
An engine compression test can reveal a lot about what's going on inside your engine. For example, it can help you pinpoint if low compression in one or more cylinders is causing a misfire or triggering a diagnostic trouble code.
It can also tell you if a 'no-start' condition might be due to a broken timing belt or internal engine damage.
In this tutorial, I'll walk you through how to perform a compression test and, more importantly, how to interpret the results to diagnose your engine issues.
Contents of this tutorial:
ES ![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar La Compresión Del Motor (2.2L Toyota Camry) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar La Compresión Del Motor (2.2L Toyota Camry) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 2.2L Toyota Camry: 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001.
- 2.2L Toyota Celica: 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999.
- 2.2L Toyota MR2: 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995.
Important Tips And Suggestions
TIP 1: If your 2.2L Toyota's engine starts and runs, let it warm up for about 15 minutes before you start your compression test. Don't let the engine reach normal operating temperature. The idea here is for your Toyota's engine to be 'slightly warmed up', it should not be hot.
Why warm up the engine? Because a slightly warmed up engine will improve the accuracy of your compression test results.
TIP 2: Take all necessary safety precautions as you work around a cranking engine. Please use common sense and think safety all of the time.
TIP 3: The cylinder head, on your 2.2L Toyota, is made of aluminum so you should never remove the spark plugs if the engine is hot (hot = normal operating temperature). Removing the spark plugs from a hot engine can/will damage the spark plug hole threads in the aluminum cylinder head.
Symptoms Of Low Or No Cylinder Compression
Engine compression issues usually fall into two main categories:
- Compression problems causing a rough idle (misfire) while the engine is running.
- Compression problems causing the engine to crank but not start.
Let's take a closer look at each type:
- Rough idle (misfire) due to low compression.
- Low compression in one or two cylinders can cause your 2.2L Toyota Camry (Celica, or MR2) to misfire or shake at idle. This issue often clears up when you accelerate.
- On OBD II-equipped 2.2L Toyotas, the PCM may store one or more of the following misfire codes:
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder #1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder #2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder #3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder #4 Misfire.
- However, it's worth noting that the PCM doesn't always register a misfire trouble code, even when the engine is experiencing cylinder issues.
- Engine cranks but does not start.
- Zero compression in two or more cylinders can prevent your engine from starting, even though it will still crank. When all four cylinders have no compression, you'll typically observe:
- Faster cranking: The engine cranks noticeably faster than normal, indicating a serious issue.
- Spark is present: All four cylinders are getting spark, ruling out ignition system problems.
- Fuel is being injected: The fuel injectors are delivering fuel to the engine.
- You can confirm this by checking the injector pulse with a Noid light.
- Alternatively, you can remove the spark plugs and verify they're soaked in gasoline.
- Zero compression across all cylinders is often due to one of the following:
- A blown head gasket.
- A broken timing belt.
- The engine has thrown a rod.
- Zero compression in two or more cylinders can prevent your engine from starting, even though it will still crank. When all four cylinders have no compression, you'll typically observe:
With this overview of the types of compression issues, let's get started with testing!
Which Compression Tester Should I Buy?
There are lot of engine compression testers to choose from and many places to buy them. I'm gonna' make some recommendations to you:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
TEST 1: Dry Compression Test
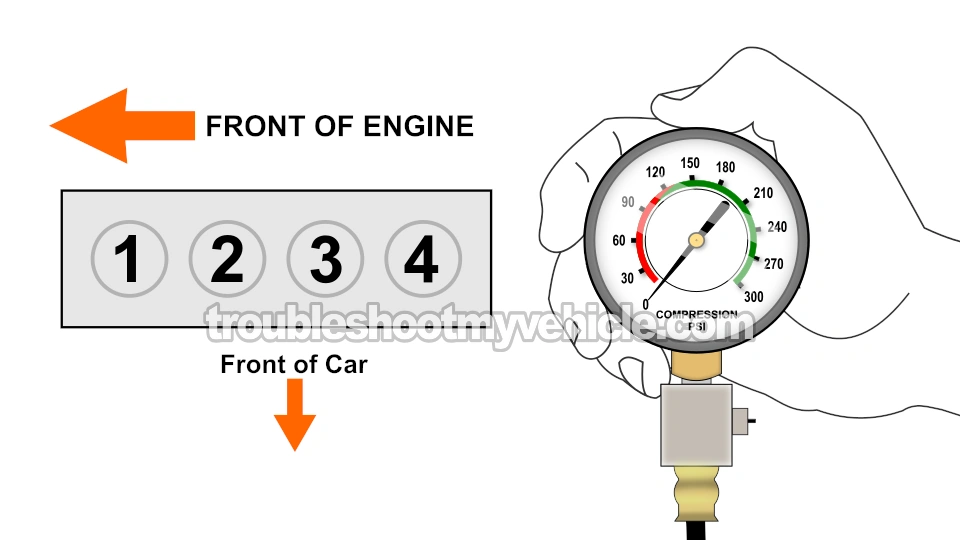
In this tutorial, you'll be doing two types of compression tests:
- Dry compression test.
- Wet compression test.
The difference between the two is that the wet compression test involves adding a small amount of oil to the cylinder with low compression to help pinpoint the issue.
The purpose of the dry compression test is to find out the compression values of all 4 cylinders. If your Toyota doesn't start, then these values will tell you if the engine compression is behind the 'no-start' condition.
If your Toyota is misfiring, then these values will let us know if there's a cylinder with too low compression that's causing the misfire problem.
CAUTION: Be careful and be alert at all times since you'll be working around a cranking engine.
NOTE: If your Toyota's engine is hot, wait for it to cool down before removing 4 spark plugs. Removing the spark plugs from a hot engine can damage the spark plug threads in the cylinder head.
Alright, these are the test steps:
- 1
Disable the ignition system by disconnecting the ignition coil (ignition system with mechanical distributor) or the ignition coil pack from its electrical connector.
This will prevent the ignition system from firing spark during the test. - 2
Remove the spark plugs from a slightly warmed up engine (if it starts and runs). Remember, the engine can not be hot!
When removing the spark plugs, be careful not to drop any of them on the floor, or you run the risk of having the spark plugs porcelain insulator crack and then you'll have a misfire on your hands.
If the engine does not start, don't worry about it being warmed up. - 3
Thread the engine compression gauge into the spark plug hole for the number 1 engine cylinder. Hand tighten the compression gauge only! Do not use any type of tool to get it tight.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine till the needle on the compression gauge stops climbing.
- 5
Now, record on paper the value at which the needle stopped and the number of the engine cylinder on a piece of paper. Release the pressure on the gauge and repeat this step one more time.
- 6
Repeat this test step on the remaining 3 cylinders.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: You got 0 PSI compression on all 4 cylinders. This is not good and tells you that one of the following conditions exists:
- Timing belt problem.
- Blown head gasket.
- Blown engine.
Any compression value below 100 PSI (even if it does not 0 PSI) means internal mechanical engine trouble.
CASE 2: Some, but not all, of the cylinders had a low compression value. Up to a certain point this is normal -especially if the engine has a lot of miles.
What is NOT normal is if the values vary too much. With a bit of math we can find out if the lowest compression values are normal or not. Go to: Interpreting Your Compression Test Results.
The rule of thumb is that the lowest compression value cannot vary more than 15% from the highest value you recorded. Any cylinder with a compression value lower than 15% of the highest will misfire.
Interpreting Your Compression Test Results
Depending on the amount of wear and tear on your Toyota's engine, you'll see that some of the cylinders' compression values differ from one another.
If the difference is small enough, then this low compression value does not affect engine performance.
When the difference is too big, you'll have a rough idle or a misfire condition on your hands.
To find out if the lower compression value is causing a problem, you need to find out if it's lower than 15% of the highest compression value you got.
You can do this (figuring out the 15%) in one of two ways: You can calculate this 15% difference with pen and paper or you can use my low compression calculator. You can find the low compression calculator here: Online Low Engine Compression Calculator (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
If you want to manually calculate the 15% difference, here's what you'll need to do:
- STEP 1: Multiply the highest compression value by 0.15 (this is the decimal value of 15%).
- STEP 2: Round the result to the nearest one (for example: 25.6 would become 26).
- STEP 3: Subtract the result (the number that was rounded) from the highest compression value.
- ANSWER: The result of this subtraction is the lowest possible compression value any cylinder can have.
Now, let me give you a more specific example: Let's say that I got the following compression readings:
| Cylinder | Pressure |
|---|---|
| #1 | 165 PSI |
| #2 | 95 PSI |
| #3 | 155 PSI |
| #4 | 175 PSI |
My next step is to do the following calculation:
- STEP 1: 175 x 0.15 = 26.25.
- STEP 2: 26.25 = 26 (rounded to nearest one).
- STEP 3: 175 - 26 = 149.
- ANSWER: 149 PSI. Any cylinder with this compression (or lower) value will misfire.
Since cylinder #2 is only producing 95 PSI, I can now conclude that it's 'dead' and causing a misfire.
To find out if the lowest compression value you got from your engine compression test is within a good range, you'll need to do the same calculation. Of course, you'll need to use the highest compression value you got and not the one in the example.
Once you've found the 'dead' cylinder, the next step is to find out what's causing the low compression value. For this step, go to: TEST 2: Wet Compression Test.
TEST 2: Wet Compression Test
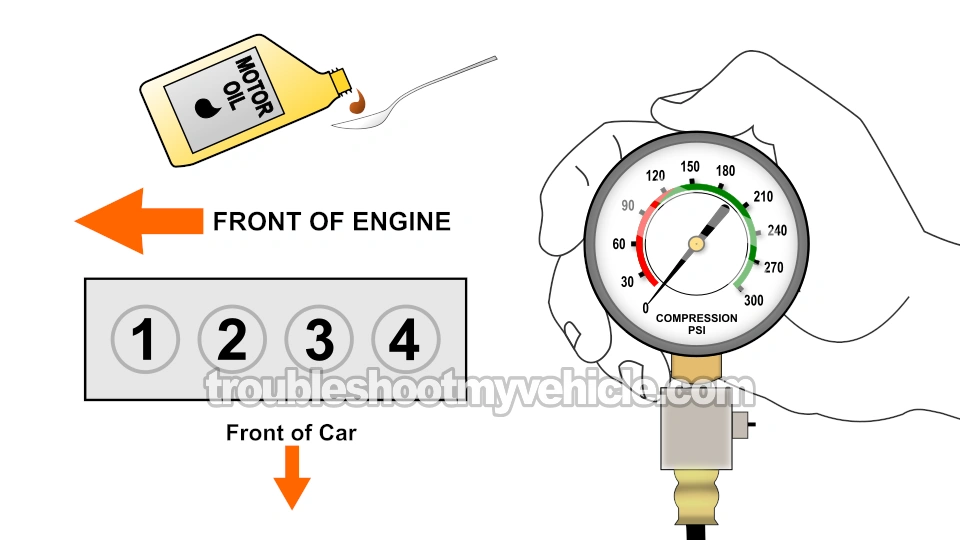
If in TEST 1 you found a cylinder with a compression value lower than 15% of the highest compression value you recorded, then your next step is to find out if it's the end result of severe wear or damage to the cylinder head valves or the piston rings.
You can easily find out by adding a little oil to the affected cylinder and checking its compression once again. This is known as a 'wet' compression test.
If the low cylinder compression is due to worn rings, the compression value of the affected cylinder will go up (with the oil added). If the problem is caused by worn cylinder head valves, the compression value will stay the same.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Add a tablespoon (or two) of engine oil in the cylinder you need to retest.
I suggest using a small and long funnel so that the oil will reach the inside of the cylinder. - 2
Once you've added the oil, install the compression gauge, and as before just hand tighten it.
- 3
Have your helper crank the engine till the needle stops climbing on the compression gauge.
- 4
You'll see one of two results:
A.) The needle will climb higher than the previous compression number you recorded for this specific cylinder.
B.) The needle will not move at all or stay at the same number you recorded earlier.
What ever value your compression tester reads, write it down again. - 5
If you have another cylinder that needs to be tested, then repeat steps 1 thru' 4 on it now.
Let's take a look at what test results mean:
CASE 1: The compression value went up after adding motor oil and retesting. This tells you that the low compression problem is due to worn piston compression rings.
Here's why: The motor oil you just added helped the piston rings to create a tighter seal. With the piston rings now sealing the compression inside the cylinder, the compression value on your compression tester went up. This type of test result only happens when the problem is due to worn piston rings.
CASE 2: The compression value DID NOT go up after adding oil and retesting (in other words, it stayed the same). This result tells you that the low compression value registered in this cylinder (in the dry test) is due to worn/damaged cylinder head valves.
More 2.2L Toyota Camry And Celica Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 2.2L Toyota Camry and Celica tutorials and wiring diagrams in this index:
Here's a sample of the tutorials you'll find there:
- How To Test The TPS With A Multimeter (1997-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (1990-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry, Celica).
- How To Test The Throttle Position Sensor (1992-1996 2.2L Toyota Camry).
- How To Test The MAP Sensor (1997-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!





