
The ignition system on the 1992-1993 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry uses a mechanical distributor to supply spark to all six cylinders.
Testing the ignition system to see if it's causing the engine to not start (due to a lack of spark) isn't difficult. In this tutorial, I'll walk you thru how to do this step-by-step.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Ignition System Basics.
- Engine No-Start Diagnostic Basics.
- TEST 1: Checking The Spark Plug Wires For Spark.
- TEST 2: Checking The Ignition Coil's High Tension Wire For Spark.
- TEST 3: Checking The Distributor Cap For Spark.
- TEST 4: Testing The Ignition Coil For Spark.
- TEST 5: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Power.
- TEST 6: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Its Activation Signal.
- More 3.0L Toyota Camry Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry: 1992, 1993.
Wiring Diagram:
1994-2001 Ignition Coil Tests: The following tutorial will help you test the ignition coils on the 1994-2001 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry:
- How To Test The Ignition Coils (1994-1995 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry).
- How To Test The Ignition Coils (1996-2001 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry).
Engine No-Start Diagnostics:
Ignition System Basics
The ignition system is responsible for generating the high voltage spark needed to ignite the fuel-air mixture in your 1992-1993 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry's engine. A malfunctioning in one of the ignition system components can prevent the engine from starting or running properly.
Here are the key components that make up the ignition system:
- Mechanical distributor: This is the heart of the ignition system, responsible for distributing the high voltage spark to the correct spark plug at the right time.
- Pick-up coil (inside distributor): Located inside the mechanical distributor, this coil is responsible for generating three low-voltage signals that tell the ignition system when to fire.
When the engine is cranking or running, the pick-up coil sends a signal to the fuel injection computer whenever the camshaft and crankshaft rotates, signaling it's time to generate a spark. - Distributor cap: The distributor cap is a plastic cap with metal terminals. It's attached to the mechanical distributor and distributes the high voltage spark from the ignition coil to the correct spark plug wire.
- Distributor rotor: The rotor is the moving part inside the mechanical distributor that rotates as the engine turns over.
Its primary function is to align with the metal terminals inside the distributor cap, which are connected to the spark plug wires. As it rotates, the rotor directs the high-voltage spark from the ignition coil to the correct spark plug wire at the appropriate time, ensuring proper firing and combustion in each cylinder. - Spark plug wires: These wires carry the high voltage spark from the ignition coil through the distributor cap and out to the spark plugs, where they ignite the fuel-air mixture in each cylinder.
- Igniter (located on the driver side strut tower): The igniter plays a crucial role in the ignition system, acting as a switch that triggers the ignition coil to produce a high-voltage spark. It works in tandem with the pick-up coil and mechanical distributor to ensure the correct timing of the spark.
- Ignition coil: Located near the battery, this coil is responsible for generating the high voltage needed to create the spark in the ignition system. It converts the low-voltage signal from the igniter into a high-voltage pulse that's sent through the spark plug wires.
If any of these components fail or become damaged, it can prevent the engine from starting due to a lack of spark.
In this tutorial, we'll cover how to test each component and diagnose common issues with the ignition system on your 1992-1993 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry.
Engine No-Start Diagnostic Basics
The ignition system plays a crucial role in starting the engine in your 1992-1993 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry. When one or more components fail, the engine won't start. Here are the common culprits:
- Bad Spark Plug Wires: As they age, they lose their ability to transmit spark from the distributor cap to the spark plugs. While they rarely fail all at once, if enough wires go bad the engine won't start (especially in cold weather).
- Bad Distributor Cap: Over time, the cap's metal terminals become pitted and covered in carbon buildup due to electrical arcing and oxidation. If enough terminals are affected, the spark can't reach the spark plugs, and the engine won't start.
- Bad Distributor Rotor: The distributor rotor's metal strip can become pitted and coated in carbon buildup at the center contact point and the terminal end due to constant arcing and oxidation. If the buildup becomes excessive, the spark won't transfer to the cap terminals, and the engine will fail to start.
- Bad Distributor Pick-Up Coil: Without the CKP and CMP signals it generates, the computer can't tell the igniter to activate the ignition coil. As a result, no spark is generated, and the engine won't start.
- Bad Igniter: If the igniter fails, the ignition coil isn't activated, and none of the six cylinders receive spark, preventing the engine from starting.
- Bad Ignition Coil: If the coil fails, spark isn't generated for any of the six cylinders and the engine won't start.
TEST 1: Checking The Spark Plug Wires For Spark
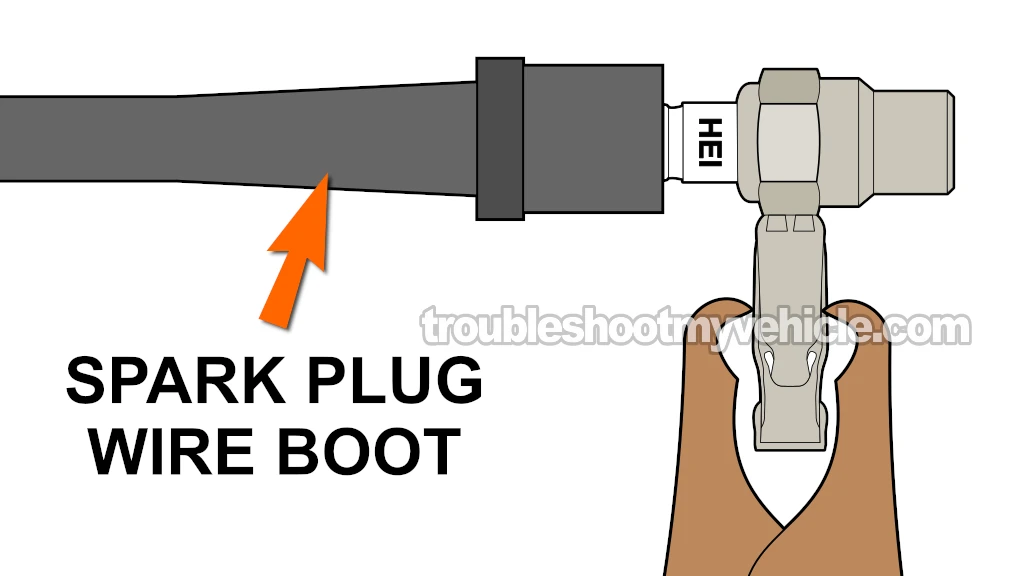
The first thing we need to do is to check for spark at all six spark plug wires. This is an important diagnostic test that'll help us determine if a lack of spark is causing the engine's no-start problem.
To get an accurate spark test result, it's important that you use a dedicated spark tester. The one I recommend and personally use is the HEI Spark Tester. You can see an example of this tool (and buy it) here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester (at: amazon.com).
Let's get started:
- 1
Disconnect the spark plug wire from its spark plug.
- 2
Connect the spark plug wire to the spark tester.
- 3
Connect the spark tester to the battery negative (-) terminal using a battery jump start cable.
- 4
Have a helper crank the engine while you observe the spark tester.
- 5
You'll see one of two results: Spark or no spark.
- 6
Remove the spark tester and reconnect the spark plug wire to its spark plug.
- 7
Repeat steps 1 thru 5 on the remaining spark plug wires.
Let's interpret your test result:
CASE 1: All six spark plug wires sparked. This is the correct and expected test result and it tells you that the ignition system is NOT behind the engine's no-start problem.
You can also conclude that the following components are OK:
- The igniter (ignition control module).
- The ignition coil.
- The pickup coil (located in the distributor).
- The distributor can and rotor.
Since the engine isn't starting, the following tutorial will help you to further diagnose the issue:
If the engine isn't starting, it's not due to a fault in the ignition system.
CASE 2: Some, but not all, spark plug wires sparked. This usually means that the spark plug wires that did not spark are bad or that the distributor cap is bad.
To further diagnose this, go to TEST 3: Checking The Distributor Cap For Spark.
CASE 3: None of the spark plug wires sparked. This test result confirms that the engine isn't starting due to a lack of spark.
Your next step is to check that the ignition coil's high tension wire is delivering spark to the distributor cap. Go to: TEST 2: Checking The Ignition Coil's High Tension Wire For Spark.
TEST 2: Checking The Ignition Coil's High Tension Wire For Spark
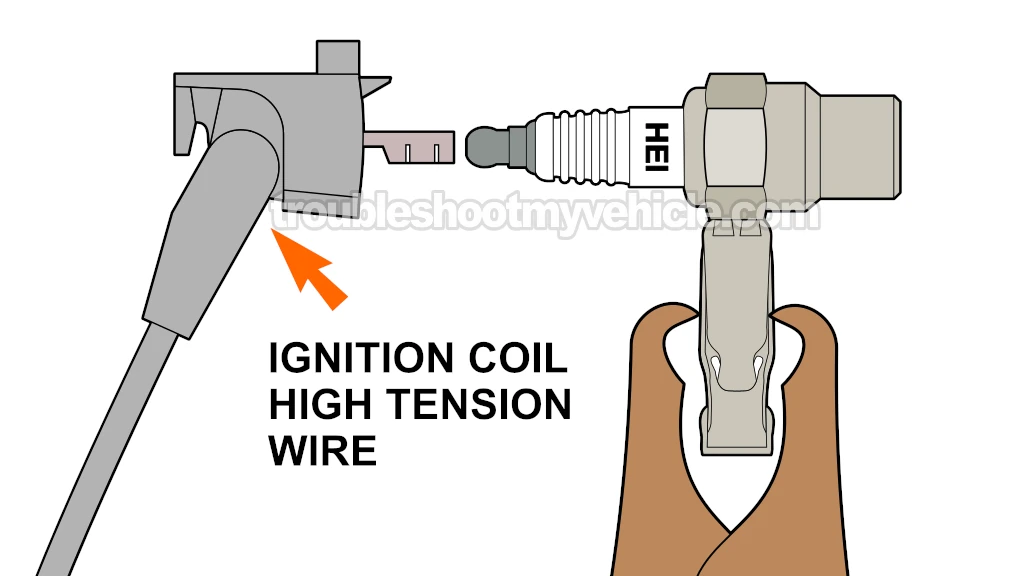
The high tension wire that connects the ignition coil to the distributor cap can fail. When it does, it'll prevent the spark the ignition coil produces from reaching the distributor cap (even if the ignition coil itself is functioning properly).
In this test section, we're gonna check if the ignition coil's high tension wire is delivering the spark created by the ignition coil to the distributor cap.
These are the test steps:
Let's begin:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil's high tension wire from the distributor cap.
NOTE: The other end of the high tension wire must remain connected to the ignition coil. - 2
Connect the spark tester to the high tension wire's metal terminal using black electrical tape (to allow the components to touch and remain in contact).
NOTE: Since the spark tester can't physically insert into the terminal, we'll use black electrical tape to wrap them together and create a metal-to-metal contact between the two. This ensures that the spark tester makes proper connection with the terminal. - 3
Connect the spark tester to the battery negative (-) terminal using a jump start cable.
- 4
Have a helper crank the engine while you observe the spark tester.
- 5
You'll get 1 of 2 results: Spark or no spark.
Let's interpret your test result:
CASE 1: The spark tester sparked. This is the correct and expected test result.
You can conclude that the distributor rotor and cap are bad (and need to be replaced) if you have:
- Confirmed that all six spark plugs are not sparking (TEST 1).
- Confirmed in this test section that the ignition coil's high tension is sparking.
CASE 2: The spark tester DID NOT spark. Your next step is to check for spark directly on the ignition coil's tower.
