
OBD II trouble code P0122 TP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage is telling you that your Honda's fuel injection computer is seeing a low voltage output from the throttle position sensor (TPS) that doesn't correspond to the actual throttle plate opening (or current engine operating conditions).
Testing the TPS can easily be done with a multimeter and in this tutorial, I'm gonna' show you how in a step-by-step way.
Contents of this tutorial:
- P0122 Basics You Need To Know.
- How The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Works.
- Symptoms Of A P0122 Diagnostic Trouble Code.
- Common Causes Of A P0122 Trouble Code.
- Where To Buy Your TP Sensor And Save.
- START HERE: Troubleshooting DTC P0122.
- TPS TEST 1: Testing The TPS Signal.
- TPS TEST 2: Verifying The TPS Has Power.
- TPS TEST 3: Verifying The TPS Has Ground.
- More Honda 2.2L, 2.3L Test Tutorials.
P0122 Basics You Need To Know
Throttle plate position, without saying, has a direct impact on the amount of fuel your Honda's fuel injection computer injects into the engine's cylinders.
The more the throttle plate opens, to let the engine breathe in more air, the more fuel the fuel injection computer (known as the PCM = Powertrain Control Module) needs to inject. When the throttle closes, and lessens the amount of air flow into the engine, the less fuel the PCM needs to inject.
So when the PCM gets the wrong throttle opening info from the throttle position sensor (TPS), either because the TP sensor has failed or there's a problem in the sensor's wires, it can no longer control fuel injection to maximize performance and a host of other things.
So, when the PCM sees the TP sensor producing a low voltage that indicates a closed throttle plate even though other sensor inputs indicate otherwise, it sets a code P0122 TP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage and lights up the check engine light (CEL) on your Honda's instrument cluster.
How The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Works
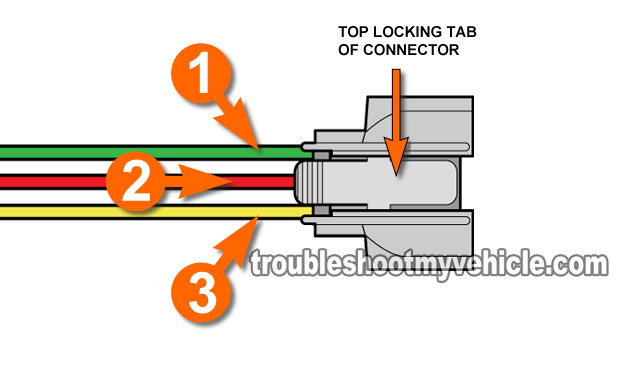
The throttle position sensor (TPS) is one of the easiest sensors to test on your Honda (or Acura).
In this section, I'm gonna describe what the 3 TP sensor wires do and how it works.
Although I'm not going to go into minute technical detail about the inner workings of the sensor, the following brief description of how the throttle position sensor (TPS) works will help make sense of what exactly we're gonna' be testing for in the next pages of this tutorial:
- The TP sensor is a 3 wire sensor.
- Wire labeled with the number 1.
- Feeds Ground to the TP sensor and is provided by the PCM (internally).
- Wire labeled with the number 2.
- Feeds the throttle angle voltage signal to the PCM.
- This voltage signal varies depending on the amount of throttle plate opening.
- Wire labeled with the number 3.
- Feeds power to the TP sensor.
- In the form of 5 Volts DC and is supplied only with Key On Engine Off (KOEO) or Key On Engine Running (KOER).
- Power comes directly from the PCM.
- Wire labeled with the number 1.
- The TP sensor is a potentiometer. Its resistance changes in response to changes in the throttle plate's angle.
- With throttle closed, the smaller the voltage the TP sensor creates and sends to the PCM.
- At closed throttle the TP sensor outputs about 0.5 Volts DC.
- With throttle open to wide open, the higher the voltage the TP sensor creates and sends to the PCM.
- At wide open throttle the TP sensor outputs about 4.5 Volts DC.
- With throttle closed, the smaller the voltage the TP sensor creates and sends to the PCM.
The thing to remember about the throttle position sensor (TPS) is that at closed throttle, the TPS outputs about 0.5 Volts DC. As the throttle plate starts to open (as you accelerate the engine), this voltage starts to increase. At wide open throttle, the TP sensor will output about 4.5 Volts DC.
With this bit of information, let's move on to the next subheading.
Symptoms Of A P0122 Diagnostic Trouble Code
Since the angle of the throttle plate is crucial for proper fuel injection and a host of other things, when your Honda's PCM sees the wrong throttle angle information, then it's not gonna' to be able to keep your Honda's engine running smoothly.
You may see one or more of the following symptoms when the throttle position sensor (TPS) fails:
- Check engine light (CEL) is on.
- DTC P0122 is present.
- Won't pass the state mandated emissions test.
- Gas mileage will suffer.
- Hard start and/or extended cranking time (after shut off).
- Black smoke coming out of the tailpipe.
- Hesitation when accelerating your Honda.
Let's find out what are the common causes of a P0122 DTC, in the next subheading.
Common Causes Of A P0122 Trouble Code
The 3 most common cause of trouble code P0122 are:
- A bad throttle position sensor (TPS).
- A broken TP sensor connector.
- A problem in the sensor 3 wires. Specifically, a short in one of them.
Although extremely rare for this to happen, a bad PCM can also cause a false P0122 trouble code.
In this tutorial, I'll help you troubleshoot all three of the above. With this basic info under our belts, let's turn the page and get testing!
Where To Buy Your TP Sensor And Save
The Honda service manual tells you to replace the entire throttle body when the TP sensor fails but you don't have to.
The TP sensor is sold separately and can be installed as a stand-alone part.
Where can you buy the TP sensor? You can buy it at your local auto parts store but it's gonna' cost a whole lot more. I suggest taking a look at the price of the TP sensor in the following links and compare:
Not sure the TP sensor listed fits your particular Honda? Don't worry, they'll make sure it fits your Honda, once you get to the TP sensor site, or they'll find the right one for you.



