TEST 4: Testing The Power (12 Volts) Circuit
Each individual ignition coil within the coil pack assembly shares the same power circuit. In other words:
- One wire of the coil pack's 4-wire connector delivers battery power to the coil pack with the key in either the RUN or START position.
- That battery voltage gets distributed to all three individual ignition coils.
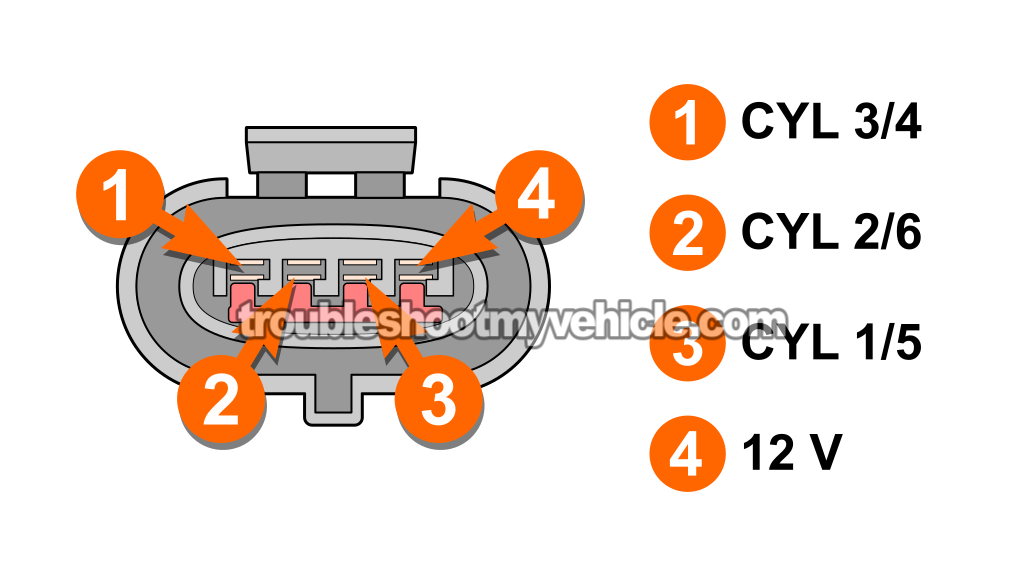
In this test section, we're going to make sure that male terminal 4 is getting 12 Volts.
The wire that delivers this battery voltage to terminal 4 of the coil pack is the:
- 1996-1999: White with light blue stripe (WHT/LT BLU) wire.
- 2000: Red (RED) wire.
For our test, we're going to make sure that the power-supply wire has 10 to 12 Volts with the key in the RUN position but with the engine OFF.
NOTE: This test is done on the 4-wire coil pack connector, which has female terminals. There's a good chance your multimeter's test-lead probe may be too thick to probe the terminal, so be careful. If the female terminal gets damaged, you'll need to replace the entire connector.
Let's get going:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil from its connector.
- 2
Put the multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 3
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 4
Gently probe the front of female terminal 4 with the red multimeter test lead (using an appropriate tool).
Female terminal 4 should connect to the WHT/LT BLU iwre (1996-1999) or RED wire (2000) of the coil pack's 4-wire connector. - 5
Have your helper turn the key to the ON position (no need to crank the engine).
- 6
You should see 10-12 Volts on your multimeter.
Let's find out what your test result means:
CASE 1: The coil pack is getting power. This is the correct and expected test result.
Now that we've confirmed the coil pack is getting the power it needs to generate spark for all six cylinders, our next step is to check that it's getting all three individual ignition coil activation signals from your Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable's PCM. For this test, head over to: TEST 8: Checking The IC Activation Signals.
CASE 2: The coil pack isn't getting power. Make sure you're testing the correct terminal and wire. Confirm that the terminal you're probing actually connects to the WHT/LT BLU wire (1996-1999) or RED wire (2000) of the coil pack's 4-wire connector.
If you still don't see battery power at terminal 4, then we can rule out the coil pack itself as the cause of the no-spark, no-start problem you're trying to solve. Your next step is to find out why this circuit doesn't have battery power and restore it. Once the coil pack gets power, you'll get spark and the engine will start.
TEST 5: Activation Signal For Cylinders 1 And 5

Up to this point in your diagnostic test steps, you've checked and confirmed the following:
- You've got two spark plug wires that connect to paired cylinders 1 and 5 that aren't sparking (TEST 1).
- You've checked the coil pack towers for cylinders 1 and 5, and they aren't sparking either (TEST 3).
Our next test is to make sure that the individual ignition coil within the coil pack —the one that fires spark for cylinders 1 and 5— is getting its activation signal from your Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable's PCM.
This is a super easy test to do, and it only requires using an automotive 12-Volt test light. This should be a non-powered test light that uses an incandescent light bulb.
The wire that delivers the 1/5 ignition-coil activation signal is the yellow with black stripe (YEL/BLK) wire that connects to terminal 3 of the coil pack's 4-wire connector.
IMPORTANT: When using the probe tip of your 12V test light, be very careful to avoid damaging the female terminal or the connector. If either one is damaged, you'll need to replace the entire connector.
CAUTION: This test has to be performed with the engine cranking. Be careful and take all necessary safety precautions.
NOTE: If you don't own a 12 Volt test light with an incandescent light bulb, this is the one that I use and recommend: Lisle 28400 Heavy Duty 12 Volt Test Light (Amazon affiliate link).
Alright, let's start:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil from its 4-wire electrical connector.
- 2
Connect the 12V test light's alligator clip to the battery positive (+) post.
- 3
With the test light's probing tip, gently probe terminal number 3.
Female terminal 3 should connect to the YEL/BLK wire. - 4
Have your helper crank the engine.
- 5
The 12V test light should flash ON and OFF the whole time the engine is cranking.
Let's find out what your test result means:
CASE 1: The 12-Volt test light flashed ON and OFF while cranking the engine. This is the correct and expected test result, and it tells us that the PCM is actively trying to get the individual coil for cylinders 1 and 5 to start sparking away.
If you've checked and confirmed the following, then you can conclude that the coil pack is toast and needs to be replaced:
- In TEST 1, you confirmed that the spark plug wires for cylinders 1 and 5 do not spark.
- In TEST 3, you checked for spark at the coil pack towers for cylinders 1 and 5, and they aren't sparking either.
- In this test section, you confirmed that the PCM is sending an activation signal to the ignition coil pack (to activate spark for cylinders 1 and 5).
When you're ready to replace the cold pack, these are the ones I recommend:
- Standard Motor Products FD488T Ignition Coil Pack (Amazon affiliate link).
- Delphi GN10180 Ignition Coil Pack (Amazon affiliate link).
CASE 2: The 12-Volt test light DID NOT flash ON and OFF. Without this activation signal, the coil pack isn't going to create spark for cylinders 1 and 5. Double-check your test connections and repeat the test one more time.
If you still don't see the 12-Volt test light flashing ON and OFF, then the most likely cause of this missing 1/5 activation signal is an open-circuit between the coil pack connector and the PCM connector.
Your next step is to find out why this signal is missing and restore it to the circuit. Once the coil pack starts receiving its 1/5 activation signal, you'll see spark going to cylinders 1 and 5 again.
TEST 6: Activation Signal For Cylinders 2 And 6

Your previous two tests have confirmed the following:
- The spark plug wires that connect to cylinders 2 and 6 do not spark (TEST 1).
- The coil pack towers that connect to those two spark plug wires do not spark either (TEST 2).
Since the coil pack towers for cylinders 2 and 6 aren't sparking, we need to see if the PCM is sending an activation signal to the ignition coil (within the coil pack) that's in charge of firing spark to cylinders 2 and 6.
We can easily check for this activation signal using a regular 12-Volt automotive test light. This test light is a non-powered type that uses an incandescent light bulb. If you don't have one, this is the one I use and recommend: Lisle 28400 Heavy Duty 12 Volt Test Light (Amazon affiliate link).
The terminal of the coil pack's 4-wire connector that delivers this 2/6 activation signal (to the coil pack) is female terminal 2. This terminal connects to the yellow with white stripe (YEL/WHT) wire of the coil pack's 4-wire connector.
IMPORTANT: When using the probe tip of your 12V test light, be very careful to avoid damaging the female terminal or the connector. If either one is damaged, you'll need to replace the entire connector.
CAUTION: This test has to be performed with the engine cranking. Be careful and take all necessary safety precautions.
Alright, let's start:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil from its 4-wire electrical connector.
- 2
Connect the 12V test light's alligator clip to the battery positive (+) post.
- 3
With the test light's probing tip, gently probe terminal number 2.
Female terminal 2 should connect to the YEL/WHT wire. - 4
Have your helper crank the engine.
- 5
The 12V test light should flash ON and OFF the whole time the engine is cranking.
Let's find out what your test result means:
CASE 1: The 12-Volt test light flashed ON and OFF while cranking the engine. This is the result we needed to see to confirm that your Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable's PCM is sending the coil pack a 2/6 activation signal.
The coil pack is toast and has to be replaced to solve the issue only if you've checked and confirmed the following:
- The spark plug wires that connect to cylinders 2 and 6 do not spark (TEST 1).
- Coil pack towers for cylinders 2 and 6 do not spark (TEST 3).
- In this test section, you've confirmed the presence of the 2/6 activation signal at the indicated terminal.
When you're ready to replace the cold pack, these are the ones I recommend:
- Standard Motor Products FD488T Ignition Coil Pack (Amazon affiliate link).
- Delphi GN10180 Ignition Coil Pack (Amazon affiliate link).
CASE 2: The 12-Volt test light DID NOT flash ON and OFF while cranking the engine. Without the 2/6 activation signal, the coil pack isn't going to generate and send spark to cylinders 2 and 6.
Double-check your test connections and make sure the terminal you're testing actually connects to the YEL/WHT wire of the connector.
If you still don't see the 2/6 activation signal, then we can rule out the coil pack as defective. Your next step is to find out why the 2/6 activation signal is missing from this circuit and restore it. Once the coil pack receives this signal, it'll start generating and sending spark to cylinders 2 and 6.
TEST 7: Activation Signal For Cylinders 3 And 4

The spark tests you've performed in the previous two test sections —TEST 1 and TEST 2— have confirmed the following:
- You got no spark from the spark plug wires that connect to cylinders 3 and 4.
- The coil pack towers for cylinders 3 and 4 also don't spark when cranking the engine.
For our final test, we're going to check and see if the PCM is sending the 3/4 activation signal to the coil pack. This activation signal is delivered by the yellow with red stripe (YEL/RED) wire —which connects to female terminal 1 of the coil pack's 4-wire connector.
The cool thing about testing this activation signal is that we can check it with a simple 12-Volt automotive test light. This is a regular non-powered test light with an incandescent light bulb. If you don't have one and need to buy one, this is the one I use and recommend: Lisle 28400 Heavy Duty 12 Volt Test Light (Amazon affiliate link).
IMPORTANT: When using the probe tip of your 12V test light, be very careful to avoid damaging the female terminal or the connector. If either one is damaged, you'll need to replace the entire connector.
CAUTION: This test has to be performed with the engine cranking. Be careful and take all necessary safety precautions.
Alright, let's start:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil from its 4-wire electrical connector.
- 2
Connect the 12V test light's alligator clip to the battery positive (+) post.
- 3
With the test light's probing tip, gently probe terminal number 1.
Female terminal 1 should connect to the YEL/RED wire. - 4
Have your helper crank the engine.
- 5
The 12V test light should flash ON and OFF the whole time the engine is cranking.
Let's find out what your test result means:
CASE 1: The 12V test light flashed ON and OFF the entire time you cranked the engine. This is exactly what we want to see. It tells us the PCM is sending out the 3/4 activation signal and the circuit itself is doing its job.
You can call the ignition coil pack bad only if you've already confirmed all of the following:
- The spark plug wires for cylinders 3 and 4 aren't firing spark (TEST 1).
- The coil pack towers for cylinders 3 and 4 also show no spark (TEST 3).
- The coil pack is indeed receiving the 3/4 activation signal from the PCM (this test section).
When you're ready to replace the cold pack, these are the ones I recommend:
- Standard Motor Products FD488T Ignition Coil Pack (Amazon affiliate link).
- Delphi GN10180 Ignition Coil Pack (Amazon affiliate link).
CASE 2: The 12V test light DID NOT flash ON and OFF while cranking the engine. When the light stays dark (no ON/OFF flashes), it usually means there's an open in the circuit between the connector and the PCM —or, in rare cases, the PCM itself has failed.
This result rules out the coil pack as the culprit behind your misfire or no-spark issue. Your next move is to track down what's keeping that 3/4 activation signal from reaching the coil pack and fix it.
