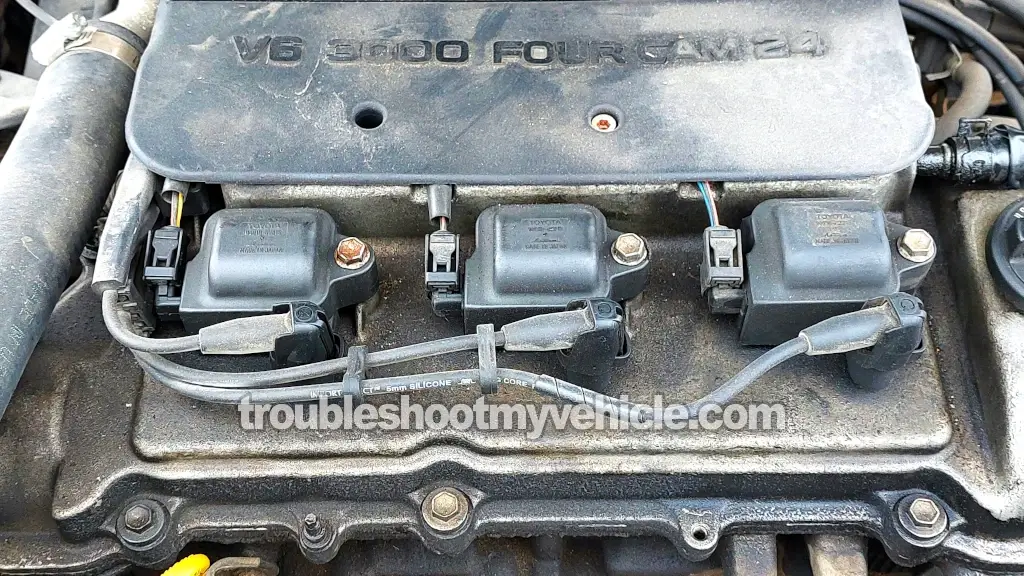
The 1996-2001 3.0L V6 Camry's ignition system is equipped with three ignition coils, each of which supplies spark simultaneously to two spark plugs.
The cool thing is that testing them isn't difficult, and you don't need any expensive diagnostic equipment to find out if they're good or bad.
In this tutorial, I'll explain the entire testing process step by step. You'll be able to quickly and easily diagnose the ignition coils as either good or bad.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Ignition Coil System Basics.
- Common Symptoms Of A Bad Ignition Coil.
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Coil?
- Where To Buy The Ignition Coils And Save.
- TEST 1: Testing The Ignition Coil For Spark.
- TEST 2: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Power.
- TEST 3: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Its Activation Signal.
- TEST 4: Checking For Spark On The Ignition Coil Tower.
- More 3.0L Toyota Camry Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry: 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001.
Ignition System Wiring Diagrams:
- Ignition System Wiring Diagram (1996 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry).
- Ignition System Wiring Diagram (1997-1998 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry).
- Ignition System Wiring Diagram (1999-2001 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry).
1994-1995 Ignition Coil Tests: The following tutorial will help you test the COP ignition coils on the 1994-1995 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry:
Ignition Coil System Basics
The ignition system setup, on the 1996-2001 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry, is basically a waste-spark system with three ignition coils —each one fires spark to two cylinders simultaneously.
This design works by firing spark to one spark plug on the compression stroke and the other on the exhaust stroke. The spark during the exhaust stroke is "wasted," but it doesn't affect engine performance.
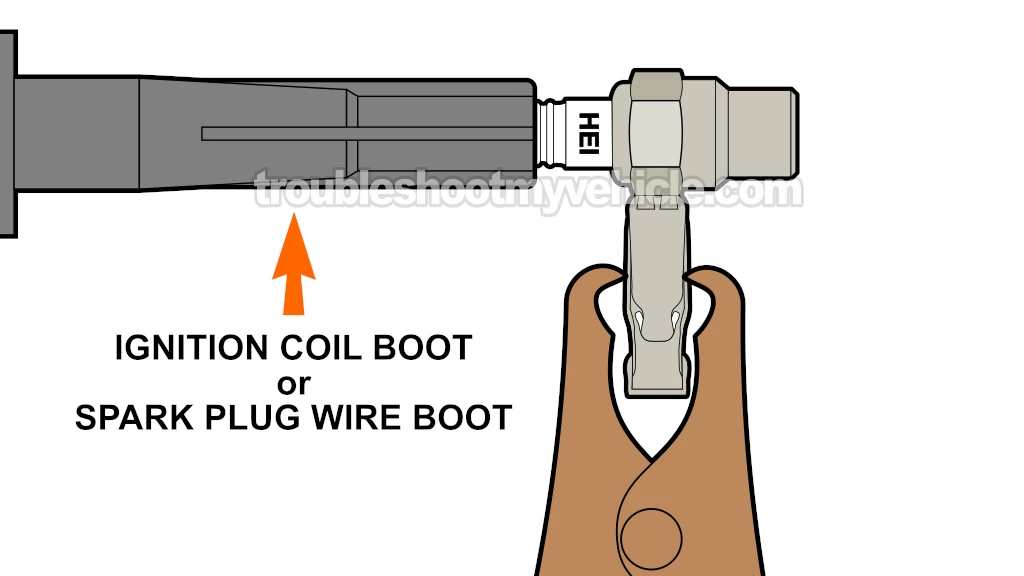
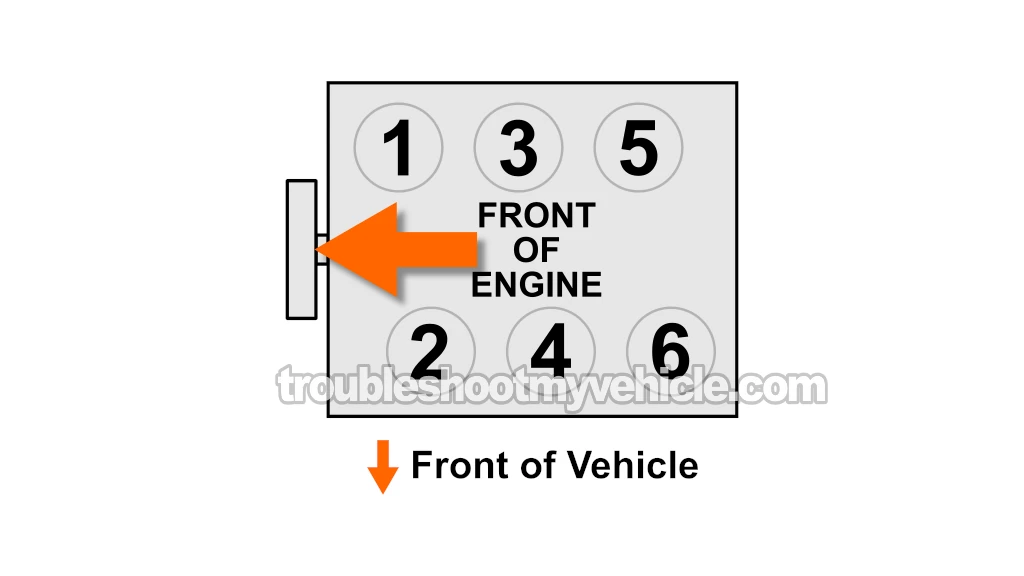
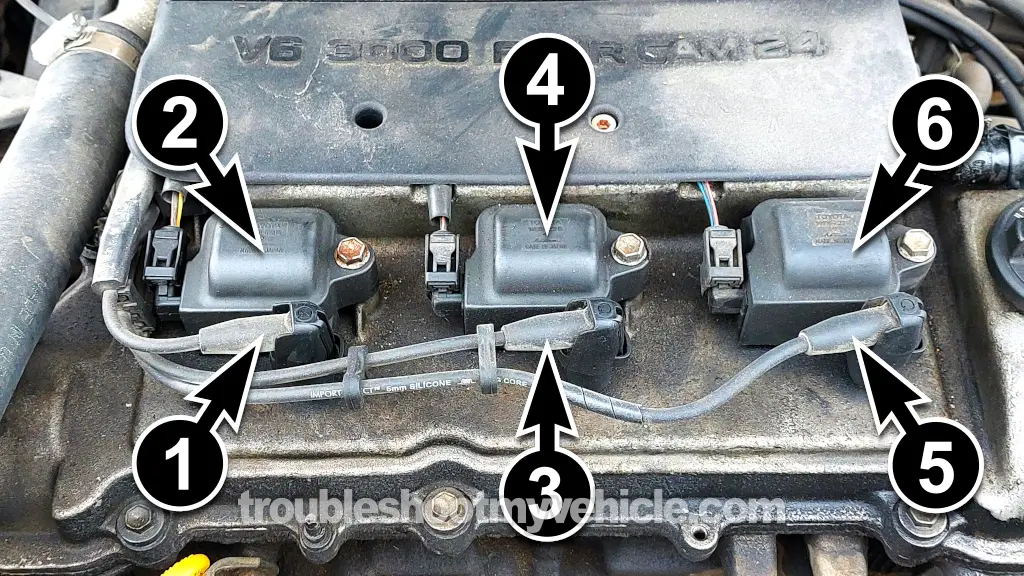
One side of the coil sits right on top of a spark plug (for cylinders 2, 4, and 6), and the other side (the coil tower) runs a plug wire to the opposite bank's corresponding cylinder (1, 3, or 5).
Here's how the pairs are arranged:
- Ignition Coil 1:
- Cylinder 2 (Bank 2) → Directly under the coil.
- Cylinder 1 (Bank 1) → Connected via a spark plug wire.
- Ignition Coil 2:
- Cylinder 4 (Bank 2) → Directly under the coil.
- Cylinder 3 (Bank 1) → Connected via a spark plug wire.
- Ignition Coil 3:
- Cylinder 6 (Bank 2) → Directly under the coil.
- Cylinder 5 (Bank 1) → Connected via a spark plug wire.
When you turn the key to crank and start the engine:
- The ignition coil receives 10 to 12 Volts on the:
- 1996: black with orange stripe (BLK/ORG) wire.
- 1997-2001: black with red stripe (BLK/RED) wire.
- It also receives an activation signal from the igniter (ignition control module) on the other wire of its connector.
- The color of these wires is unique to each ignition coil.
When both signals are present, the ignition coil generates and delivers a high-voltage spark to the two spark plugs it's connected to:
- One spark plug is connected via a spark plug wire.
- The other is connected through the spark plug boot directly under the ignition coil.
Once the spark reaches the spark plug electrodes, it ignites the fuel-air mixture in the cylinder.
If one or more ignition coils fail, you'll experience engine performance issues, misfires, or an engine no-start problem.
Common Symptoms Of A Bad Ignition Coil
When an ignition coil malfunctions, engine performance is gonna suffer. Here are some common signs to look for when diagnosing a potential ignition coil problem:
- Cylinder misfire: One or more cylinders aren't getting spark due to a bad ignition coil, leading to a rough-running or jerking engine (when accelerating the vehicle).
- Misfire trouble codes: The cylinders that aren't getting spark (from a bad ignition coil) are gonna set one or more of the following misfire diagnostic trouble codes:
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder #1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder #2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder #3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder #4 Misfire.
- P0305: Cylinder #5 Misfire.
- P0306: Cylinder #6 Misfire.
- Idling problems: A malfunctioning ignition coil may cause the engine to run rough when idling and may cause it to stall.
- Engine hard-start: If multiple cylinders don't receive spark from an ignition coil, it might be a challenge to start your Camry's engine.
- Bad gas mileage: When a cylinder malfunctions due to a bad ignition coil, it essentially becomes "dead" and doesn't contribute to the engine's power. This causes the other cylinders to work harder, resulting in poor gas mileage.
- Raw gasoline smell from the engine's exhaust: If an ignition coil fails to ignite fuel in one or more cylinders, the fuel exits the exhaust system as raw gasoline vapor. This creates a strong, noticeable odor of fuel emanating from the tailpipe.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition Coil?
To test the ignition coils on your 1996-2001 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry, these are the three essential tools you'll need to follow this tutorial:
- Spark tester: A spark tester is crucial to get an accurate spark test result. You can use any spark tester, but I recommend and personally use the OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester. You can find it (as well as purchase it) here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester (at: amazon.com).
- Multimeter: A multimeter will you help confirm that the ignition coil is receiving power in TEST 2. If you don't have one, check this one out: Tekpower TP8268 AC/DC Auto/Manual Range Digital (at: amazon.com).
- 12 Volt automotive test light: This test light will help you confirm that the ignition coil is receiving its activation signal during TEST 3. If you don't have one yet, I suggest the: Lisle 28400 Heavy Duty 12 Volt Test Light (at: amazon.com).
Where To Buy The Ignition Coils And Save
I'm recommending the Standard Motor Products UF204 Ignition Coil as the one you should purchase, since it's a well-known after-market brand. Once you get to amazon. Com thru the links below, you can also choose other brands too!
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
NOTE: Not sure if the ignition coil fits your particular vehicle? Don't worry. Once you click on the link and get to the site, they'll make sure it fits by asking you the particulars of your vehicle. If it isn't the right one, they find it for you.
TEST 1: Testing The Ignition Coil For Spark
To get started, we're gonna check for spark. When checking for spark, you have one of two choices:
- If you know which cylinders are misfiring, because you have specific cylinder misfire codes stored in the PCM's memory, then test those cylinders for spark.
- If you don't have any misfire codes, I suggest that you test all six cylinders for spark.
To accurately interpret your spark test results, it's very important that you keep in mind that the following cylinders are "paired," meaning they get spark at the exact same time and from the same ignition coil:
- Cylinders 2 and 1.
- Cylinders 4 and 3.
- Cylinders 6 and 5.
The instructions below assume that you're testing all six cylinders for spark, but you can modify them to suit your particular needs.
Let's get started:
PART 1:- 1
Disconnect the cylinder 1 spark plug wire from its spark plug. See the image 2 of 2 above to identify the correct cylinder.
NOTE: The ignition coil itself must remain installed in its place on the valve cover of bank 2 of the engine and connected to its 2-wire connector. - 2
Attach the spark tester to the spark plug wire.
- 3
Have a helper crank the engine while you observe the spark tester.
- 4
You'll see one of two results: Spark or no spark.
- 5
Write down the spark test result along with the cylinder number.
- 6
Remove the spark tester and reconnect the spark plug wire back to its spark plug.
- 7
Repeat PART 1 steps 1 thru 6 on the cylinders 3 and 5 spark plug wires.
- 1
Remove the ignition coil sitting on top of cylinder 2.
- 2
Connect the spark tester to the ignition coil's boot.
NOTE: The spark plug wire that connects to its side tower (and feeds spark to the spark plug on bank 1 of the engine) must remain connected to the tower. - 3
Have your helper crank the engine while you observe the spark tester for spark.
- 4
You'll see one of two results: Spark or no spark.
- 5
Write down the spark test result along with the cylinder number.
- 6
Remove the spark tester.
- 7
Install and bolt down the ignition coil back to its place on the engine.
- 8
Repeat PART 2 steps 1 thru 7 on the ignition coils for cylinders 2 and 6.
Let's interpret your test result:
CASE 1: All six cylinders are getting spark. This is the correct and expected test result and it lets you know that the ignition coils are OK.
CASE 2: One or more spark plug wires did not spark (cylinders 1, 3, or 5 only). We need to further investigate this no spark test result.
Your next step is to go to: TEST 4: Checking For Spark On The Ignition Coil Tower.
CASE 3: One or more coil plug boots did not spark (cylinders 2, 4, or 6 only). If the spark plug wire connected to this ignition coil is sparking, but the spark plug boot directly under the ignition coil is not sparking, this confirms that the ignition coil is bad and needs to be replaced.
Here's why: The ignition coil must create and deliver spark to both its spark plug wire and its spark plug boot. Since the spark plug boot (sitting directly under the coil) isn't sparking, but its spark plug wire is, the ignition coil is bad.
CASE 4: Two "paired" cylinders DID NOT spark. This usually means that the ignition coil is bad.
To make sure the ignition coil is bad, let's make sure it's getting power. For this test, go to: TEST 2: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Power.
CASE 5: None of the six cylinders are getting spark. This no-spark result on all six cylinders can be caused by one of several issues. The two most common are:
- The ignition coils are not getting power.
- The ignition coils are not getting an activation signal because the crankshaft or camshaft position sensor has failed.
The following tutorials will help you with the CKP and CMP sensor tests:
- How To Test The Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor (1994-2006 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry.
- How To Test The Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor (1994-2003 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry.
TEST 2: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Power
IMPORTANT: This test section only applies if in TEST 1 you got a no-spark test result from a spark plug wire and a spark plug boot that belong to the same ignition coil.
In this test section, we're gonna check that ignition coil whose spark plug wire and spark plug boot did not spark in TEST 1 is getting power (10 to 12 Volts).
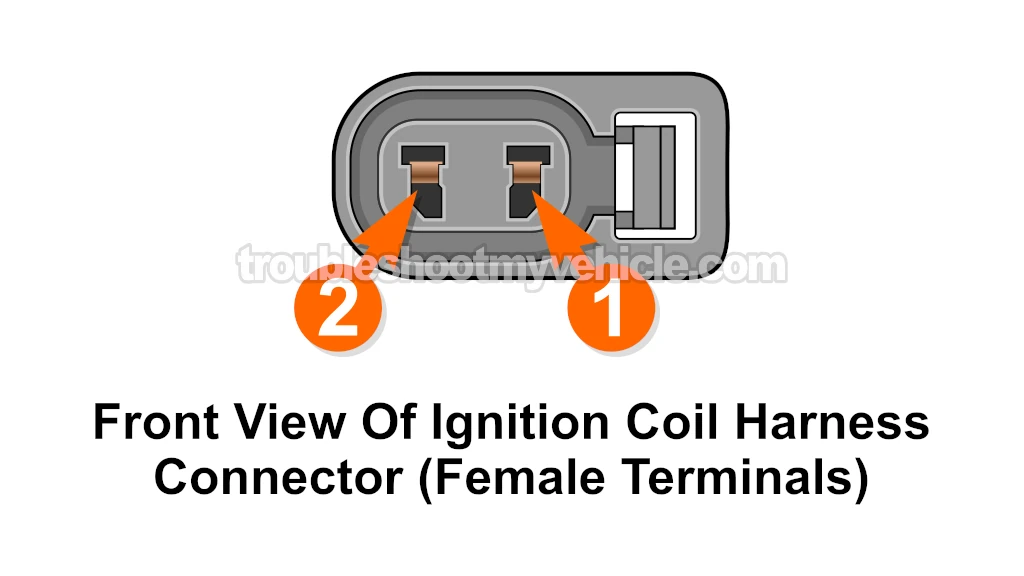
As you're already aware, the ignition coils have a 2-wire connector. One wire delivers 10 to 12 Volts and the other delivers an activation signal.
The wire that delivers 10 to 12 Volts to the ignition coil:
- 1996: Black with orange stripe (BLK/ORG) wire.
- 1997-2001: Black with red stripe (BLK/RED) wire.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil from its 2-wire connector.
- 2
Set your multimeter to Volts DC mode.
- 3
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the battery negative (-) post.
- 4
Probe the terminal that corresponds the BLK/RED (or BLK/ORG) wire.
- 5
Turn the ignition switch to the ON position but don't crank the engine.
- 6
Your multimeter should register 10-12 Volts.
Let's interpret your test result:
CASE 1: 10 to 12 Volts are present. This is the correct and expected test result.
Now that you have confirmed the ignition coil is getting power, the next step is to make sure it's getting an activation signal. Go to: TEST 3: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Its Activation Signal.
CASE 2: 10 to 12 Volts ARE NOT present. Without this voltage, the ignition coil is not gonna create and deliver spark to its two spark plugs.
The most likely cause of this missing voltage is:
- The ignition coil's connector is bad. The BLK/RED (BLK/ORG) wire has become disconnected from its female terminal inside the connector.
- The BLK/RED (BLK/ORG) wire has an open-circuit problem.
Although it's beyond the scope of this tutorial to troubleshoot this issue, your next step is to find out why this voltage is missing at this connector and restore it.