
PART 1: Checking The Injector's Internal Resistance
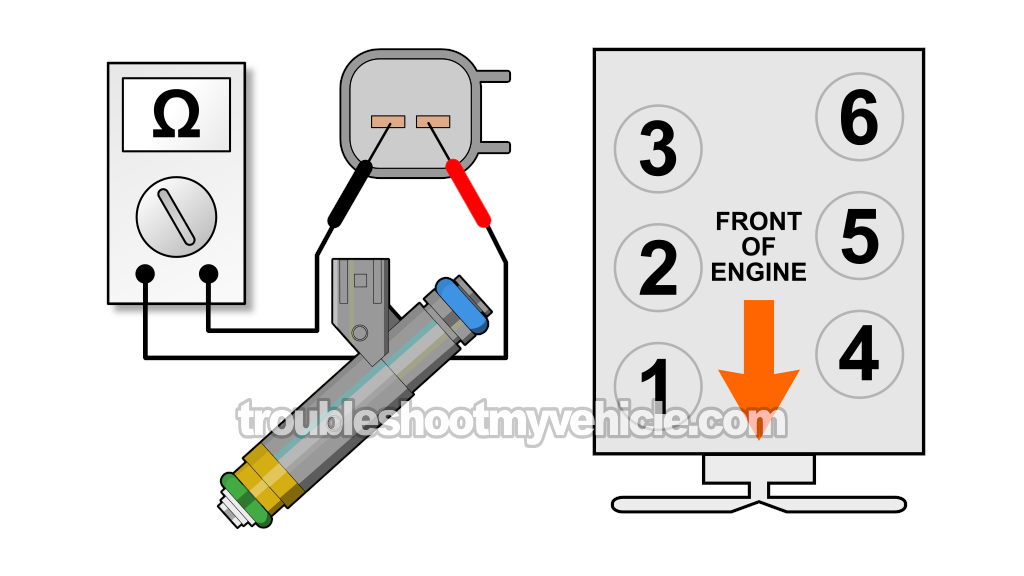
Alright, as you're already aware, the upper intake manifold plenum has to come off to access the fuel injectors. While I don't have any detailed remove and replace (R&R) instructions for you, I do want to pass along some important tips before you get started. You can find them here:
Another thing to note: Testing the resistance of some fuel injectors can be challenging due to their position on the engine (even with the plenum removed). I've found that it can be a little tricky to probe the male spade terminals of the fuel injector with the multimeter test leads (to get a resistance reading).
I've found that using a fuel injector pigtail connector, which I buy online, is the best way to tackle this. Once I've connected the pigtail to the fuel injector, I can easily measure the resistance by probing the connector's exposed wire ends.
By using the fuel injector pigtail connector, you'll get an accurate resistance measurement, not to mention that you'll also avoid the difficulty of accessing the injector's male spade terminals directly with the test leads.
NOTE: Don't have a multimeter or need to upgrade yours? Check out my recommendation: Buying A Digital Multimeter For Automotive Diagnostic Testing (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
Alright, here are the steps:
- 1
Remove the intake manifold plenum.
- 2
Disconnect the fuel injector from its electrical connector.
NOTE: The illustration above will help you identify the cylinder the fuel injector belongs to. - 3
Place your multimeter in Ohms (Ω) mode.
- 4
Measure the resistance of the fuel injector across its two male spade terminals with the multimeter test leads (see the illustration above).
You should see a resistance value between 11 to 18 Ohms (with the engine completely cold).
Measure the resistance of the same fuel injectors several times so that you can be sure of your multimeter's Ohms result. - 5
Write down the resistance value that your multimeter records for the specific fuel injector you're testing.
- 6
Repeat steps 2 through 5 on any other fuel injector you need to test.
Let's find out what your specific multimeter test results mean:
CASE 1: The resistance of the 'dead' cylinder's fuel injector is within specification. This tells you that this particular fuel injector doesn't have an internal short or open-circuit problem.
Your next step is to check that the fuel injector isn't clogged. Go to: PART 2: Checking The Fuel Injector Spray Pattern.
CASE 2: The resistance of the 'dead' cylinder's fuel injector IS NOT within specification. This tells you that the fuel injector is bad. Replace the fuel injector.






