
The ignition coil pack is the ignition system component that creates and distributes spark to all six cylinders in the 1996-1999 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable.
In this tutorial, I'm going to show you how easy it is to test the coil pack to find out if it's behind a cylinder misfire issue or an engine no-start problem.
You'll also be able to test the spark plug wires to see if any of them are causing the issue instead of the ignition coil pack.
All the test steps are explained in a step-by-step manner so you can easily and quickly figure out if the coil pack is toast and needs to be replaced.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of A Bad Ignition Coil Pack.
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Coil?
- Circuit Descriptions Of The Ignition Coil Pack.
- Ignition Coil Pack Basic Operating Theory.
- Where To Buy The Ignition Coil And Save.
- TEST 1: Testing For Spark At The Spark Plug Wire.
- TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
- TEST 3: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack (Paired Cylinders).
- TEST 4: Testing The Power (12 Volts) Circuit.
- TEST 5: Activation Signal For Cylinders 1 And 5.
- TEST 6: Activation Signal For Cylinders 2 And 6.
- TEST 7: Activation Signal For Cylinders 3 And 4.
- TEST 8: Checking The IC Activation Signals.
- Other Things That Can Cause A Misfire.
- More 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus And Mercury Sable Diagnostic Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.0L V6 (OHV) Ford Taurus: 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000.
- 3.0L V6 (OHV) Mercury Sable: 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000.
COIL PACK CIRCUIT WIRING DIAGRAM:
CKP SENSOR DIAGNOSTIC TESTS:
2001-2007 COIL PACK TESTS:
CYLINDER MISFIRE DIAGNOSTICS:
Symptoms Of A Bad Ignition Coil Pack
The ignition coil pack is made up of three individual ignition coils in one assembly. And as I mentioned at the beginning of the tutorial, it's the component that generates the spark the engine needs to start.
Sooner or later, one of the ignition coils that make up the assembly is going to fail. And when it does, you're going to see one or more of the following engine performance problems.
- Misfire Codes: You'll see one or more of the following codes:
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder 1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder 2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder 3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder 4 Misfire.
- P0305: Cylinder 5 Misfire.
- P0306: Cylinder 6 Misfire.
- Engine Performance Issues: You may see one or more of the following:
- The engine idles rough and wants to stall.
- When you accelerate the van, it has no power.
- Bad Gas Mileage: Since the engine isn't running all six cylinders, it has to work harder, thus consuming more fuel.
- Engine No-Start: The engine will crank but not start (if more than 3 ignition coil towers are not firing spark).
- Rotten egg smell: You'll notice a rotten egg smell coming out of the tailpipe from the unburned fuel overloading the catalytic converter.
CYLINDER MISFIRE DIAGNOSTICS: This tutorial explains how to troubleshoot a cylinder misfire: How To Troubleshoot A Cylinder Misfire (1996-2007 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus, Mercury Sable).
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Coil?
One of the cool things about testing the ignition coil pack yourself is that you don't need any expensive diagnostic equipment to do it. You'll need some tools, but nothing that's gonna break the bank. This is what you'll need to follow this tutorial:
- A multimeter: The multimeter will help you check that the ignition coil is getting power.
- A 12 Volt automotive test light: We'll use the test light to check for the ignition coil activation signals while cranking the engine. Don't have one? You can buy one here: Lisle 28400 Heavy Duty 12 Volt Test Light (Amazon affiliate link).
- A spark tester: This the most critical tool to have and use to check the condition of the ignition coil pack. Any spark tester will do. The one I use and recommend is the OTC 6589 Spark Tester and you can buy it here:
- OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester (at: amazon.com).
- Battery jump start cables: We'll be using a battery jump start cable to Ground the spark tester.
- Spark plug wire pullers: This tool will help you remove the spark plug wires from the spark plugs and help you avoid the very common hassle of having the spark plug wire's metal terminal stay stuck on the spark plug: Performance Tool W80519 Adjustable Spark Plug Boot And Wire Remover (Amazon affiliate link).
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
Alright, before we move on, I do want to point out that you'll need a helper to crank the engine for some of the tests in this tutorial. And lastly, I want to emphasize that the most important tool you'll need is a spark tester. Any spark tester will work —I recommend the HEI spark tester only because I've been using it my entire automotive repair career, and I can tell you from personal experience that it's an accurate and simple way to check for spark.
The thing to remember here is that the wrong tool or method can lead you to an incorrect diagnostic conclusion —and that'll have you chasing ghosts, spending time and money on parts that won't solve the issue.
Circuit Descriptions Of The Ignition Coil Pack
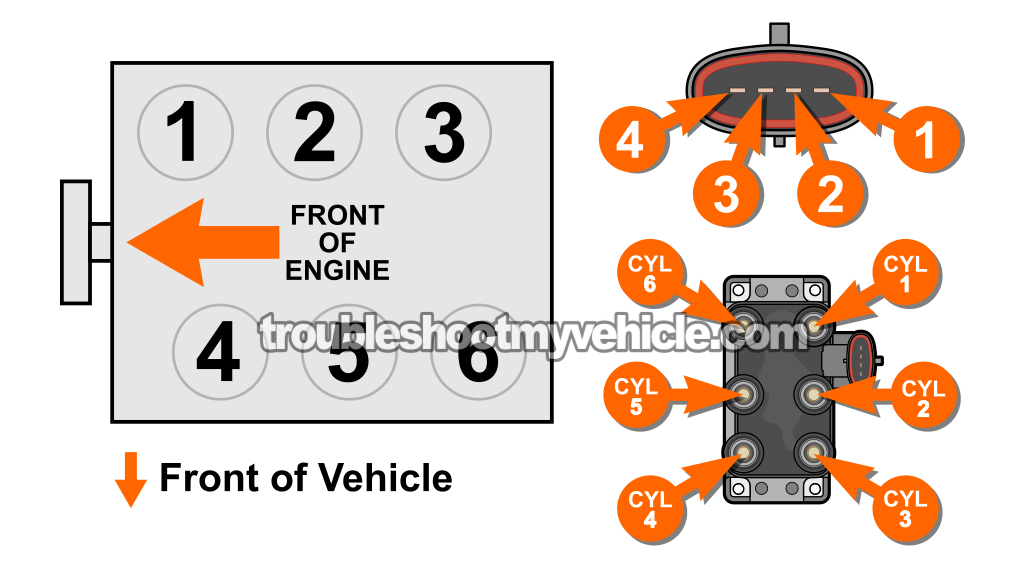
Since the ignition coil pack is made up of three individual ignition coils —each one having two towers to deliver spark to two cylinders simultaneously— each coil needs battery voltage and its own individual activation signal to fire (spark).
This is the reason why the connector has four wires, as each one (or rather circuit) has a specific function. In the table below, you'll find a brief overview of each:
| Pin | Wire | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yellow with red stripe (YEL/RED) | Activation Signal Cylinders 3 & 4 |
| 2 | Yellow with white stripe (YEL/WHT) | Activation Signal Cylinders 2 & 6 |
| 3 | Yellow with black stripe (YEL/BLK) | Activation Signal Cylinders 1 & 5 |
| 4 | White with blue stripe (WHT/BLU) —1996-1999 | 12 Volts (in START/RUN) |
| Red (RED) —2000 |
Ignition Coil Pack Basic Operating Theory
To be able to successfully diagnose the ignition coil pack as good or bad, we need to know how it generates spark. Now don't worry —I'm not going to go into a detailed breakdown of how it works. After all, we're not reverse engineering the thing.
Here's a brief explanation of what happens when you turn the key to crank and start the engine:
- The ignition coil pack gets battery voltage:
- Even though there's only one wire delivering this voltage to the coil pack, this battery power is shared by all three individual ignition coils inside the pack.
- In automotive terms, these 12 Volts are known as the ignition coil's primary current.
- As the engine is turning over to start, the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor starts generating its signal, which gets sent directly to your Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable's powertrain control module (PCM).
- Now that the PCM is receiving a CKP signal —along with other sensor input— it begins activating each ignition coil by switching the ignition coil's primary current ON and OFF.
- This switching ON and OFF the primary current (by the PCM) is accomplished by interrupting its Ground path.
- This turning ON and OFF of the primary current is what that makes the ignition coil fire spark and is what I refer to as the ignition coil's activation signal.
- Each ignition coil within the coil pack gets its own activation signal from the PCM.
- Since each ignition coil has two towers (that's why the ignition coil pack has six towers), when an individual coil gets its activation signal, it fires spark to two "paired cylinders" at the exact same time —in what's known as the Waste Spark method.
- Cylinders 1 and 5 get spark simultaneously from coil 1.
- Cylinders 2 and 6 get spark simultaneously from coil 3.
- Cylinders 3 and 4 get spark simultaneously from coil 2.
The most important thing to take away from this basic operating theory of the ignition coil pack is that it's made up of three individual ignition coils. Each one has two towers, so as each individual ignition coil is activated by the PCM, that coil fires spark simultaneously to two "paired cylinders". And in this tutorial, you're gonna see the term "paired cylinders" quite a bit.
Keep in mind, as we test the coil pack in the next sections of this tutorial, that the "paired cylinders" are the following:
- Cylinders 1 and 5.
- Cylinders 2 and 6.
- Cylinders 3 and 4.
Where To Buy The Ignition Coil And Save
When it comes time to replace the ignition coil-pack, I want to recommend two brands: Standard Motor Products and Delphi. These are brands I've used for all of my automotive-repair career, and I don't hesitate to recommend them:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
NOTE: Not sure if the ignition coil pack fits your particular Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable? Don't worry. Once you get to the site, they'll make sure it fit by asking you the details of you specific vehicle. If it doesn't fit, they'll find you the right one.
TEST 1: Testing For Spark At The Spark Plug Wire
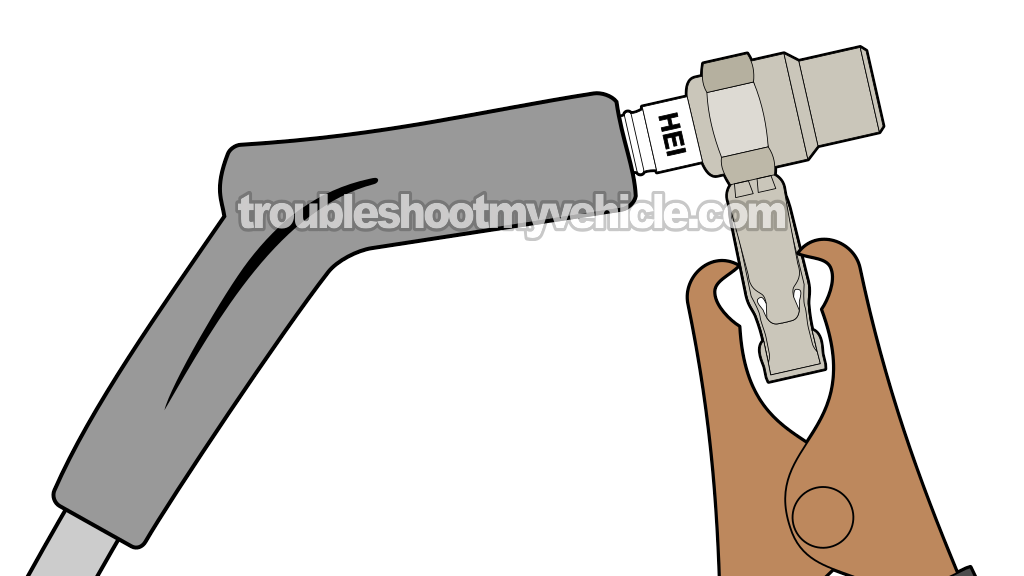
The first order of business to start our ignition coil pack diagnostic is to check all six cylinders for spark. Now, you don't have to check all six if you don't need to, but for the accuracy of your diagnostic —and if I were in your shoes— I'd check all six spark plug wires for spark.
NOTE: Before you yank off the spark plug wire from the spark plug to attach your spark tester, I do want to make you aware of something: the spark plug wires on your Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable are infamous for having their metal terminal stay stuck on the spark plug when you pull them off with your bare hand. I'm not here to sell you a tool —I'm just letting you know, from personal experience, one of the most common issues with this type of ignition system.
So, what I recommend you do is use spark plug wire puller pliers to disconnect the wire from the spark plug. This helps you avoid having the terminal stay stuck on the plug. Now, if this does happen to you, you can reattach the metal terminal back to the wire, but it's a hassle you're better off not dealing with.
If you don't have a pair of spark plug wire–puller pliers, these are the ones I use and recommend: Performance Tool W80519 Adjustable Spark Plug Boot And Wire Remover (Amazon affiliate link)
Lastly —and I apologize if I'm starting to sound like a broken record— I want to emphasize that you need to use a spark tester for all of your spark tests. Any spark tester you've got on hand will do.
If you don't have a spark tester and need to buy one, the one I've personally used for the past three decades of my automotive repair career is the OTC HEI spark tester. If you're curious about it, you can take a look at it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester (Amazon affiliate link).
These are the test steps:
- 1
Remove the spark plug wire (high tension cable) from the spark plug.
- 2
Attach your spark tester to high tension wire.
- 3
Connect the spark tester to the battery negative (-) terminal with a battery jump start cable.
- 4
Have your helper crank the vehicle as you stand at a safe distance from the engine.
The engine may or may not start, either way be careful. - 5
As the vehicle cranks or starts, observe the spark tester.
- 6
You're gonna get one of two results: Spark or NO spark.
- 7
Now repeat this test on the other spark plug wires.
IMPORTANT: Read the following options carefully to interpret your NO SPARK result or results. Remember that some cylinders get spark from the same ignition coil within the coil pack (since the coil pack is made up of 3 individual ignition coils that have two towers each). So if you get a NO SPARK result from two spark plug wires, you need to verify if they're from paired cylinders or from unpaired cylinders.
CASE 1: You got spark from all six spark plug wires. With this test result, you can rule out the coil pack and the spark plug wires as the cause of the engine no-start issue or a cylinder misfire problem. For more troubleshooting tips and suggestions, head over to: Other Things That Can Cause A Misfire.
CASE 2: You got NO spark from only one spark plug wire. The next step is to check for spark directly on the coil pack tower that feeds that spark plug wire with spark. Go to: TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
CASE 3: Spark plug wires that connect to "paired" cylinders 1 and 5 DID NOT spark. The next step is check for spark directly on both towers (one at a time of course).
For this test go to: TEST 3: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack (Paired Cylinders).
CASE 4: Spark plug wires that connect to "paired" cylinders 2 and 6 DID NOT spark.. The next step is check for spark directly on both towers (one at a time of course).
For this test go to: TEST 3: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack (Paired Cylinders).
CASE 5: Spark plug wires that connect to "paired" cylinders 3 and 4 DID NOT spark. The next step is check for spark directly on both towers (one at a time of course).
For this test go to: TEST 3: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack (Paired Cylinders).
CASE 6: You got NO spark from two spark plug wires and they DO NOT connect to paired cylinders. The next step is to test each coil pack tower directly for spark one at a time.
For this test go to: TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack.
CASE 7: You got NO spark from none of the spark plug wires. This usually indicates that power is missing from the power circuit or that the crankshaft position sensor is bad.
To find out, go to: TEST 4: Testing The Power (12 Volts) Circuit.
TEST 2: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack
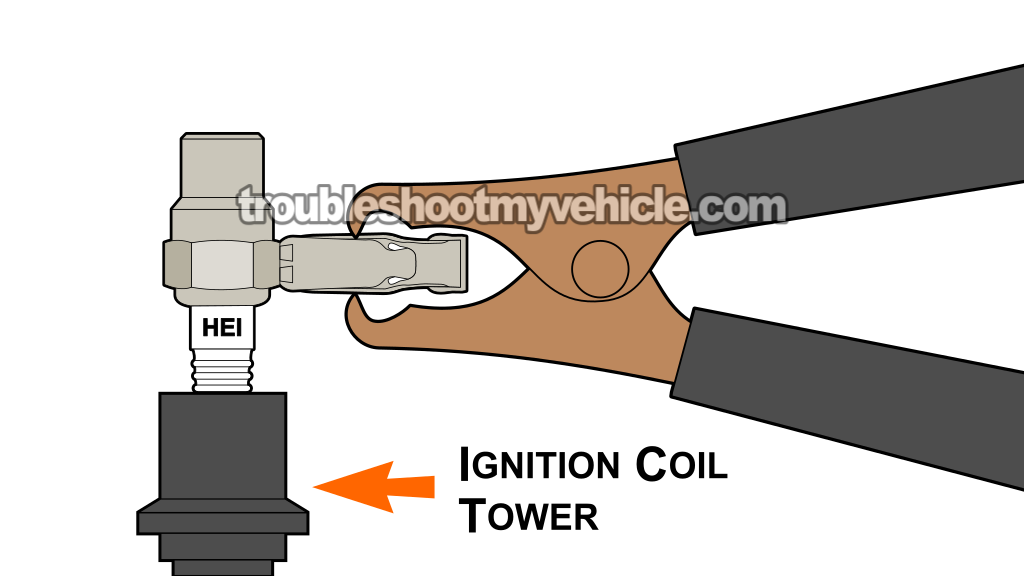
IMPORTANT: This test section only applies if one or two spark plug wires that are connected to non-paired cylinders did not fire spark in TEST 1.
If you're about to perform the spark test in this section, then TEST 1 has confirmed that you've got one or two spark plug wires —that connect to two non-paired cylinders— that aren't sparking.
This lack of spark is going to be caused by one of two things:
- The spark plug wires are bad.
- The ignition coil itself is toast.
The cool thing is that we can easily find out by checking for spark directly on the coil pack towers of those non-sparking spark plug wires. And the spark test result will let us know what the issue is.
OK, here's what we've gotta do:
- 1
Remove the non-sparking spark plug wire from its tower on the ignition coil pack.
- 2
Place the spark tester directly on the ignition coil tower of the spark plug wire you just removed (see illustration above).
- 3
Connect the spark tester to the battery negative (-) terminal with a battery jump start cable.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine. The engine may start, so be careful.
- 5
You're gonna get one of two results: Spark or NO spark.
- 6
Remove the spark tester and reconnect the spark plug wire to the ignition coil tower.
- 7
Repeat steps 1 thru 6 on the other ignition coil tower of the other non-sparking spark plug wire (if applicable).
Let's take a look at what your test result means:
CASE 1: The ignition coil tower sparked. This is the correct test result, and it confirms that the tower is delivering spark to its spark plug wire.
Now, since the spark plug wire that connects to this tower isn't sparking, we can conclude that the wire itself is defective. Replace all of the spark plug wires with a new set to solve the issue.
CASE 2: The ignition coil tower DID NOT spark. This no-spark test result from the ignition coil pack tower tells us, beyond a shadow of a doubt, that the ignition coil pack itself is toast and needs to be replaced.
Replacing the ignition coil pack will solve the cylinder misfire issue that's causing the check engine light to come on with a cylinder misfire trouble code.
TEST 3: Testing For Spark At The Ignition Coil Pack (Paired Cylinders)

IMPORTANT: This test section only applies if two spark plug wires that are connected to paired cylinders 1 & 5, or cylinders 2 & 6, or cylinders 3 & 4 did not fire spark in TEST 1.
If you're about to perform the test in this section, then TEST 1 has confirmed that you've got two spark plug wires —that connect to paired cylinders— that aren't sparking. Our next step is to figure out if this no-spark result is because the spark plug wires themselves are bad or if the ignition coil pack is toast.
We can easily confirm which one it is by checking for spark directly on the coil pack towers of those non-sparking spark plug wires.
Since we need to test two coil pack towers, we're gonna start with one, check it for spark, and then test the second one.
OK, let's get to it:
- 1
Remove one of the spark plug wires that did not fire off spark from the ignition coil pack.
- 2
Place the spark tester directly in the ignition coil tower (see photo above).
- 3
Connect the spark tester to the battery negative (-) terminal with a battery jump start cable.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine.
- 5
The spark tester should spark as the engine cranks.
- 6
Remove the spark tester and reconnect the spark plug wire to the ignition coil tower.
- 7
Repeat tests 1 thru' 5 on the other ignition coil tower whose spark plug wire did not fire off spark.
Let's take a look at what your test result means:
CASE 1: Only one coil pack tower sparked. With this test result, we can conclude that the coil pack itself is bad, and to resolve the cylinder misfire issue, we need to replace the coil pack with a new one.
CASE 2: Both coil pack towers sparked. Since both coil pack towers are sparking, we can conclude that the non-sparking spark plug wires that connect to them are bad and need to be replaced.
Of course, you'll need to replace all of the spark plug wires as a set. This will resolve the cylinder misfire issue so you can clear the cylinder misfire codes lighting up the check engine light on your Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable.
CASE 3: You got no spark from both coil pack towers. Usually, this no-spark test result from both towers tells you that the coil pack is bad, but we need to check one more thing.
To be absolutely sure the coil pack is bad, we need to verify the ignition coil (that connects to those two non-sparking towers) is getting an activation signal from your Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable's powertrain control module (PCM).
If you got no spark from the towers that feed spark to cylinders 1 and 5 go to: TEST 5: Activation Signal For Cylinders 1 And 5.
If you got no spark from the towers that feed spark to cylinders 2 and 6 go to: TEST 6: Activation Signal For Cylinders 2 And 6.
If you got no spark from the towers that feed spark to cylinders 3 and 4 go to: TEST 7: Activation Signal For Cylinders 3 And 4.


