
Testing the ignition coil, spark plug wires, and distributor cap and rotor is not difficult at all on the 1990–1995 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable.
I can tell you from experience that there's a method to the madness when it comes to diagnosing these ignition system components to see if they're causing a cylinder misfire or an engine no-start problem.
In this tutorial, I'm going to show you, step by step and with just some basic tools, how to do this.
By the end of your tests, you'll quickly and easily know if the ignition coil is behind an engine no-start issue or if one of the other ignition system components is causing a cylinder misfire or rough idle problem.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Symptoms Of An Ignition System Fault.
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition System?
- TEST 1: Checking For Spark At The Spark Plug Wires.
- TEST 2: Checking For Spark At The Distributor Cap.
- TEST 3: Checking The Ignition Coil High Tension Wire For Spark.
- TEST 4: Checking The Ignition Coil Tower For Spark.
- TEST 5: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Power.
- TEST 6: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting An Activation Signal.
- More 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus Diagnostic Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus: 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995.
- 3.0L V6 Mercury Sable: 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995.
RELATED IGNITION SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC TESTS:
- How To Test The Ignition Control Module (1990-1995 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus, Mercury Sable).
- How To Test The PIP Sensor (1990-1995 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus, Mercury Sable).
IGN SYSTEM WIRING DIAGRAMS:
- Ignition System Wiring Diagram (1990 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus, Mercury Sable).
- Ignition System Wiring Diagram (1991 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus, Mercury Sable).
- Ignition System Wiring Diagram (1992-1995 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus, Mercury Sable).
ENGINE NO-START DIAGNOSTICS:
Symptoms Of An Ignition System Fault
Since quite a few components make up the ignition system on your 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable, when one of them fails, you're going to run into one of two problems:
- An engine cylinder misfire or rough idle.
- An engine no-start issue.
When an ignition system malfunction causes a cylinder misfire, you'll still notice one or more of the following performance issues that let you know something's wrong:
- Rough or unstable idle.
- Lack of power under load or during acceleration.
- Engine hesitation or stumbling when you press the accelerator.
- Intermittent misfire at idle or while driving.
- Hard starting or extended cranking time.
- Poor fuel mileage.
- Occasional backfire through the intake or exhaust.
Although the 1990–1995 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable isn't equipped with OBD II misfire diagnostics, we can still easily pinpoint the exact cause of a cylinder misfire, rough idle, or engine no-start problem. In this tutorial, I'll show you how to test the distributor cap and rotor, spark plug wires, and ignition coil —all explained in a clear, step-by-step manner.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition System?
The cool thing about testing the ignition system on your 3.0L Taurus or Sable is that you don't need any expensive or fancy diagnostic equipment —not even a scan tool. The only things you'll need to perform the tests outlined in this tutorial are:
- Spark tester: A dedicated spark tester is the most accurate way to check for spark. Any spark tester will do, but the one I use and recommend for its ease of use and accuracy is the OTC HEI Spark Tester. You can see an example of it here and purchase it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester (Amazon affiliate link).
- 12V automotive test light: A regular 12V incandescent test light will help us check the ignition coil's activation signal in TEST 5. If you don't have one, this is the one I recommend —you can see it here: Lisle 28400 Heavy Duty 12 Volt Test Light (Amazon affiliate link).
- Multimeter: The multimeter will help us make sure the ignition coil's receiving battery power in TEST 4. If you don't have one, or if you're looking to upgrade, this is the one I use and recommend: Tekpower TP8268 AC/DC Auto/Manual Range Digital Multimeter (Amazon affiliate link).
- Spark plug wire puller: Spark plug wire pliers are almost a must-have tool for disconnecting the spark plug wires from the spark plugs. The main reason is that if you pull on the wire with your hand, the metal terminal inside the boot usually stays stuck on the spark plug. It can be reattached, but it's a hassle —and using spark plug wire pliers helps you avoid that altogether. These are the ones I recommend: Performance Tool W80519 Adjustable Spark Plug Boot And Wire Remover (Amazon affiliate link).
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
TEST 1: Checking For Spark At The Spark Plug Wires
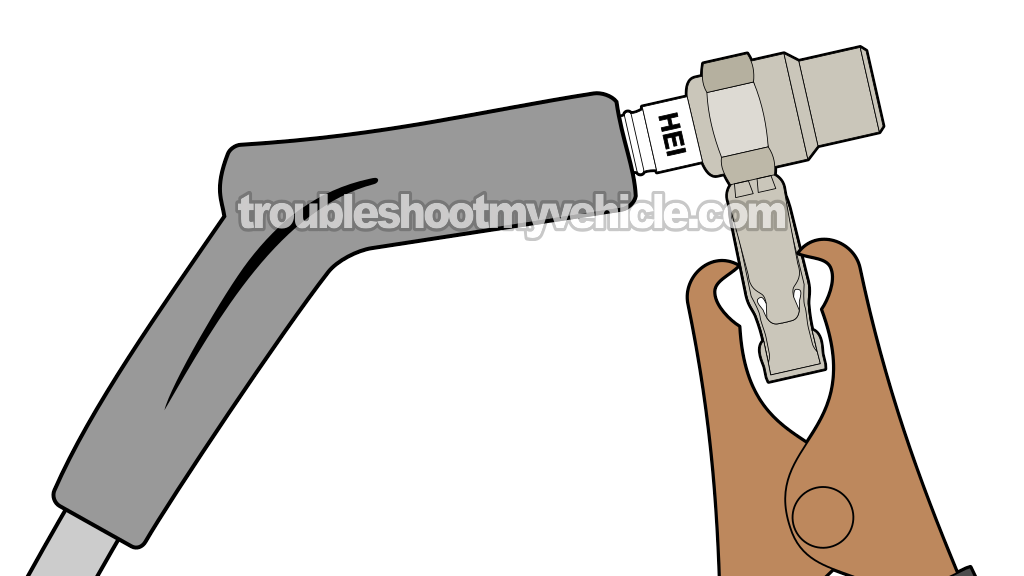
Our very first diagnostic test involves checking all 6 spark plug wires for spark. It's super important that you use a spark tester for this.
It doesn't matter which one you use —but if you don't have one, this is the one I use and recommend OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester (Amazon affiliate link).
One more thing that'll save you time and frustration: when removing the spark plug wires from the spark plugs, use spark plug wire pullers.
Sure, you can pull the wires off by hand, but what usually happens is the wire's metal terminal stays stuck on the spark plug. You can reconnect the terminal to the wire, but trust me —it's a hassle you're better off avoiding.
If you don't have a set, these are the spark plug wire pullers I use and recommend —you can find them here: Performance Tool W80519 Adjustable Spark Plug Boot And Wire Remover (Amazon affiliate link).
CAUTION: You'll be working around a cranking engine. Keep your hands, tools, loose clothing, and test leads clear of moving engine parts such as belts and pulleys. Secure any long hair and avoid leaning over the engine while performing the test. Always stay alert and aware of your surroundings when working near moving components.
Let's take it from the top:
- 1
Disconnect the spark plug wire from its spark plug.
- 2
Connect the spark plug wire to the spark tester.
- 3
Connect the spark tester to the battery negative (-) terminal using a battery jump start cable.
- 4
Have a helper crank the engine while you observe the spark tester.
- 5
You'll see one of two results: Spark or no spark.
- 6
Remove the spark tester and reconnect the spark plug wire to its spark plug.
- 7
Repeat steps 1 thru 6 on the remaining spark plug wires.
Let's interpret your spark test results:
CASE 1: All six spark plug wires are sparking. This is exactly what we want to see, and this test result confirms several important things:
- The engine no-start or cylinder misfire problem isn't being caused by the ignition system. Of course, you should still remove the spark plugs and inspect them.
- The ignition coil, ignition control module (ICM) and Profile Ignition Pickup (PIP) sensor are good —if any were bad, you wouldn't see spark at any of the spark plug wires.
To continue troubleshooting a cylinder misfire issue, I recommend removing the spark plugs and checking them for damage or heavy wear, performing an engine compression test, and making sure the fuel injectors are actually delivering fuel into the cylinders.
If you're troubleshooting an engine no-start, your next step should be to check fuel pump pressure. If fuel pressure is OK, then move on to checking engine compression.
- How To Test The Fuel Pump (1990-1999 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus, Mercury Sable).
- How To Do And Interpret An Engine Compression Test (1990-2007 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus, Mercury Sable).
- How To Test The Fuel Injectors (1991-1995 3.0L V6 Ford Taurus).
CASE 2: One or more spark plug wires —but not all— did not spark. This confirms that the cylinder misfire or rough idle issue you're troubleshooting is being caused by the ignition system.
Our next step is to figure out whether the problem's being caused by the spark plug wires or the distributor cap. To continue, head over to: TEST 2: Checking For Spark At The Distributor Cap.
CASE 3: None of the spark plug wires sparked. This complete lack of spark across all six cylinders will definitely keep the engine from starting.
Now that you've confirmed there's no spark to any of the cylinders, our next step is to check if the ignition coil's high-tension wire is delivering spark to the center of the distributor cap. For this spark test, head over to: TEST 3: Checking The Ignition Coil High Tension Wire For Spark.
TEST 2: Checking For Spark At The Distributor Cap
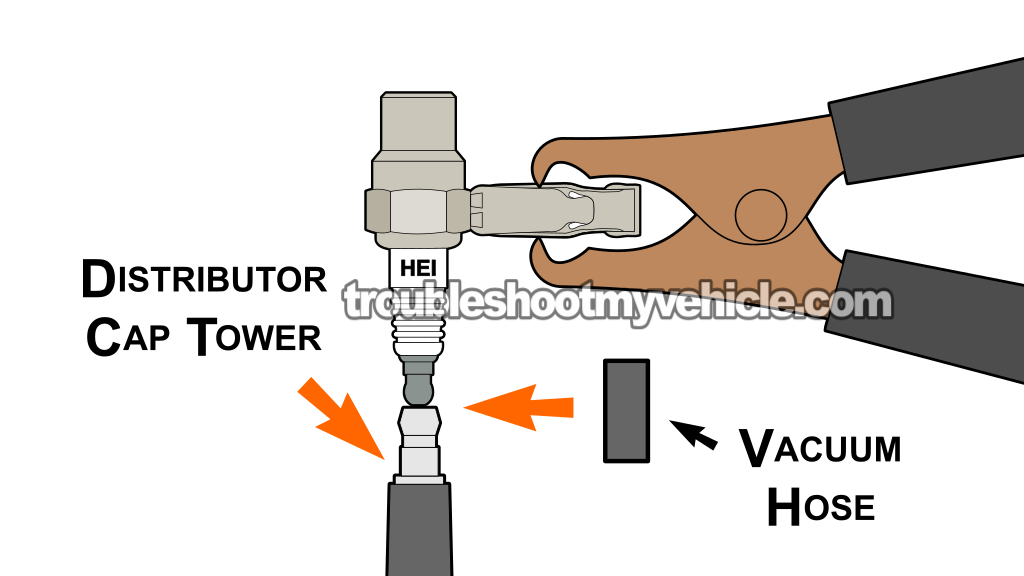
It's not uncommon for the distributor cap to fail, and for one or more of its towers —the towers the spark plug wires connect to— to stop transmitting spark. This is especially true if the distributor cap is several years old.
In this test section, we're going to check for spark directly at the distributor cap towers corresponding to the spark plug wires that didn't spark in TEST 1.
We can expect one of two results:
- The tower sparks: This indirectly tells us that the spark plug wire that didn't spark in TEST 1 is bad.
- The tower doesn't spark: This tells us the non-sparking spark plug wire isn't sparking because the distributor cap itself is toast.
This is a simple test to perform, but you'll need to use a small piece of vacuum hose to keep the spark tester attached to the distributor cap tower.
In the illustration of the test procedure above, you can see exactly how this test should be done using a spark tester and a small piece of vacuum hose.
All right, here are the test steps:
- 1
Connect the spark plug wires to their respective spark plugs (if any are currently disconnected).
- 2
Disconnect the spark plug wire that did not spark from its tower on the distributor cap.
NOTE: If you have multiple non-sparking spark plug wires, we'll test them one at a time. For this step, disconnect only one wire from its distributor cap tower. In Step 8, we'll move on to the next one. - 3
Connect the spark tester to the distributor cap tower with a small piece of vacuum hose.
In the photo above, the orange arrow points to the short piece of vacuum hose that is connecting the spark tester to the metal terminal of the distributor tower being tested. - 4
Ground the spark tester on the battery negative (-) terminal using a battery jump start cable.
NOTE: The battery jump start cable will also help you hold the spark tester in the distributor tower. - 5
Have a helper crank the engine.
CAUTION: The engine may start during this test. Take all necessary safety precautions and remain alert. - 6
You'll get 1 of 2 results: Spark or no spark.
- 7
Remove the spark tester from the tower and reconnect the spark plug wire.
- 8
Repeat the test for any other distributor cap towers connected to non-sparking spark plug wires from TEST 1.
Here's what your test result is telling you:
CASE 1: The spark tester sparked on the tower of the non-sparking spark plug wire. This is the correct and expected test result.
With this result, we can conclude that the non-sparking spark plug wire —the one connected to that distributor cap tower— is bad. Replace all of the spark plug wires with a new set to resolve the ignition system fault that's causing the engine to run with a cylinder misfire or rough idle.
CASE 2: The spark tester DID NOT spark on the tower of the non-sparking spark plug wire. This no-spark result tells you the distributor cap is toast and needs to be replaced.
In situations like this, it's standard practice to replace the distributor cap and rotor together. And if the spark plug wires are as old as the cap and rotor —even though the issue's been pinpointed to the cap— it's a good idea to replace them too.
TEST 3: Checking The Ignition Coil High Tension Wire For Spark
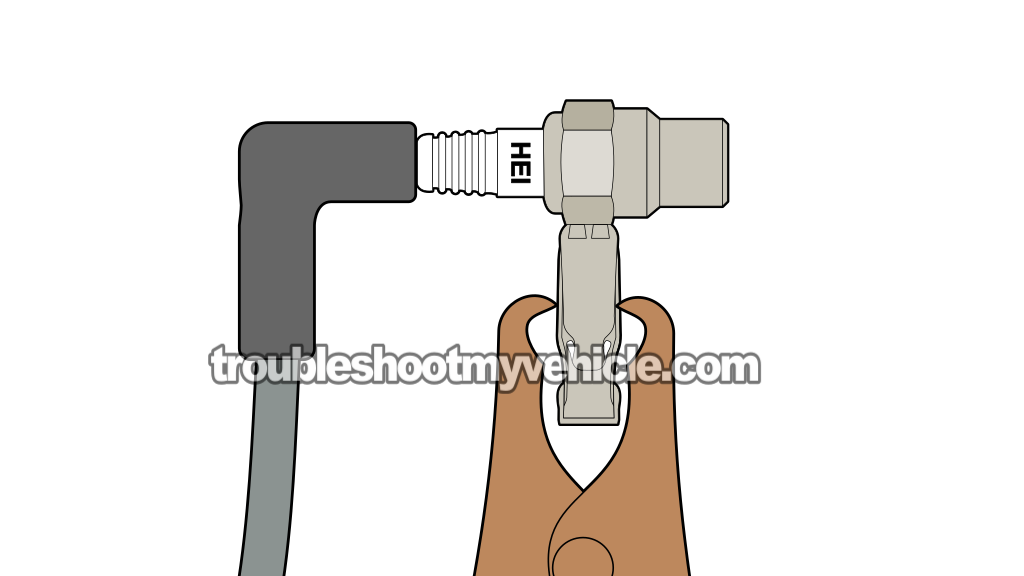
If you've reached this point, then TEST 1 has confirmed that none of your Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable's spark plug wires are sparking.
Our next diagnostic step is to see if the ignition coil's high-tension wire is actually delivering spark to the center tower of the distributor cap.
The ignition coil's high-tension wire is a hard-working part of the ignition system, and over time, it can fail. It's not uncommon for it to stop transmitting spark from the ignition coil to the distributor cap after years of service.
To check it, all we have to do is connect the spark tester to the ignition coil's high-tension wire, crank the engine, and see if it sparks.
All right, let's get going.
- 1
Disconnect the high tension wire from the center tower of the distributor cap.
NOTE: Leave the other end of the high tension wire attached to the ignition coil. - 2
Attach the HEI spark tester to the spark plug wire.
- 3
Connect the spark tester to the battery negative (-) post using a battery jump start cable (see the illustration above).
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine while you observe the spark tester from a safe distance.
- 5
You'll get one of two results:
1.) The spark tester will spark.
2.) The spark tester will NOT spark.
Let's examine your test result:
CASE 1: The high-tension spark plug wire is delivering spark. This is the correct and expected test result, and it tells us several important things:
- The ignition coil, ignition control module (ICM), and profile ignition pickup (PIP) sensor are all functioning correctly.
- The distributor cap and rotor are bad.
To fix your Ford Taurus or Mercury Sable's engine no-start issue, replace the distributor cap and its rotor. This will ensure spark gets distributed to all six spark plug wires.
CASE 2: The high-tension spark plug wire is not delivering spark. This no-spark test result confirms that the lack of spark at all six spark plug wires is due to the distributor cap not receiving spark.
Our next step is to see if the ignition coil's high-tension wire itself is bad. We'll find out in the next test. Head over to: TEST 4: Checking The Ignition Coil Tower For Spark.
