TEST 2: Making Sure The TPS Is Receiving 5 Volts
There's a good chance the TP sensor's voltage signal is stuck (at that one value) because it's probably not getting power.
For our second test, we'll check that the violet with white stripe (VIO/WHT) wire is supplying a voltage between 4.5 and 5 Volts DC.
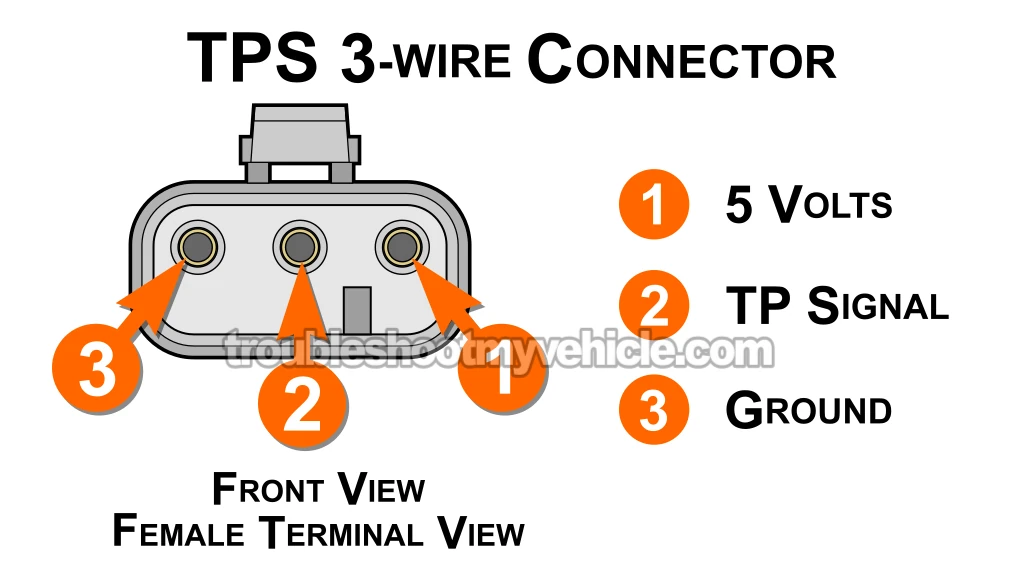
The VIO/WHT wire connects to the female terminal labeled with number 1 in the illustration above.
To make sure the VIO/WHT wire is actually delivering 5 Volts, we're going to test it with a multimeter.
Let's get right to it!
- 1
Disconnect the TP sensor from its connector.
- 2
Select the DC Volts mode on your multimeter.
- 3
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the negative (-) battery terminal.
- 4
Turn the key to the ON position but don't start the engine.
- 5
Gently probe terminal 1 of the TP sensor's 3-wire connector with the red multimeter test lead.
NOTE: Confirm that the VIO/WHT wire connects to terminal number 1. - 6
You should see a reading of 4.5 to 5 Volts DC on your multimeter.
Let's look at your test results:
CASE 1: You're seeing 4.5 to 5 Volts. It means the TPS is getting power, which is exactly what we want to see.
For the final check, let's make sure the TPS is also receiving Ground. You can find the instructions here: TEST 3: Making Sure The TPS Is Receiving Ground.
CASE 1: You don't see 4.5 to 5 Volts. Without power, the TP sensor simply won't generate its variable voltage signal.
The most common causes of these missing 5 Volts are:
- An open-circuit problem in the wire between the TP sensor's 3-wire connector and the fuel injection computer's connector.
- An internal fault within the computer itself (although very rare).
Troubleshooting this problem isn't covered in this tutorial, but you now know that the TP sensor is OK. Your next step is to figure out what's stopping that voltage from reaching the sensor.
TEST 3: Making Sure The TPS Is Receiving Ground

So far, your previous two tests have found that:
- TEST 1: Opening or closing the throttle plate doesn't change the TPS voltage signal.
- TEST 2: Power's being delivered to the TP sensor.
Now, in this final test section, we're gonna confirm that the black with blue stripe (BLK/LT BLU) wire is supplying Ground to the TP sensor.
The terminal I've labeled with the number 3 in the illustration above, is the one that connects to the BLK/LT BLU wire.
We'll use a multimeter voltage test to make sure the BLK/LT BLU wire's delivering Ground.
IMPORTANT: Ground is provided to the sensor by the fuel injection computer. It's important that you don't directly connect this circuit to battery 12 Volts –or you're gonna fry the computer! The multimeter voltage test I'm suggesting is a safe and simple way to check for Ground in this circuit.
Here's how to check for Ground:
- 1
Disconnect the TP sensor from its connector.
- 2
Select the DC Volts mode on your multimeter.
- 3
Connect the red multimeter test lead to the positive (+) battery terminal.
- 4
Turn the key to the ON position but don't start the engine.
- 5
Gently probe terminal 3 of the TP sensor's 3-wire connector with the black multimeter test lead.
NOTE: Confirm that the BLK/LT BLU wire connects to terminal number 3. - 6
You should see a reading of 10 to 12 Volts DC on your multimeter.
OK, let's find out what your test results mean:
CASE 1: Ground is present. This confirms the TP sensor is getting Ground.
Now, if you've confirmed the following conditions, your TPS needs is bad and needs replacement:
- The TP sensor isn't sending out a voltage signal that changes when you move the throttle plate (TEST 1).
- The TP sensor is receiving 4.5 to 5 Volts (TEST 2).
- You've confirmed it's getting Ground here.
CASE 2: Ground is not present. Double-check you're testing the right terminal.
If your multimeter still isn't showing 10 to 12 Volts, the throttle position sensor itself is fine. The problem causing the sensor to not generate it's variable voltage signal is it's the lack of Ground.
The most common causes of this missing Ground are:
- An open-circuit problem in the wire between the TP sensor's 3-wire connector and the fuel injection computer's connector.
- An internal fault within the computer itself (although very rare).
Troubleshooting this problem isn't covered in this tutorial, but you now know that the TP sensor is OK. Your next step is to figure out what's keeping Ground (from the computer) from reaching the sensor.
More 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram Van Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram van tutorials in this index:
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Test The Engine Compression (1989-2003 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram Van).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (1989-2003 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram Van).
- How To Test The Fuel Pump (1992-2003 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram Van).
- How To Test The MAP Sensor (1992-1997 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram Van).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!

